| Background: | Peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerases (PPIases) catalyze the cis/trans isomerization of peptidyl-prolyl peptide bonds. This gene encodes one of the PPIases, which specifically binds to phosphorylated ser/thr-pro motifs to catalytically regulate the post-phosphorylation conformation of its substrates. The conformational regulation catalyzed by this PPIase has a profound impact on key proteins involved in the regulation of cell growth, genotoxic and other stress responses, the immune response, induction and maintenance of pluripotency, germ cell development, neuronal differentiation, and survival. This enzyme also plays a key role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease and many cancers. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase (PPIase) that binds to and isomerizes specific phosphorylated Ser/Thr-Pro (pSer/Thr-Pro) motifs in a subset of proteins, resulting in conformational changes in the proteins (PubMed:21497122, PubMed:22033920). Displays a preference for an acidic residue N-terminal to the isomerized proline bond. Regulates mitosis presumably by interacting with NIMA and attenuating its mitosis-promoting activity. Down-regulates kinase activity of BTK (PubMed:16644721). Can transactivate multiple oncogenes and induce centrosome amplification, chromosome instability and cell transformation. Required for the efficient dephosphorylation and recycling of RAF1 after mitogen activation (PubMed:15664191). Binds and targets PML and BCL6 for degradation in a phosphorylation-dependent manner (PubMed:17828269). Acts as a regulator of JNK cascade by binding to phosphorylated FBXW7, disrupting FBXW7 dimerization and promoting FBXW7 autoubiquitination and degradation: degradation of FBXW7 leads to subsequent stabilization of JUN (PubMed:22608923). |
| NCBI Summary: | Peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerases (PPIases) catalyze the cis/trans isomerization of peptidyl-prolyl peptide bonds. This gene encodes one of the PPIases, which specifically binds to phosphorylated ser/thr-pro motifs to catalytically regulate the post-phosphorylation conformation of its substrates. The conformational regulation catalyzed by this PPIase has a profound impact on key proteins involved in the regulation of cell growth, genotoxic and other stress responses, the immune response, induction and maintenance of pluripotency, germ cell development, neuronal differentiation, and survival. This enzyme also plays a key role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease and many cancers. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Jun 2011] |
| UniProt Code: | Q13526 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 3024406 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5300 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q13526.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q13526,Q53X75, A8K4V9, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q13526 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | peptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerase, NIMA-interacting 1 |
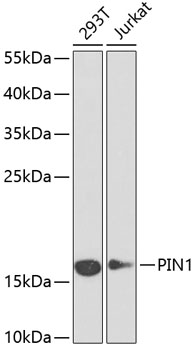
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PIN1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | DOD; UBL5 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase Pin1; PPIase Pin1; Rotamase Pin1 |
| Protein Family: | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PIN1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PIN1_HUMAN |