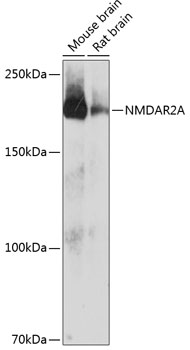
Anti-NMDAR2A Antibody (CAB19089)
- SKU:
- CAB19089
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-NMDAR2A Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB19089 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human NMDAR2A |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | Mouse brain, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human NMDAR2A |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 2903 |
| Uniprot: | Q12879 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 165kDa |
| Observed MW: | 180kDa |
| Synonyms: | EPND, FESD, GluN2A, LKS, NMDAR2A, NR2A, GRIN2A, NMDA 2A |
| Background: | This gene encodes a member of the glutamate-gated ion channel protein family. The encoded protein is an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunit. NMDA receptors are both ligand-gated and voltage-dependent, and are involved in long-term potentiation, an activity-dependent increase in the efficiency of synaptic transmission thought to underlie certain kinds of memory and learning. These receptors are permeable to calcium ions, and activation results in a calcium influx into post-synaptic cells, which results in the activation of several signaling cascades. Disruption of this gene is associated with focal epilepsy and speech disorder with or without mental retardation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2014] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | NMDAR2A: a subunit of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, members of the glutamate receptor channel superfamily. Possesses high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium and is modulated by glycine. Plays a key role in synaptic plasticity, synaptogenesis, excitotoxicity, memory acquisition and learning. Mediates neuronal functions in glutamate neurotransmission. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Membrane protein, multi-pass; Membrane protein, integral; Channel, ligand-gated Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 16p13.2 Cellular Component: presynaptic membrane; postsynaptic membrane; synaptic vesicle; cell surface; integral to plasma membrane; endoplasmic reticulum; dendrite; plasma membrane; cell junction; N-methyl-D-aspartate selective glutamate receptor complex Molecular Function:protein binding; extracellular-glutamate-gated ion channel activity; zinc ion binding; N-methyl-D-aspartate selective glutamate receptor activity; calcium channel activity Biological Process: startle response; positive regulation of apoptosis; regulation of synaptic plasticity; sensory perception of pain; dopamine metabolic process; synaptic transmission; protein localization; learning and/or memory; transport; response to wounding; visual learning; serotonin metabolic process; response to drug; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic; glutamate signaling pathway; response to amphetamine; sleep; memory; response to ethanol; neurogenesis; ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway; directional locomotion; regulation of sensory perception of pain; regulation of excitatory postsynaptic membrane potential; negative regulation of protein catabolic process Disease: Epilepsy, Focal, With Speech Disorder And With Or Without Mental Retardation |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the glutamate-gated ion channel protein family. The encoded protein is an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunit. NMDA receptors are both ligand-gated and voltage-dependent, and are involved in long-term potentiation, an activity-dependent increase in the efficiency of synaptic transmission thought to underlie certain kinds of memory and learning. These receptors are permeable to calcium ions, and activation results in a calcium influx into post-synaptic cells, which results in the activation of several signaling cascades. Disruption of this gene is associated with focal epilepsy and speech disorder with or without mental retardation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2014] |
| UniProt Code: | Q12879 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 14285603 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2903 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q12879.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q12879,O00669, Q17RZ6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q12879 |
| Molecular Weight: | 144,431 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2A |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2A |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | GRIN2A |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | LKS; EPND; FESD; NR2A; GluN2A; NMDAR2A |
| NCBI Protein Information: | glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2A; N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2A; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 2A; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel, subunit epsilon-1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2A |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit epsilon-1; N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2A; NMDAR2A; NR2A; hNR2A |
| Protein Family: | Glutamate receptor ionotropic |
| UniProt Gene Name: | GRIN2A |
| UniProt Entry Name: | NMDE1_HUMAN |