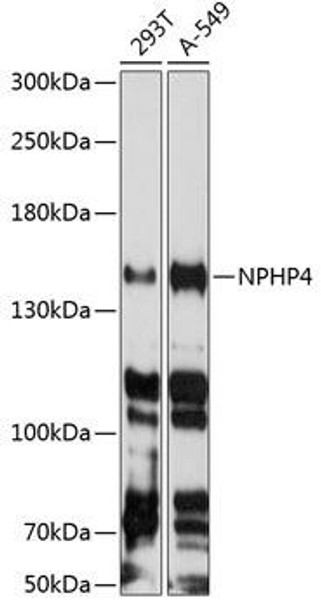
Anti-NPHP4 Antibody (CAB8934)
- SKU:
- CAB8934
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Application:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-NPHP4 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB8934 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1247-1426 of human NPHP4 (NP_055917.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | 293T, A-549 |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1247-1426 of human NPHP4 (NP_055917.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | RLSL VLRG TQTV RKVR AFTS HPQE LKTD PKGV FVLP PRGV QDLH VGVR PLRA GSRF VHLN LVDV DCHQ LVAS WLVC LCCR QPLI SKAF EIML AAGE GKGV NKRI TYTN PYPS RRTF HLHS DHPE LLRF REDS FQVG GGET YTIG LQFA PSQR VGEE EILI YIND HEDK NEEA FCVK VIYQ |
| Gene ID: | 261734 |
| Uniprot: | O75161 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell junction, Cytoplasm, centrosome, cilium basal body, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, tight junction |
| Calculated MW: | 99kDa/157kDa |
| Observed MW: | 157kDa |
| Synonyms: | NPHP4, POC10, SLSN4 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a protein involved in renal tubular development and function. This protein interacts with nephrocystin, and belongs to a multifunctional complex that is localized to actin- and microtubule-based structures. Mutations in this gene are associated with nephronophthisis type 4, a renal disease, and with Senior-Loken syndrome type 4, a combination of nephronophthisis and retinitis pigmentosa. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | NPHP4: Involved in the organization of apical junctions in kidney cells together with NPHP1 and RPGRIP1L/NPHP8. Does not seem to be strictly required for ciliogenesis. Defects in NPHP4 are the cause of nephronophthisis type 4 (NPHP4); also known as familial juvenile nephronophthisis 4. NPHP4 is an autosomal recessive inherited disease resulting in end-stage renal disease at age ranging between 6 and 35 years. It is a progressive tubulo-interstitial kidney disorder characterized by polydipsia, polyuria, anemia and growth retardation. The most prominent histological features are modifications of the tubules with thickening of the basement membrane, interstitial fibrosis and, in the advanced stages, medullary cysts. Ciliary dysfunction leads to a broad spectrum of disorders, collectively termed ciliopathies. Overlapping clinical features include retinal degeneration, renal cystic disease, skeletal abnormalities, fibrosis of various organ, and a complex range of anatomical and functional defects of the central and peripheral nervous system. The ciliopathy range of diseases includes Meckel-Gruber syndrome, Bardet-Biedl syndrome, Joubert syndrome, nephronophtisis, Senior-Loken syndrome, and Jeune asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy among others. Single-locus allelism is insufficient to explain the variable penetrance and expressivity of such disorders, leading to the suggestion that variations across multiple sites of the ciliary proteome, including NPHP4, influence the clinical outcome. Defects in NPHP4 are the cause of Senior-Loken syndrome type 4 (SLSN4). SLSN is a renal-retinal disorder characterized by progressive wasting of the filtering unit of the kidney, with or without medullary cystic renal disease, and progressive eye disease. Typically this disorder becomes apparent during the first year of life. Belongs to the NPHP4 family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cytoskeletal Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1p36 Cellular Component: centrosome; tight junction; membrane; intercellular junction; cytosol; photoreceptor connecting cilium Molecular Function:protein binding; structural molecule activity Biological Process: sperm motility; cell-cell adhesion; retina development in camera-type eye; organelle organization and biogenesis; photoreceptor cell maintenance; actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; signal transduction; visual behavior Disease: Nephronophthisis 4; Senior-loken Syndrome 4 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a protein involved in renal tubular development and function. This protein interacts with nephrocystin, and belongs to a multifunctional complex that is localized to actin- and microtubule-based structures. Mutations in this gene are associated with nephronophthisis type 4, a renal disease, and with Senior-Loken syndrome type 4, a combination of nephronophthisis and retinitis pigmentosa. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014] |
| UniProt Code: | O75161 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 615276301 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 261734 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_001278522.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O75161,Q8IWC0, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O75161 |
| Molecular Weight: | 99,953 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | nephrocystin-4 isoform b |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | nephronophthisis 4 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | NPHP4 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | POC10; SLSN4 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | nephrocystin-4 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Nephrocystin-4 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Nephroretinin |
| Protein Family: | Nephrocystin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | NPHP4 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | NPHP4_HUMAN |