Anti-TP63 Antibody (CAB2137)
- SKU:
- CAB2137
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Death
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-TP63 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB2137 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
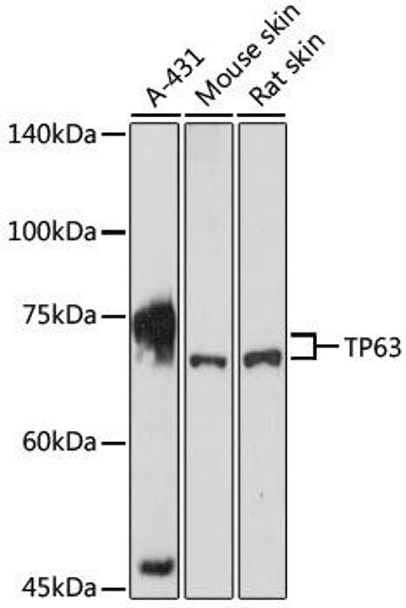
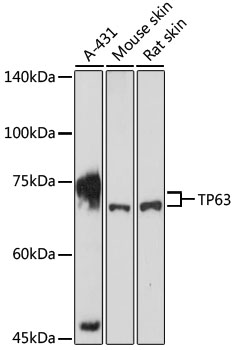
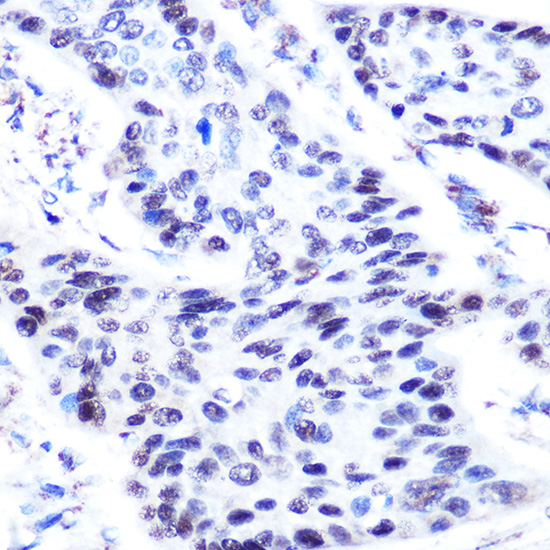
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 421-680 of human TP63 (NP_003713.3). |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | A-431, mouse skin, rat skin |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 421-680 of human TP63 (NP_003713.3). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | LELM QYLP QHTI ETYR QQQQ QQHQ HLLQ KQTS IQSP SSYG NSSP PLNK MNSM NKLP SVSQ LINP QQRN ALTP TTIP DGMG ANIP MMGT HMPM AGDM NGLS PTQA LPPP LSMP STSH CTPP PPYP TDCS IVSF LARL GCSS CLDY FTTQ GLTT IYQI EHYS MDDL ASLK IPEQ FRHA IWKG ILDH RQLH EFSS PSHL LRTP SSAS TVSV GSSE TRGE RVID AVRF TLRQ TISF PPRD EWND FNFD MDAR RNKQ QRIK EEGE |
| Gene ID: | 8626 |
| Uniprot: | Q9H3D4 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 44-76kDa |
| Observed MW: | 75kDa |
| Synonyms: | AIS, B(p51A), B(p51B), EEC3, KET, LMS, NBP, OFC8, RHS, SHFM4, TP53CP, TP53L, TP73L, p40, p51, p53CP, p63, p73H, p73L, TP63 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a member of the p53 family of transcription factors. The functional domains of p53 family proteins include an N-terminal transactivation domain, a central DNA-binding domain and an oligomerization domain. Alternative splicing of this gene and the use of alternative promoters results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms that vary in their functional properties. These isoforms function during skin development and maintenance, adult stem/progenitor cell regulation, heart development and premature aging. Some isoforms have been found to protect the germline by eliminating oocytes or testicular germ cells that have suffered DNA damage. Mutations in this gene are associated with ectodermal dysplasia, and cleft lip/palate syndrome 3 (EEC3); split-hand/foot malformation 4 (SHFM4); ankyloblepharon-ectodermal defects-cleft lip/palate; ADULT syndrome (acro-dermato-ungual-lacrimal-tooth); limb-mammary syndrome; Rap-Hodgkin syndrome (RHS); and orofacial cleft 8. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Function: Acts as a sequence specific DNA binding transcriptional activator or repressor. The isoforms contain a varying set of transactivation and auto-regulating transactivation inhibiting domains thus showing an isoform specificactivity. Isoform 2 activates RIPK4 transcription. May be required in conjunction with TP73/p73 for initiation of p53/TP53 dependent apoptosis in response to genotoxic insults and the presence of activated oncogenes. Involved in Notch signaling by probably inducing JAG1 and JAG2. Plays a role in the regulation of epithelial morphogenesis. The ratio of DeltaN-type and TA*-type isoforms may govern the maintenance of epithelial stem cell compartments and regulate the initiation of epithelial stratification from the undifferentiated embryonal ectoderm. Required for limb formation from the apical ectodermal ridge. Activates transcription of the p21 promoter. Ref.3 Ref.15 Ref.17 Ref.18 Ref.19 Ref.23 Ref.24 |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Cofactor: Binds 1 zinc ion per subunit By similarity. Subunit structure: Binds DNA as a homotetramer. Isoform compositionof the tetramer may determine transactivation activity. Isoforms Alpha and Gamma interact with HIPK2. Interacts with SSRP1, leading to stimulate coactivator activity. Isoform 1 and isoform 2 interact with WWP1. Interacts with PDS5A. Isoform 5 (via activation