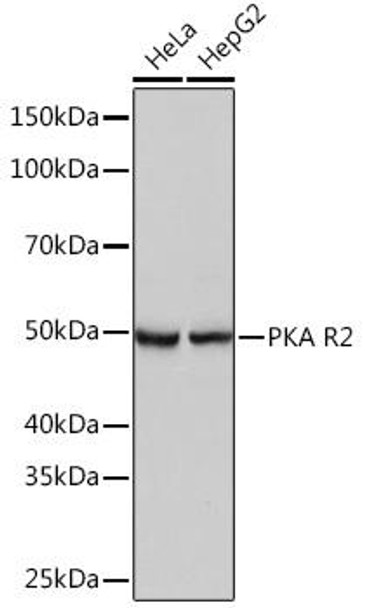
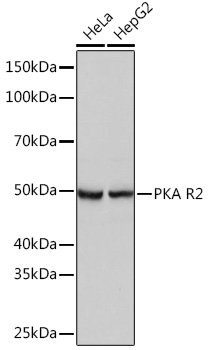
Anti-PKA R2 Antibody (CAB3889)
- SKU:
- CAB3889
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-PKA R2 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB3889 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human PKA R2 |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, HepG2 |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human PKA R2 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 5576 |
| Uniprot: | P13861 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 52kDa |
| Observed MW: | 50KDa |
| Synonyms: | PKR2, PRKAR2 |
| Background: | cAMP is a signaling molecule important for a variety of cellular functions. cAMP exerts its effects by activating the cAMP-dependent protein kinase, which transduces the signal through phosphorylation of different target proteins. The inactive kinase holoenzyme is a tetramer composed of two regulatory and two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits have been identified in humans. The protein encoded by this gene is one of the regulatory subunits. This subunit can be phosphorylated by the activated catalytic subunit. It may interact with various A-kinase anchoring proteins and determine the subcellular localization of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. This subunit has been shown to regulate protein transport from endosomes to the Golgi apparatus and further to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | PKAR2A: a regulatory subunit of cAMP-regulated protein kinase. The inactive form of the enzyme is composed of two regulatory chains and two catalytic chains. Activation by cAMP produces two active catalytic monomers and a regulatory dimer that binds four cAMP molecules. Four types of regulatory chains are found: I-alpha, I-beta, II-alpha, and II-beta. Their expression varies among tissues and is in some cases constitutive and in others inducible. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protein kinase, regulatory subunit Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 3p21.3-p21.2 Cellular Component: centrosome; focal adhesion; membrane; cytoplasm; plasma membrane; cytosol; AMP-activated protein kinase complex; cAMP-dependent protein kinase complex Molecular Function:protein binding; cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor activity; ubiquitin protein ligase binding; cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulator activity; cAMP binding Biological Process: epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; phospholipase C activation; water transport; activation of protein kinase A; energy reserve metabolic process; innate immune response; renal water homeostasis; blood coagulation; signal transduction; regulation of insulin secretion; transmembrane transport |
| NCBI Summary: | cAMP is a signaling molecule important for a variety of cellular functions. cAMP exerts its effects by activating the cAMP-dependent protein kinase, which transduces the signal through phosphorylation of different target proteins. The inactive kinase holoenzyme is a tetramer composed of two regulatory and two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits have been identified in humans. The protein encoded by this gene is one of the regulatory subunits. This subunit can be phosphorylated by the activated catalytic subunit. It may interact with various A-kinase anchoring proteins and determine the subcellular localization of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. This subunit has been shown to regulate protein transport from endosomes to the Golgi apparatus and further to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P13861 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 125198 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5576 |
| NCBI Accession: | P13861.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P13861,Q16823, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P13861 |
| Molecular Weight: | 45,518 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | cAMP-dependent protein kinase type II-alpha regulatory subunit |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type II, alpha |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PRKAR2A |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | PKR2; PRKAR2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | cAMP-dependent protein kinase type II-alpha regulatory subunit; protein kinase A, RII-alpha subunit; cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulatory subunit RII alpha |
| UniProt Protein Name: | cAMP-dependent protein kinase type II-alpha regulatory subunit |
| Protein Family: | CD99 antigen |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PRKAR2A |
| UniProt Entry Name: | KAP2_HUMAN |