Anti-PYGL Antibody (CAB6710)
- SKU:
- CAB6710
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Metabolism
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-PYGL Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB6710 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
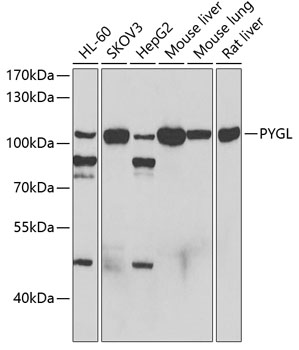
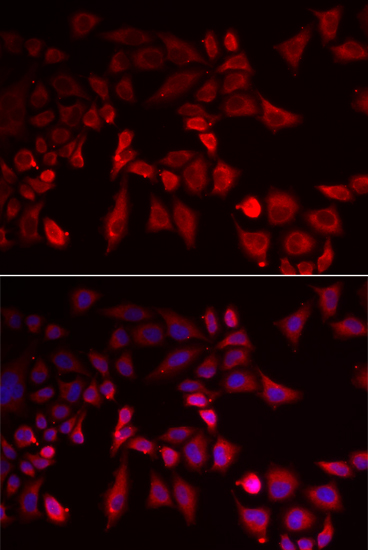
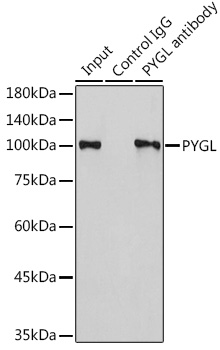
| Application: | WB IF IP |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-280 of human PYGL (NP_002854.3). |
| Application: | WB IF IP |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 IP 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, HL-60, SKOV3, HepG2, Mouse liver, Mouse lung, Rat liver |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-280 of human PYGL (NP_002854.3). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MAKP LTDQ EKRR QISI RGIV GVEN VAEL KKSF NRHL HFTL VKDR NVAT TRDY YFAL AHTV RDHL VGRW IRTQ QHYY DKCP KRVY YLSL EFYM GRTL QNTM INLG LQNA CDEA IYQL GLDI EELE EIEE DAGL GNGG LGRL AACF LDSM ATLG LAAY GYGI RYEY GIFN QKIR DGWQ VEEA DDWL RYGN PWEK SRPE FMLP VHFY GKVE HTNT GTKW IDTQ VVLA LPYD TPVP GYMN NTVN TMRL WSAR APND FNLR DFNV GDYI QAVL DRNL AENI SRVL |
| Gene ID: | 5836 |
| Uniprot: | P06737 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 93kDa/97kDa |
| Observed MW: | 110kDa |
| Synonyms: | PYGL, GSD6 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a homodimeric protein that catalyses the cleavage of alpha-1, 4-glucosidic bonds to release glucose-1-phosphate from liver glycogen stores. This protein switches from inactive phosphorylase B to active phosphorylase A by phosphorylation of serine residue 15. Activity of this enzyme is further regulated by multiple allosteric effectors and hormonal controls. Humans have three glycogen phosphorylase genes that encode distinct isozymes that are primarily expressed in liver, brain and muscle, respectively. The liver isozyme serves the glycemic demands of the body in general while the brain and muscle isozymes supply just those tissues. In glycogen storage disease type VI, also known as Hers disease, mutations in liver glycogen phosphorylase inhibit the conversion of glycogen to glucose and results in moderate hypoglycemia, mild ketosis, growth retardation and hepatomegaly. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | PYGL: Phosphorylase is an important allosteric enzyme in carbohydrate metabolism. Enzymes from different sources differ in their regulatory mechanisms and in their natural substrates. However, all known phosphorylases share catalytic and structural properties. Defects in PYGL are the cause of glycogen storage disease type 6 (GSD6). A metabolic disorder characterized by mild to moderate hypoglycemia, mild ketosis, growth retardation, and prominent hepatomegaly. Heart and skeletal muscle are not affected. Belongs to the glycogen phosphorylase family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Transferase; EC 2.4.1.1; Carbohydrate Metabolism - starch and sucrose Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 14q21-q22 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; plasma membrane; cytosol Molecular Function:glycogen phosphorylase activity; protein homodimerization activity; bile acid binding; purine binding; drug binding; vitamin binding; ATP binding; glucose binding; AMP binding; pyridoxal phosphate binding Biological Process: glycogen metabolic process; glycogen catabolic process; carbohydrate metabolic process; 5-phosphoribose 1-diphosphate biosynthetic process; glucose metabolic process; pathogenesis; glucose homeostasis Disease: Glycogen Storage Disease Vi |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a homodimeric protein that catalyses the cleavage of alpha-1,4-glucosidic bonds to release glucose-1-phosphate from liver glycogen stores. This protein switches from inactive phosphorylase B to active phosphorylase A by phosphorylation of serine residue 15. Activity of this enzyme is further regulated by multiple allosteric effectors and hormonal controls. Humans have three glycogen phosphorylase genes that encode distinct isozymes that are primarily expressed in liver, brain and muscle, respectively. The liver isozyme serves the glycemic demands of the body in general while the brain and muscle isozymes supply just those tissues. In glycogen storage disease type VI, also known as Hers disease, mutations in liver glycogen phosphorylase inhibit the conversion of glycogen to glucose and results in moderate hypoglycemia, mild ketosis, growth retardation and hepatomegaly. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011] |
| UniProt Code: | P06737 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 6648082 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5836 |
| NCBI Accession: | P06737.4 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P06737,O60567, O60752, O60913, Q501V9, Q641R5, Q96G82 A6NDQ4, B4DUB7, F5H816, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P06737 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Glycogen phosphorylase, liver form |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | phosphorylase, glycogen, liver |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PYGL |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | GSD6 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | glycogen phosphorylase, liver form |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Glycogen phosphorylase, liver form |
| Protein Family: | Glycogen phosphorylase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PYGL |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PYGL_HUMAN |