| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is highly similar to Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad50, a protein involved in DNA double-strand break repair. This protein forms a complex with MRE11 and NBS1. The protein complex binds to DNA and displays numerous enzymatic activities that are required for nonhomologous joining of DNA ends. This protein, cooperating with its partners, is important for DNA double-strand break repair, cell cycle checkpoint activation, telomere maintenance, and meiotic recombination. Knockout studies of the mouse homolog suggest this gene is essential for cell growth and viability. Mutations in this gene are the cause of Nijmegen breakage syndrome-like disorder.[provided by RefSeq, Apr 2010] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Component of the MRN complex, which plays a central role in double-strand break (DSB) repair, DNA recombination, maintenance of telomere integrity and meiosis. The complex possesses single-strand endonuclease activity and double-strand-specific 3'-5' exonuclease activity, which are provided by MRE11. RAD50 may be required to bind DNA ends and hold them in close proximity. This could facilitate searches for short or long regions of sequence homology in the recombining DNA templates, and may also stimulate the activity of DNA ligases and/or restrict the nuclease activity of MRE11 to prevent nucleolytic degradation past a given point (PubMed:11741547, PubMed:9590181, PubMed:9705271, PubMed:9651580). The complex may also be required for DNA damage signaling via activation of the ATM kinase (PubMed:15064416). In telomeres the MRN complex may modulate t-loop formation (PubMed:10888888). |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is highly similar to Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad50, a protein involved in DNA double-strand break repair. This protein forms a complex with MRE11 and NBS1. The protein complex binds to DNA and displays numerous enzymatic activities that are required for nonhomologous joining of DNA ends. This protein, cooperating with its partners, is important for DNA double-strand break repair, cell cycle checkpoint activation, telomere maintenance, and meiotic recombination. Knockout studies of the mouse homolog suggest this gene is essential for cell growth and viability. Mutations in this gene are the cause of Nijmegen breakage syndrome-like disorder.[provided by RefSeq, Apr 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | Q92878 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 60392986 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 10111 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q92878.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q92878,O43254, Q6GMT7, Q6P5X3, Q9UP86, B9EGF5, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q92878 |
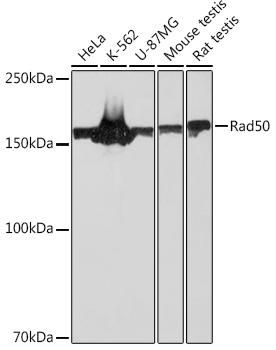
| Molecular Weight: | 155 kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | DNA repair protein RAD50 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | RAD50 double strand break repair protein |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | RAD50 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | NBSLD; RAD502; hRad50 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | DNA repair protein RAD50 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | DNA repair protein RAD50 |
| Protein Family: | RAD50-interacting protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | RAD50 |