domain) interacts with NOC2L. Ref.10 Ref.13 Ref.16 Ref.19 Ref.21 Ref.22 Ref.23 Subcellular location: Nucleus Ref.17 Ref.23. Tissue specificity: Widely expressed, notably in heart, kidney, placenta, prostate, skeletal muscle, testis and thymus, although the precise isoform variesaccording to tissue type. Progenitor cell layers of skin, breast, eye and prostate express high levels of DeltaN-type isoforms. Isoform 10 is predominantly expressed in skin squamous cell carcinomas, but not in normal skin tissues. Ref.3 Ref.8 Ref.14 Domain: The transactivation inhibitory domain (TID) can interact with, and inhibit the activity of the N-terminal transcriptional activation domain of TA*-type isoforms. Ref.17 Ref.18 Post-translational modification: May be sumoylated By similarity.Ubiquitinated. Polyubiquitination involves WWP1 and leads to proteasomal degradation of this protein. Ref.21 Involvement in Disease: Acro-dermato-ungual-lacrimal-tooth syndrome (ADULT syndrome) [MIM:103285]: A form of ectodermal dysplasia. Ectodermal dysplasia defines a heterogeneous group of disorders due to abnormal development of two or more ectodermal structures. ADULT syndrome involves ectrodactyly, syndactyly, finger- and toenail dysplasia, hypoplastic breasts and nipples, intensive freckling, lacrimal duct atresia, frontal alopecia, primary hypodontia and loss of permanent teeth. ADULT syndrome differs significantly from EEC3 syndrome by the absence of facial clefting.Note: The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.Ankyloblepharon-ectodermal defects-cleft lip/palate (AEC) [MIM:106260]: An autosomal dominant condition characterized by congenital ectodermal dysplasia with coarse, wiry, sparse hair, dystrophic nails, slight hypohidrosis, scalp infections, ankyloblepharon filiform adnatum, maxillary hypoplasia, hypodontia and cleft lip/palate.Note: The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Ref.29Ectrodactyly, ectodermal dysplasia, and cleft lip/palate syndrome 3 (EEC3) [MIM:604292]: A form of ectodermal dysplasia, a heterogeneous group of disorders due to abnormal development of two or more ectodermal structures. It is an autosomal dominant syndrome characterized by ectrodactyly of hands and feet, ectodermal dysplasia and facial clefting.Note: The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Ref.26 Ref.27 Ref.30 Ref.32Split-hand/foot malformation 4 (SHFM4) [MIM:605289]: A limb malformation involving the central rays of the autopod and presenting with syndactyly, median clefts of the hands and feet, and aplasia and/or hypoplasia of the phalanges, metacarpals, and metatarsals. Some patients have been found to have mental retardation, ectodermal and craniofacial findings, and orofacial clefting.Note: The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Ref.27 Ref.30Limb-mammary syndrome (LMS) [MIM:603543]: Characterized by ectrodactyly, cleft palate and mammary-gland abnormalities.Note: The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Ref.30Defects in TP63 are a cause of cervical, colon, head and neck, lung and ovarian cancers.Ectodermal dysplasia, Rapp-Hodgkin type (EDRH) [MIM:129400]: A form of ectodermal dysplasia, a heterogeneous group of disorders due to abnormal development of two or more ectodermal structures. Characterized by the combination of anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, cleft lip, and cleft palate. The clinical syndrome is comprised of a characteristic facies (narrow nose and small mouth), wiry, slow-growing, and uncombable hair, sparse eyelashes and eyebrows, obstructed lacrimal puncta/epiphora, bilateral stenosis of external auditory canals, microsomia, hypodontia, cone-shaped incisors, enamel hypoplasia, dystrophic nails, and cleft lip/cleft palate.Note: