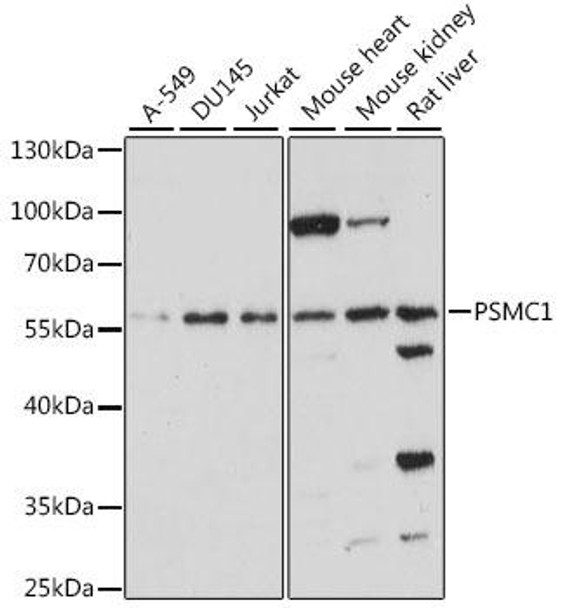
Anti-PSMC1 Antibody (CAB15712)
- SKU:
- CAB15712
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-PSMC1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB15712 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 77-440 of human PSMC1 (NP_002793.2). |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:100 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | A-549, DU145, Jurkat, HeLa, Mouse brain, Mouse heart, Mouse kidnay, Rat liver |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 77-440 of human PSMC1 (NP_002793.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | EFIR NQEQ MKPL EEKQ EEER SKVD DLRG TPMS VGTL EEII DDNH AIVS TSVG SEHY VSIL SFVD KDLL EPGC SVLL NHKV HAVI GVLM DDTD PLVT VMKV EKAP QETY ADIG GLDN QIQE IKES VELP LTHP EYYE EMGI KPPK GVIL YGPP GTGK TLLA KAVA NQTS ATFL RVVG SELI QKYL GDGP KLVR ELFR VAEE HAPS IVFI DEID AIGT KRYD SNSG GERE IQRT MLEL LNQL DGFD SRGD VKVI MATN RIET LDPA LIRP GRID RKIE FPLP DEKT KKRI FQIH TSRM TLAD DVTL DDLI MAKD DLSG ADIK AICT EAGL MALR ERRM KVTN EDFK KSKE NVLY KKQE GTPE GLYL |
| Gene ID: | 5700 |
| Uniprot: | P62191 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Lipid-anchor, Membrane, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 41kDa/49kDa |
| Observed MW: | 58kDa |
| Synonyms: | PSMC1, P26S4, S4, p56, ATPase 1 |
| Background: | The 26S proteasome is a multicatalytic proteinase complex with a highly ordered structure composed of 2 complexes, a 20S core and a 19S regulator. The 20S core is composed of 4 rings of 28 non-identical subunits; 2 rings are composed of 7 alpha subunits and 2 rings are composed of 7 beta subunits. The 19S regulator is composed of a base, which contains 6 ATPase subunits and 2 non-ATPase subunits, and a lid, which contains up to 10 non-ATPase subunits. Proteasomes are distributed throughout eukaryotic cells at a high concentration and cleave peptides in an ATP/ubiquitin-dependent process in a non-lysosomal pathway. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides. This gene encodes one of the ATPase subunits, a member of the triple-A family of ATPases which have a chaperone-like activity. This subunit and a 20S core alpha subunit interact specifically with the hepatitis B virus X protein, a protein critical to viral replication. This subunit also interacts with the adenovirus E1A protein and this interaction alters the activity of the proteasome. Finally, this subunit interacts with ataxin-7, suggesting a role for the proteasome in the development of spinocerebellar ataxia type 7, a progressive neurodegenerative disorder. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | RPT2: The 26S protease is involved in the ATP-dependent degradation of ubiquitinated proteins. The regulatory (or ATPase) complex confers ATP dependency and substrate specificity to the 26S complex. Belongs to the AAA ATPase family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protease; Proteasome complex Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 14q32.11 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; cytosol; membrane; nucleoplasm; nucleus; proteasome complex Molecular Function:ATP binding; ATPase activity; protein binding; TATA-binding protein binding Biological Process: activation of MAPKK activity; anaphase-promoting complex-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I, TAP-dependent; antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class I; apoptosis; axon guidance; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; ER-associated protein catabolic process; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle; gene expression; innate immune response; insulin receptor signaling pathway; MAPKKK cascade; mitotic cell cycle; negative regulation of apoptosis; negative regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity during mitotic cell cycle; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; polyamine metabolic process; positive regulation of transcriptional preinitiation complex assembly; positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity during mitotic cell cycle; programmed cell death; protein polyubiquitination; Ras protein signal transduction; regulation of amino acid metabolic process; regulation of apoptosis; regulation of mRNA stability; regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity during mitotic cell cycle; small GTPase mediated signal transduction; stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway; T cell receptor signaling pathway; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway; viral reproduction |
| NCBI Summary: | The 26S proteasome is a multicatalytic proteinase complex with a highly ordered structure composed of 2 complexes, a 20S core and a 19S regulator. The 20S core is composed of 4 rings of 28 non-identical subunits; 2 rings are composed of 7 alpha subunits and 2 rings are composed of 7 beta subunits. The 19S regulator is composed of a base, which contains 6 ATPase subunits and 2 non-ATPase subunits, and a lid, which contains up to 10 non-ATPase subunits. Proteasomes are distributed throughout eukaryotic cells at a high concentration and cleave peptides in an ATP/ubiquitin-dependent process in a non-lysosomal pathway. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides. This gene encodes one of the ATPase subunits, a member of the triple-A family of ATPases which have a chaperone-like activity. This subunit and a 20S core alpha subunit interact specifically with the hepatitis B virus X protein, a protein critical to viral replication. This subunit also interacts with the adenovirus E1A protein and this interaction alters the activity of the proteasome. Finally, this subunit interacts with ataxin-7, suggesting a role for the proteasome in the development of spinocerebellar ataxia type 7, a progressive neurodegenerative disorder. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P62191 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 49065817 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5700 |
| NCBI Accession: | P62191.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P62191,P62193, P62192, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P62191 |
| Molecular Weight: | 49185 |
| NCBI Full Name: | 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 4 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | proteasome 26S subunit, ATPase 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PSMC1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | S4; p56; P26S4 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 4 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | 26S protease regulatory subunit 4 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunit RPT2; Proteasome 26S subunit ATPase 1 |
| Protein Family: | Ribose-phosphate pyrophosphokinase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PSMC1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PRS4_HUMAN |