Anti-SLIT2 Antibody (CAB15353)
- SKU:
- CAB15353
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-SLIT2 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB15353 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
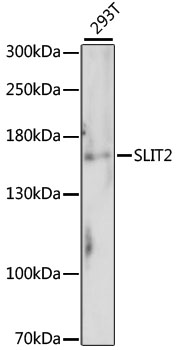
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1330-1529 of human SLIT2 (NP_004778.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:200 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Positive Samples: | 293T |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1330-1529 of human SLIT2 (NP_004778.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | LPGC EPCH KKVC AHGT CQPS SQAG FTCE CQEG WMGP LCDQ RTND PCLG NKCV HGTC LPIN AFSY SCKC LEGH GGVL CDEE EDLF NPCQ AIKC KHGK CRLS GLGQ PYCE CSSG YTGD SCDR EISC RGER IRDY YQKQ QGYA ACQT TKKV SRLE CRGG CAGG QCCG PLRS KRRK YSFE CTDG SSFV DEVE KVVK CGCT RCVS |
| Gene ID: | 9353 |
| Uniprot: | O94813 |
| Cellular Location: | Secreted |
| Calculated MW: | 168kDa/169kDa |
| Observed MW: | 170kDa |
| Synonyms: | SLIT2, SLIL3, Slit-2 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a member of the slit family of secreted glycoproteins, which are ligands for the Robo family of immunoglobulin receptors. Slit proteins play highly conserved roles in axon guidance and neuronal migration and may also have functions during other cell migration processes including leukocyte migration. Members of the slit family are characterized by an N-terminal signal peptide, four leucine-rich repeats, nine epidermal growth factor repeats, and a C-terminal cysteine knot. Proteolytic processing of this protein gives rise to an N-terminal fragment that contains the four leucine-rich repeats and five epidermal growth factor repeats and a C-terminal fragment that contains four epidermal growth factor repeats and the cysteine knot. Both full length and cleaved proteins are secreted extracellularly and can function in axon repulsion as well as other specific processes. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | SLIT2: Thought to act as molecular guidance cue in cellular migration, and function appears to be mediated by interaction with roundabout homolog receptors. During neural development involved in axonal navigation at the ventral midline of the neural tube and projection of axons to different regions. SLIT1 and SLIT2 seem to be essential for midline guidance in the forebrain by acting as repulsive signal preventing inappropriate midline crossing by axons projecting from the olfactory bulb. In spinal chord development may play a role in guiding commissural axons once they reached the floor plate by modulating the response to netrin. In vitro, silences the attractive effect of NTN1 but not its growth- stimulatory effect and silencing requires the formation of a ROBO1-DCC complex. May be implicated in spinal chord midline post- crossing axon repulsion. In vitro, only commissural axons that crossed the midline responded to SLIT2. In the developing visual system appears to function as repellent for retinal ganglion axons by providing a repulsion that directs these axons along their appropriate paths prior to, and after passage through, the optic chiasm. In vitro, collapses and repels retinal ganglion cell growth cones. Seems to play a role in branching and arborization of CNS sensory axons, and in neuronal cell migration. In vitro, Slit homolog 2 protein N-product, but not Slit homolog 2 protein C-product, repels olfactory bulb (OB) but not dorsal root ganglia (DRG) axons, induces OB growth cones collapse and induces branching of DRG axons. Seems to be involved in regulating leukocyte migration. 3 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted; Secreted, signal peptide; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Extracellular matrix Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 4p15.2 Cellular Component: extracellular space; cell surface; membrane; cytoplasm; plasma membrane; extracellular region Molecular Function:heparin binding; laminin-1 binding; identical protein binding; proteoglycan binding; protein binding; Roundabout binding; protein homodimerization activity; chemorepellent activity; calcium ion binding; GTPase inhibitor activity Biological Process: negative regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction; axon guidance; positive regulation of apoptosis; negative chemotaxis; motor axon guidance; negative regulation of axon extension; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell migration; induction of negative chemotaxis; corticospinal neuron axon guidance through the spinal cord; negative regulation of cell proliferation; cell-cell adhesion; response to cortisol stimulus; negative regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; ureteric bud development; negative regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis; negative regulation of cell migration; negative regulation of actin filament polymerization; in utero embryonic development; chemorepulsion involved in postnatal olfactory bulb interneuron migration; dorsal/ventral axon guidance; cellular response to hormone stimulus; axon extension involved in axon guidance; chemorepulsion involved in embryonic olfactory bulb interneuron migration; branching morphogenesis of a tube; cell migration during sprouting angiogenesis; negative regulation of catalytic activity; negative regulation of vascular permeability; positive regulation of axonogenesis; negative regulation of cell growth; metanephros development; retinal ganglion cell axon guidance |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the slit family of secreted glycoproteins, which are ligands for the Robo family of immunoglobulin receptors. Slit proteins play highly conserved roles in axon guidance and neuronal migration and may also have functions during other cell migration processes including leukocyte migration. Members of the slit family are characterized by an N-terminal signal peptide, four leucine-rich repeats, nine epidermal growth factor repeats, and a C-terminal cysteine knot. Proteolytic processing of this protein gives rise to an N-terminal fragment that contains the four leucine-rich repeats and five epidermal growth factor repeats and a C-terminal fragment that contains four epidermal growth factor repeats and the cysteine knot. Both full length and cleaved proteins are secreted extracellularly and can function in axon repulsion as well as other specific processes. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015] |
| UniProt Code: | O94813 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 33112440 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 9353 |
| NCBI Accession: | O94813.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O94813,O95710, Q17RU3, Q9Y5Q7, B7ZLR5, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O94813 |
| Molecular Weight: | 168,893 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Slit homolog 2 protein |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | slit homolog 2 (Drosophila) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | SLIT2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | SLIL3; Slit-2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | slit homolog 2 protein |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Slit homolog 2 protein |
| Protein Family: | Slit homolog 2 protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | SLIT2 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | SLIT2_HUMAN |