Anti-Parkin Antibody (CAB0968)
- SKU:
- CAB0968
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Autophagy
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Parkin Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB0968 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
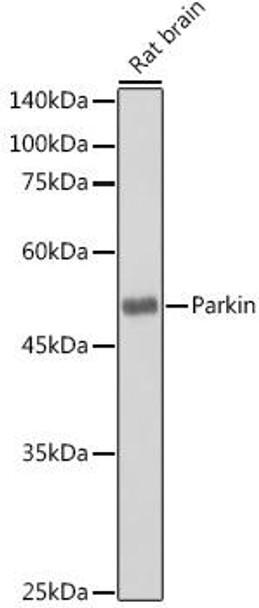
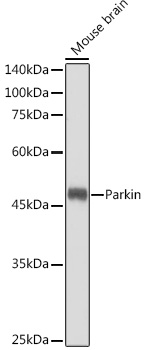
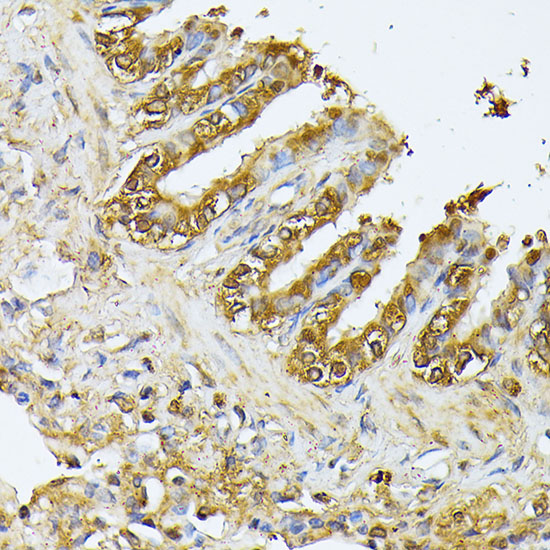
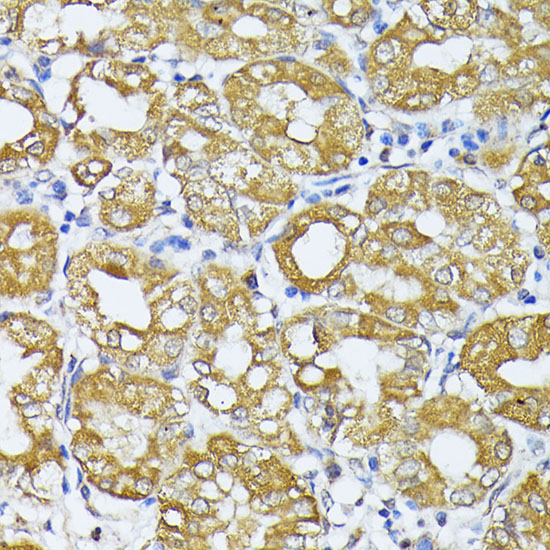
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-300 of human Parkin |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | Mouse brain, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-300 of human Parkin |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MIVF VRFN SSHG FPVE VDSD TSIF QLKE VVAK RQGV PADQ LRVI FAGK ELRN DWTV QNCD LDQQ SIVH IVQR PWRK GQEM NATG GDDP RNAA GGCE REPQ SLTR VDLS SSVL PGDS VGLA VILH TDSR KDSP PAGS PAGR SIYN SFYV YCKG PCQR VQPG KLRV QCST CRQA TLTL TQGP SCWD DVLI PNRM SGEC QSPH CPGT SAEF FFKC GAHP TSDK ETSV ALHL IATN SRNI TCIT CTDV RSPV LVFQ CNSR HVIC LDCF HLYC VTRL NDRQ FVHD PQLG YSLP CVGT GDTV VLRG |
| Gene ID: | 5071 |
| Uniprot: | O60260 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Endoplasmic reticulum, Mitochondrion, Nucleus, cytosol |
| Calculated MW: | 23kDa/30-51kDa |
| Observed MW: | 52KDa |
| Synonyms: | PRKN, AR-JP, LPRS2, PARK2, PDJ, Parkin |
| Background: | The precise function of this gene is unknown; however, the encoded protein is a component of a multiprotein E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that mediates the targeting of substrate proteins for proteasomal degradation. Mutations in this gene are known to cause Parkinson disease and autosomal recessive juvenile Parkinson disease. Alternative splicing of this gene produces multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. Additional splice variants of this gene have been described but currently lack transcript support. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | PARK2: a component of a multiprotein E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, catalyzing the covalent attachment of ubiquitin moieties onto substrate proteins, such as BCL2, SYT11, CCNE1, GPR37, STUB1, a 22 kDa O-linked glycosylated isoform of SNCAIP, SEPT5, ZNF746 and AIMP2. Mediates monoubiquitination as well as 'Lys-48'-linked and 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of substrates depending on the context. Participates in the removal and/or detoxification of abnormally folded or damaged protein by mediating 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of misfolded proteins such as PARK7: 'Lys-63'- linked polyubiquitinated misfolded proteins are then recognized by HDAC6, leading to their recruitment to aggresomes, followed by degradation. Mediates 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of SNCAIP, possibly playing a role in Lewy-body formation. Mediates monoubiquitination of BCL2, thereby acting as a positive regulator of autophagy. Promotes the autophagic degradation of dysfunctional depolarized mitochondria. Mediates 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitination of ZNF746, followed by degradation of ZNF746 by the proteasome; possibly playing a role in role in regulation of neuron death. Limits the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Loss of this ubiquitin ligase activity appears to be the mechanism underlying pathogenesis of PARK2. May protect neurons against alpha synuclein toxicity, proteasomal dysfunction, GPR37 accumulation, and kainate-induced excitotoxicity. May play a role in controlling neurotransmitter trafficking at the presynaptic terminal and in calcium-dependent exocytosis. Regulates cyclin-E during neuronal apoptosis. May represent a tumor suppressor gene. Forms an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex with UBE2L3 or UBE2L6. Mediates 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination by associating with UBE2V1. Part of a SCF-like complex, consisting of PARK2, CUL1 and FBXW7. Part of a complex, including STUB1, HSP70 and GPR37. The amount of STUB1 in the complex increases during ER stress. STUB1 promotes the dissociation of HSP70 from PARK2 and GPR37, thus facilitating PARK2-mediated GPR37 ubiquitination. HSP70 transiently associates with unfolded GPR37 and inhibits the E3 activity of PARK2, whereas, STUB1 enhances the E3 activity of PARK2 through promotion of dissociation of HSP70 from PARK2-GPR37 complexes. Interacts with PSMD4 and PACRG. Interacts with LRRK2. Interacts with RANBP2. Interacts with SUMO1 but not SUMO2, which promotes nuclear localization and autoubiquitination. Interacts (via first RING- type domain) with AIMP2 (via N-terminus). Interacts with PSMA7 and RNF41. Interacts with PINK1. Highly expressed in the brain including the substantia nigra. Expressed in heart, testis and skeletal muscle. Expression is down-regulated or absent in tumor biopsies, and absent in the brain of PARK2 patients. Overexpression protects dopamine neurons from kainate-mediated apoptosis. Found in serum. Belongs to the RBR family. Parkin subfamily. 