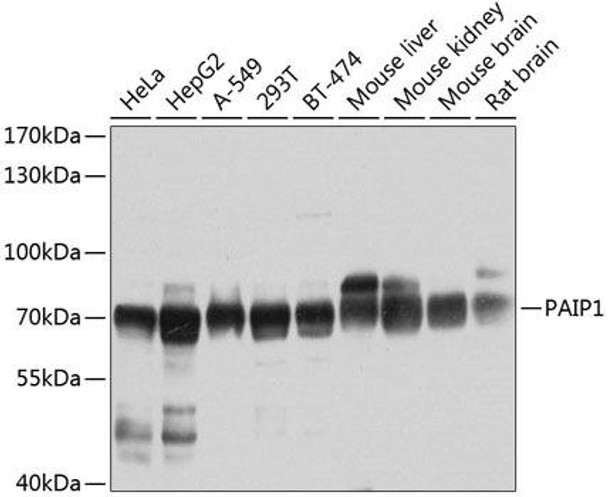
Anti-PAIP1 Antibody (CAB6042)
- SKU:
- CAB6042
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-PAIP1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB6042 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-260 of human PAIP1 (NP_877590.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:1000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, HepG2, A-549, 293T, BT-474, Mouse liver, Mouse kidney, Mouse brain, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-260 of human PAIP1 (NP_877590.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MSDG FDRA PEQT RPLR APPS SQDK IPQQ NSES AMAK PQVV VAPV LMSK LSVN APEF YPSG YSSS YTES YEDG CEDY PTLS EYVQ DFLN HLTE QPGS FETE IEQF AETL NGCV TTDD ALQE LVEL IYQQ ATSI PNFS YMGA RLCN YLSH HLTI SPQS GNFR QLLL QRCR TEYE VKDQ AAKG DEVT RKRF HAFV LFLG ELYL NLEI KGTN GQVT RADI LQVG LREL LNAL FSNP MDDN LICA VKLL KLTG SVLE DAWK EKGK |
| Gene ID: | 10605 |
| Uniprot: | Q9H074 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm |
| Calculated MW: | 42kDa/45kDa/53kDa |
| Observed MW: | 70kDa |
| Synonyms: | PAIP1 |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene interacts with poly(A)-binding protein and with the cap-binding complex eIF4A. It is involved in translational initiation and protein biosynthesis. Overexpression of this gene in COS7 cells stimulates translation. Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and three transcript variants encoding three distinct isoforms have been identified. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | PAIP1: Acts as a coactivator in the regulation of translation initiation of poly(A)-containing mRNAs. Its stimulatory activity on translation is mediated via its action on PABPC1. Competes with PAIP2 for binding to PABPC1. Its association with EIF4A and PABPC1 may potentiate contacts between mRNA termini. May also be involved in translationally coupled mRNA turnover. Implicated with other RNA-binding proteins in the cytoplasmic deadenylation/translational and decay interplay of the FOS mRNA mediated by the major coding-region determinant of instability (mCRD) domain. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Translation Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 5p12 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; cytosol Molecular Function:protein binding; translation activator activity Biological Process: mRNA stabilization; poly(A) tail shortening; translational initiation |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene interacts with poly(A)-binding protein and with the cap-binding complex eIF4A. It is involved in translational initiation and protein biosynthesis. Overexpression of this gene in COS7 cells stimulates translation. Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and three transcript variants encoding three distinct isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9H074 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 46397025 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 10605 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q9H074.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9H074,O60455, Q96B61, Q9BS63, A6NKV8, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9H074 |
| Molecular Weight: | 42,007 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Polyadenylate-binding protein-interacting protein 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | poly(A) binding protein interacting protein 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PAIP1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | polyadenylate-binding protein-interacting protein 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Polyadenylate-binding protein-interacting protein 1 |
| Protein Family: | Polyadenylate-binding protein-interacting protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PAIP1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PAIP1_HUMAN |