Anti-MAPK11 Antibody (CAB7717)
- SKU:
- CAB7717
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Metabolism
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-MAPK11 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB7717 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
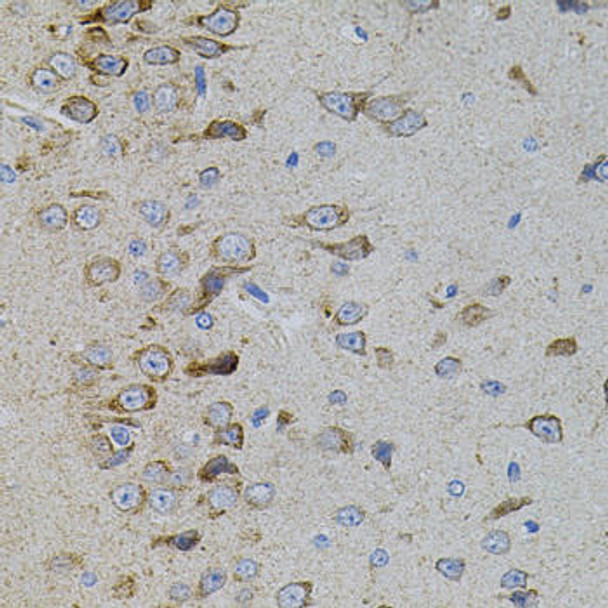
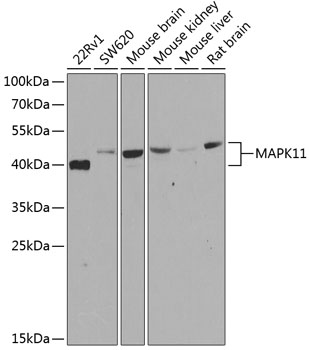
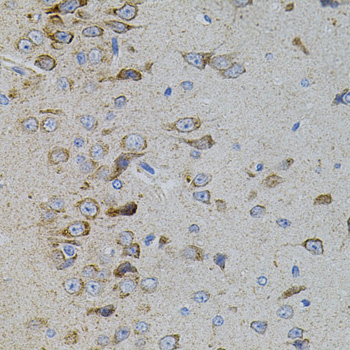
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human MAPK11 |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | 22Rv1, SW620, Mouse brain, Mouse kidney, Mouse liver, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human MAPK11 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 5600 |
| Uniprot: | Q15759 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 23kDa/41kDa |
| Observed MW: | 41kDa |
| Synonyms: | MAPK11, P38B, P38BETA2, PRKM11, SAPK2, SAPK2B, p38-2, p38Beta |
| Background: | This gene encodes a member of a family of protein kinases that are involved in the integration of biochemical signals for a wide variety of cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, transcriptional regulation, and development. The encoded protein can be activated by proinflammatory cytokines and environmental stresses through phosphorylation by mitogen activated protein kinase kinases (MKKs). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Function: Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. MAPK11 is one of the four p38 MAPKs which play an important role in the cascades of cellular responses evoked by extracellular stimuli such as proinflammatory cytokines or physical stress leading to direct activation of transcription factors. Accordingly, p38 MAPKs phosphorylate a broad range of proteins and it has been estimated that they may have approximately 200 to 300 substrates each. MAPK11 functions are mostly redundant with those of MAPK14. Some of the targets are downstream kinases which are activated through phosphorylation and further phosphorylate additional targets. RPS6KA5/MSK1 and RPS6KA4/MSK2 can directly phosphorylate and activate transcription factors such as CREB1, ATF1, the NF-kappa-B isoform RELA/NFKB3 STAT1 and STAT3, but can also phosphorylate histone H3 and the nucleosomal protein HMGN1. RPS6KA5/MSK1 and RPS6KA4/MSK2 play important roles in the rapid induction of immediate-early genes in response to stress or mitogenic stimuli, either by inducing chromatin remodeling or by recruiting the transcription machinery. On the other hand, two other kinase targets, MAPKAPK2/MK2 and MAPKAPK3/MK3, participate in the control of gene expression mostly at the post-transcriptional level, by phosphorylating ZFP36 (tristetraprolin) and ELAVL1, and by regulating EEF2K, which is important for the elongation of mRNA during translation. MKNK1/MNK1 and MKNK2/MNK2, two other kinases activated by p38 MAPKs, regulate protein synthesis by phosphorylating the initiation factor EIF4E2. In the cytoplasm, the p38 MAPK pathway is an important regulator of protein turnover. For example, CFLAR is an inhibitor of TNF-induced apoptosis whose proteasome-mediated degradation is regulated by p38 MAPK phosphorylation. Ectodomain shedding of transmembrane proteins is regulated by p38 MAPKs as well. In response to inflammatory stimuli, p38 MAPKs phosphorylate the membrane-associated metalloprotease ADAM17. Such phosphorylation is required for ADAM17-mediated ectodomain shedding of TGF-alpha family ligands, which results in the activation of EGFR signaling and cell proliferation. Additional examples of p38 MAPK substrates are the FGFR1. FGFR1 can be translocated from the extracellular space into the cytosol and nucleus of target cells, and regulates processes such as rRNA synthesis and cell growth. FGFR1 translocation requires p38 MAPK activation. In the nucleus, many transcription factors are phosphorylated and activated by p38 MAPKs in response to different stimuli. Classical