Anti-macroH2A.1 Antibody (CAB9059)
- SKU:
- CAB9059
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-macroH2A.1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB9059 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
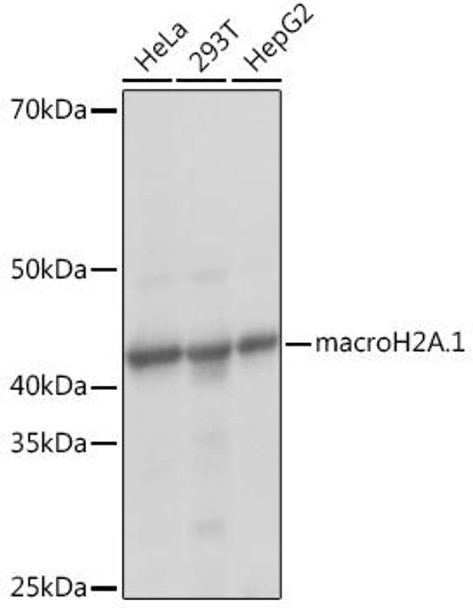
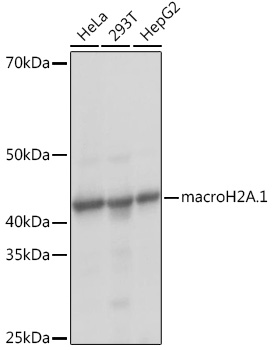
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human macroH2A.1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, 293T, HepG2 |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human macroH2A.1 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 9555 |
| Uniprot: | O75367 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 40kDa |
| Observed MW: | 41KDa |
| Synonyms: | H2A.y, H2A/y, H2AF12M, MACROH2A1.1, mH2A1, macroH2A1.2 |
| Background: | Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Nucleosomes consist of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene encodes a replication-independent histone that is a member of the histone H2A family. It replaces conventional H2A histones in a subset of nucleosomes where it represses transcription and participates in stable X chromosome inactivation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2015] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | H2AFY: Variant histone H2A which replaces conventional H2A in a subset of nucleosomes where it represses transcription. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post- translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. Involved in stable X chromosome inactivation. Inhibits the binding of transcription factors and interferes with the activity of remodeling SWI/SNF complexes. Inhibits histone acetylation by EP300 and recruits class I HDACs, which induces an hypoacetylated state of chromatin. In addition, isoform 1, but not isoform 2, binds ADP-ribose and O-acetyl-ADP- ribose, and may be involved in ADP-ribose-mediated chromatin modulation. The nucleosome is a histone octamer containing two molecules each of H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 assembled in one H3-H4 heterotetramer and two H2A-H2B heterodimers. Interacts with SPOP. Part of a complex consisting of H2AFY, CUL3 and SPOP. Interacts with HDAC1 and HDAC2. Ubiquitous. 3 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 5q31.1 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; centric heterochromatin; sex chromatin; ESC/E(Z) complex; nuclear chromatin; nucleolus; Barr body; condensed chromosome; nucleosome; nucleus Molecular Function:rDNA binding; protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity; protein binding; DNA binding; double-stranded methylated DNA binding; chromatin DNA binding; protein heterodimerization activity; protein kinase binding Biological Process: nucleosome assembly; negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic; dosage compensation; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; chromatin modification; regulation of cell growth; negative regulation of histone phosphorylation |
| NCBI Summary: | Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Nucleosomes consist of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene encodes a member of the histone H2A family. It replaces conventional H2A histones in a subset of nucleosomes where it represses transcription and participates in stable X chromosome inactivation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | O75367 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 90110023 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 9555 |
| NCBI Accession: | O75367.4 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O75367,O75377, Q503A8, Q7Z5E3, Q96D41, Q9H8P3, Q9UP96 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O75367 |
| Molecular Weight: | 372 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Core histone macro-H2A.1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | H2A histone family, member Y |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | H2AFY |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | H2A.y; H2A/y; H2AFJ; mH2A1; H2AF12M; MACROH2A1.1; macroH2A1.2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | core histone macro-H2A.1; histone H2A.y; histone macroH2A1; histone macroH2A1.1; histone macroH2A1.2; medulloblastoma antigen MU-MB-50.205 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Core histone macro-H2A.1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Histone H2A.y; H2A/y; Medulloblastoma antigen MU-MB-50.205 |
| Protein Family: | Core histone macro |
| UniProt Gene Name: | H2AFY |
| UniProt Entry Name: | H2AY_HUMAN |

![Anti-macroH2A.1 Antibody (CAB7045)[KO Validated] Anti-macroH2A.1 Antibody (CAB7045)[KO Validated]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-39x6lpnvxv/images/stencil/590x590/products/30673/28862/anti-macroh2a.1-antibody-cab7045ko-validated__69492__47289.1644317126.jpg?c=1)
![Anti-macroH2A.1 Antibody (CAB18091)[KO Validated] Anti-macroH2A.1 Antibody (CAB18091)[KO Validated]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-39x6lpnvxv/images/stencil/590x590/products/19218/17418/anti-macroh2a.1-antibody-cab18091ko-validated__17856__49007.1644251923.jpg?c=1)





