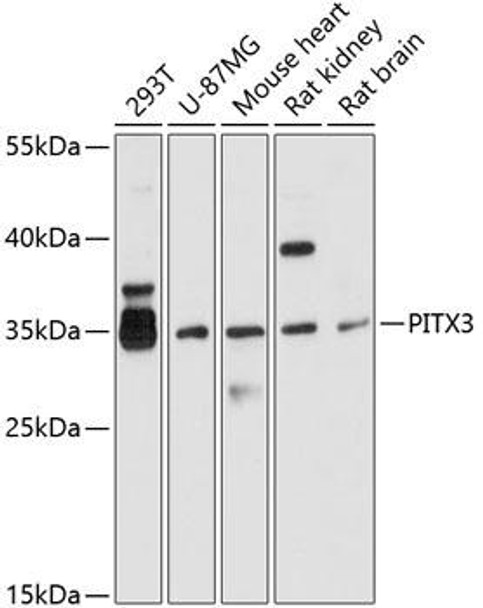
Anti-PITX3 Antibody (CAB10569)
- SKU:
- CAB10569
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-PITX3 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB10569 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-70 of human PITX3 (NP_005020.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | 293T, U-87MG, Mouse heart, Rat kidney, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-70 of human PITX3 (NP_005020.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MEFG LLSE AEAR SPAL SLSD AGTP HPQL PEHG CKGQ EHSD SEKA SASL PGGS PEDG SLKK KQRR QRTH FT |
| Gene ID: | 5309 |
| Uniprot: | O75364 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 31kDa |
| Observed MW: | 32kDa |
| Synonyms: | PITX3, ASGD1, ASMD, ASOD, CTPP4, CTRCT11, PTX3 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a member of the RIEG/PITX homeobox family, which is in the bicoid class of homeodomain proteins. Members of this family act as transcription factors. This protein is involved in lens formation during eye development. Mutations of this gene have been associated with anterior segment mesenchymal dysgenesis and congenital cataracts. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | PITX3: Transcriptional regulator which is important for the differentiation and maintenance of meso-diencephalic dopaminergic (mdDA) neurons during development. In addition to its importance during development, it also has roles in the long-term survival and maintenance of the mdDA neurons. Activates NR4A2/NURR1- mediated transcription of genes such as SLC6A3, SLC18A2, TH and DRD2 which are essential for development of mdDA neurons. Acts by decreasing the interaction of NR4A2/NURR1 with the corepressor NCOR2/SMRT which acts through histone deacetylases (HDACs) to keep promoters of NR4A2/NURR1 target genes in a repressed deacetylated state. Essential for the normal lens development and differentiation. Plays a critical role in the maintenance of mitotic activity of lens epithelial cells, fiber cell differentiation and in the control of the temporal and spatial activation of fiber cell-specific crystallins. Positively regulates FOXE3 expression and negatively regulates PROX1 in the anterior lens epithelium, preventing activation of CDKN1B/P27Kip1 and CDKN1C/P57Kip2 and thus maintains lens epithelial cells in cell cycle. Defects in PITX3 are a cause of cataract autosomal dominant (ADC). Cataract is an opacification of the crystalline lens of the eye that frequently results in visual impairment or blindness. Opacities vary in morphology, are often confined to a portion of the lens, and may be static or progressive. In general, the more posteriorly located and dense an opacity, the greater the impact on visual function. Cataract is the most common treatable cause of visual disability in childhood. Defects in PITX3 are a cause of anterior segment mesenchymal dysgenesis (ASMD); also known as anterior segment ocular dysgenesis (ASOD). ASMD consists of a range of developmental defects in structures at the front of the eye, resulting from abnormal migration or differentiation of the neural crest derived mesenchymal cells that give rise to the cornea, iris, and other components of the anterior chamber during eye development. Mature anterior segment anomalies are associated with an increased risk of glaucoma and corneal opacity. Conditions falling within the phenotypic spectrum include aniridia, posterior embryotoxon, Axenfeld anomaly, Reiger anomaly/syndrome, Peters anomaly, and iridogoniodysgenesis. Defects in PITX3 are the cause of cataract posterior polar type 4 (CTPP4). A subcapsular opacity, usually disk-shaped, located at the back of the lens. It can have a marked effect on visual acuity. Some patients affected by cataract posterior polar type 4 can present a severe phenotype including microphthalmia and neurological dysfunction. Belongs to the paired homeobox family. Bicoid subfamily. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cell development/differentiation; DNA-binding; Transcription factor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 10q24.32 Cellular Component: nucleus Biological Process: lens development in camera-type eye; lens morphogenesis in camera-type eye; midbrain development; organ morphogenesis; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent Disease: Anterior Segment Mesenchymal Dysgenesis; Cataract 11, Multiple Types |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the RIEG/PITX homeobox family, which is in the bicoid class of homeodomain proteins. Members of this family act as transcription factors. This protein is involved in lens formation during eye development. Mutations of this gene have been associated with anterior segment mesenchymal dysgenesis and congenital cataracts. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | O75364 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 6093723 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5309 |
| NCBI Accession: | O75364.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O75364,Q5VZL2, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O75364 |
| Molecular Weight: | 32kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Pituitary homeobox 3 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | paired like homeodomain 3 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PITX3 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ASMD; ASOD; PTX3; ASGD1; CTPP4; CTRCT11 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | pituitary homeobox 3 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Pituitary homeobox 3 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Homeobox protein PITX3; Paired-like homeodomain transcription factor 3 |
| Protein Family: | Pituitary homeobox |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PITX3 |