examples include ATF1, ATF2, ATF6, ELK1, PTPRH, DDIT3, TP53/p53 and MEF2C and MEF2A. The p38 MAPKs are emerging as important modulators of gene expression by regulating chromatin modifiers and remodelers. The promoters of several genes involved in the inflammatory response, such as IL6, IL8 and IL12B, display a p38 MAPK-dependent enrichment of histone H3 phosphorylation on 'Ser-10' (H3S10ph) in LPS-stimulated myeloid cells. This phosphorylation enhances the accessibility of the cryptic NF-kappa-B-binding sites marking promoters for increased NF-kappa-B recruitment. Ref.4 Ref.13 Ref.14 Ref.16 Ref.17 |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Catalytic activity: ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein. Cofactor: Magnesium By similarity. Enzyme regulation: Activated by phosphorylation on threonine and tyrosine by MAP2K3/MKK3, MAP2K4/MKK4 and MAP2K6/MKK6. MAP2K3/MKK3 and MAP2K6/MKK6 are both essential for the activation of MAPK11 induced by environmental stress. HDAC3 interacts directly and selectively with MAPK11 to repress ATF2 transcriptional activity, and regulate TNF gene expression in LPS-stimulated cells. Inhibited by SB203580 and pyridinyl-imidazole related compounds. Ref.4 Ref.5 Ref.15 Ref.17 Subunit structure: Interacts with HDAC3 and DUSP16. Ref.15 Ref.17 Subcellular location: Cytoplasm By similarity. Nucleus By similarity. Tissue specificity: Highest levels in the brain and heart. Also expressed in the placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney and pancreas. Domain: The TXY motif contains the threonine and tyrosine residues whose phosphorylation activates the MAP kinases. Post-translational modification: Dually phosphorylated on Thr-180 and Tyr-182 by MAP2K3/MKK3, MAP2K4/MKK4 and MAP2K6/MKK6, which activates the enzyme. Ref.17 Sequence similarities: Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. MAP kinase subfamily.Contains 1 protein kinase domain. |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the MAP kinase family. MAP kinases act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals, and are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation, and development. This kinase is most closely related to p38 MAP kinase, both of which can be activated by proinflammatory cytokines and environmental stress. This kinase is activated through its phosphorylation by MAP kinase kinases (MKKs), preferably by MKK6. Transcription factor ATF2/CREB2 has been shown to be a substrate of this kinase. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q15759 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 134047835 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5600 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q15759.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q15759,O00284, O15472, Q2XNF2, B0LPG1, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q15759 |
| Molecular Weight: | 41,357 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 11 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | mitogen-activated protein kinase 11 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | MAPK11 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | P38B; SAPK2; p38-2; PRKM11; SAPK2B; p38Beta; P38BETA2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | mitogen-activated protein kinase 11; MAPK 11; MAP kinase 11; MAP kinase p38 beta; stress-activated protein kinase 2; stress-activated protein kinase-2; stress-activated protein kinase 2b; stress-activated protein kinase-2b; mitogen-activated protein kinase p38-2; mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 beta |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 11 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 beta; MAP kinase p38 beta; p38b; Stress-activated protein kinase 2b; SAPK2b; p38-2 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | MAPK11 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | MK11_HUMAN |