6 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Ubiquitin ligase; Ligase; Ubiquitin conjugating system; EC 6.3.2.19; EC 6.3.2.- Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 6q25.2-q27 Cellular Component: Golgi apparatus; neuron projection; mitochondrion; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; endoplasmic reticulum; cytoplasm; SCF ubiquitin ligase complex; nucleus; cytosol; ubiquitin ligase complex Molecular Function:tubulin binding; identical protein binding; ubiquitin binding; zinc ion binding; histone deacetylase binding; ubiquitin-protein ligase activity; Hsp70 protein binding; actin binding; protein kinase binding; PDZ domain binding; protein binding; G-protein-coupled receptor binding; ubiquitin conjugating enzyme binding; chaperone binding; ubiquitin protein ligase binding; heat shock protein binding; kinase binding; SH3 domain binding; ligase activity Biological Process: protein monoubiquitination; proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; negative regulation of JNK cascade; negative regulation of actin filament bundle formation; startle response; central nervous system development; protein polyubiquitination; adult locomotory behavior; regulation of protein ubiquitination; protein ubiquitination during ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; regulation of neurotransmitter secretion; protein ubiquitination; mitochondrion localization; norepinephrine metabolic process; dopamine metabolic process; regulation of dopamine secretion; negative regulation of insulin secretion; negative regulation of glucokinase activity; zinc ion homeostasis; negative regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; regulation of lipid transport; dopamine uptake; negative regulation of neuron apoptosis; positive regulation of DNA binding; mitochondrion organization and biogenesis; mitochondrial fission; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic; protein autoubiquitination; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; transcription, DNA-dependent; protein stabilization; learning; regulation of protein transport; cellular protein catabolic process; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; mitochondrion degradation; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; regulation of autophagy; response to oxidative stress Disease: Parkinson Disease 2, Autosomal Recessive Juvenile; Leprosy, Susceptibility To, 2; Lung Cancer; Ovarian Cancer |
| NCBI Summary: | The precise function of this gene is unknown; however, the encoded protein is a component of a multiprotein E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that mediates the targeting of substrate proteins for proteasomal degradation. Mutations in this gene are known to cause Parkinson disease and autosomal recessive juvenile Parkinson disease. Alternative splicing of this gene produces multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. Additional splice variants of this gene have been described but currently lack transcript support. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | O60260 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 116242725 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5071 |
| NCBI Accession: | O60260.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O60260,Q5TFV8, Q5VVX4, Q6Q2I6, Q8NI41, Q8NI43, Q8NI44 Q8WW07, A3FG77, A8K975, D3JZW7, D3K2X0, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O60260 |
| Molecular Weight: | 465 |
| NCBI Full Name: | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin protein ligase |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PARK2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | PDJ; PRKN; AR-JP; LPRS2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin; parkinson juvenile disease protein 2; parkinson protein 2, E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (parkin); Parkinson disease (autosomal recessive, juvenile) 2, parkin |
| UniProt Protein Name: | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Parkinson juvenile disease protein 2; Parkinson disease protein 2 |
| Protein Family: | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PARK2 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PRKN2_HUMAN |