The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Ref.33 Ref.34 Ref.35 Ref.36Non-syndromic orofacial cleft 8 (OFC8) [MIM:129400]: A birth defect consisting of cleft lips with or without cleft palate. Cleft lips are associated with cleft palate in two-third of cases. A cleft lip can occur on one or both sides and range in severity from a simple notch in the upper lip to a complete opening in the lip extending into the floor of the nostril and involving the upper gum.Note: The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Sequence similarities: Belongs to the p53 family.Contains 1 SAM (sterile alpha motif) domain. Sequence caution: The sequence AAF43486.1 differs from that shown. Reason: Erroneous initiation. The sequence AAF43487.1 differs from that shown. Reason: Erroneous initiation. The sequence AAF43488.1 differs from that shown. Reason: Erroneous initiation. The sequence AAF43489.1 differs from that shown. Reason: Erroneous initiation. The sequence AAF61624.1 differs from that shown. Reason: Frameshift at position 26. The sequence BAA32592.1 differs from that shown. Reason: Frameshift at position 26. The sequence BAA32593.1 differs from that shown. Reason: Frameshift at position 26. |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the p53 family of transcription factors. An animal model, p63 -/- mice, has been useful in defining the role this protein plays in the development and maintenance of stratified epithelial tissues. p63 -/- mice have several developmental defects which include the lack of limbs and other tissues, such as teeth and mammary glands, which develop as a result of interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium. Mutations in this gene are associated with ectodermal dysplasia, and cleft lip/palate syndrome 3 (EEC3); split-hand/foot malformation 4 (SHFM4); ankyloblepharon-ectodermal defects-cleft lip/palate; ADULT syndrome (acro-dermato-ungual-lacrimal-tooth); limb-mammary syndrome; Rap-Hodgkin syndrome (RHS); and orofacial cleft 8. Both alternative splicing and the use of alternative promoters results in multiple transcript variants encoding different proteins. Many transcripts encoding different proteins have been reported but the biological validity and the full-length nature of these variants have not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9H3D4 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 57013009 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 8626 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q9H3D4.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9H3D4,O75080, O75195, O75922, O76078, Q6VEG2, Q6VEG3 Q6VEG4, Q6VFJ1, Q6VFJ2, Q6VFJ3, Q6VH20, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9H3D4 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Tumor protein 63 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | tumor protein p63 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | TP63 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | AIS; KET; LMS; NBP; RHS; p40; p51; p63; EEC3; OFC8; p73H; p73L; SHFM4; TP53L; TP73L; p53CP; TP53CP; B(p51A); B(p51B) |
| NCBI Protein Information: | tumor protein 63; CUSP; transformation-related protein 63; tumor protein p53-competing protein; amplified in squamous cell carcinoma; chronic ulcerative stomatitis protein; keratinocyte transcription factor KET; tumor protein p63 deltaN isoform delta |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Tumor protein 63 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Chronic ulcerative stomatitis protein; CUSP; Keratinocyte transcription factor KET; Transformation-related protein 63; TP63; Tumor protein p73-like; p73L; p40; p51 |
| Protein Family: | |
| UniProt Gene Name: | TP63 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | P63_HUMAN |