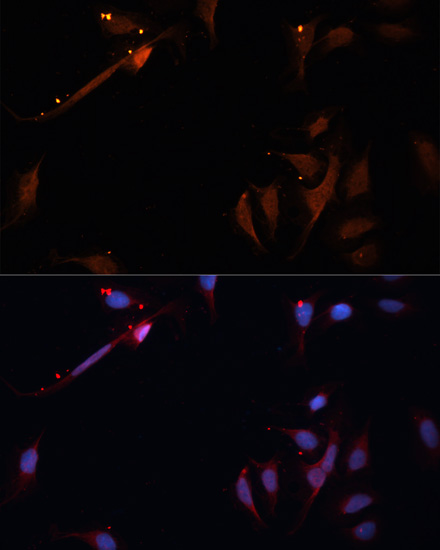
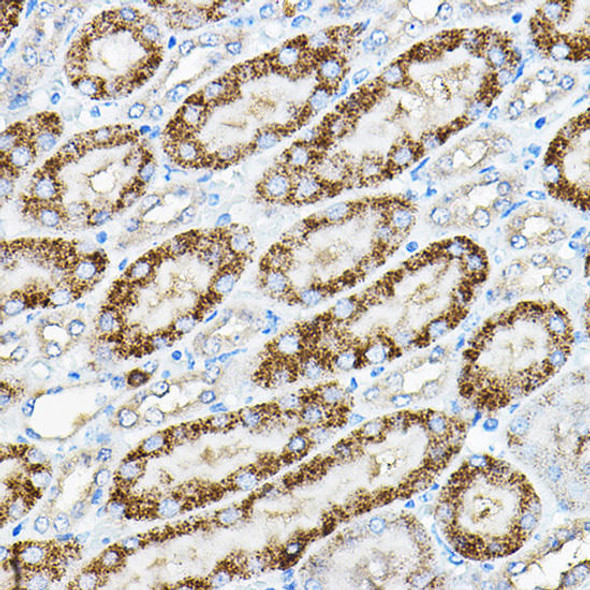
Anti-LPL Antibody (CAB16252)
- SKU:
- CAB16252
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Metabolism
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-LPL Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB16252 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
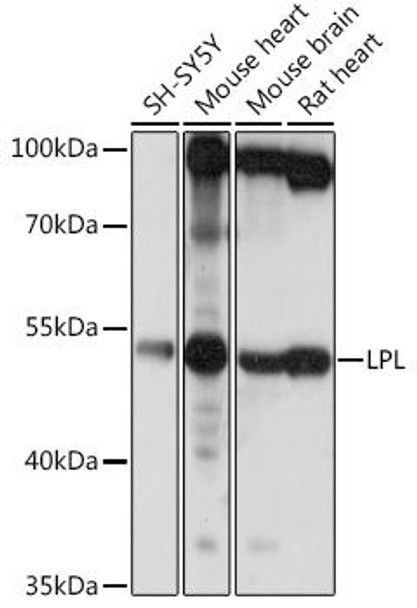
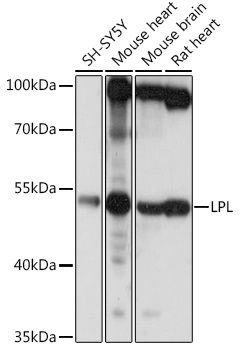
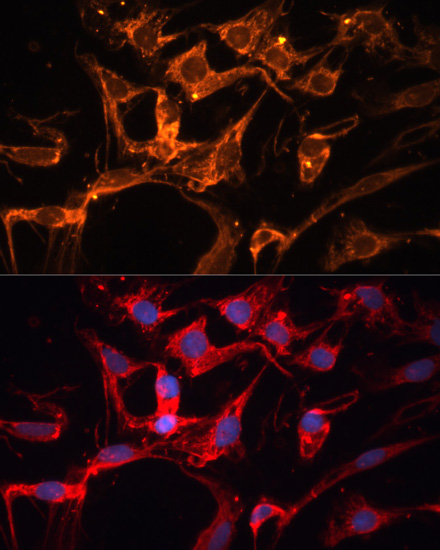
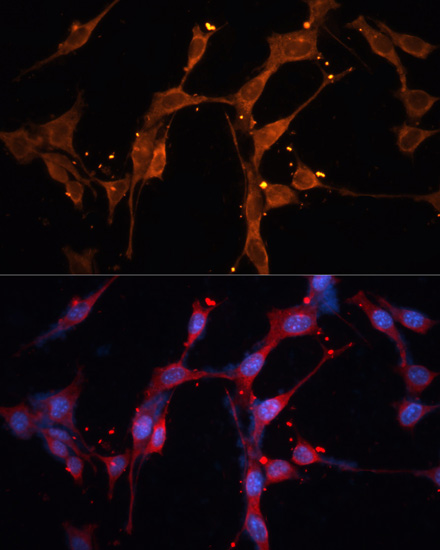
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 124-475 of human LPL (NP_000228.1). |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | SH-SY5Y, Mouse heart, Mouse brain, Rat heart |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 124-475 of human LPL (NP_000228.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | SAGY TKLV GQDV ARFI NWME EEFN YPLD NVHL LGYS LGAH AAGI AGSL TNKK VNRI TGLD PAGP NFEY AEAP SRLS PDDA DFVD VLHT FTRG SPGR SIGI QKPV GHVD IYPN GGTF QPGC NIGE AIRV IAER GLGD VDQL VKCS HERS IHLF IDSL LNEE NPSK AYRC SSKE AFEK GLCL SCRK NRCN NLGY EINK VRAK RSSK MYLK TRSQ MPYK VFHY QVKI HFSG TESE THTN QAFE ISLY GTVA ESEN IPFT LPEV STNK TYSF LIYT EVDI GELL MLKL KWKS DSYF SWSD WWSS PGFA IQKI RVKA GETQ KKVI FCSR EKVS HLQK GKAP AVFV KCHD KSLN KKSG |
| Gene ID: | 4023 |
| Uniprot: | P06858 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell membrane, GPI-anchor, Lipid-anchor, Secreted |
| Calculated MW: | 53kDa |
| Observed MW: | 53kDa |
| Synonyms: | LPL, HDLCQ11, LIPD |
| Background: | LPL encodes lipoprotein lipase, which is expressed in heart, muscle, and adipose tissue. LPL functions as a homodimer, and has the dual functions of triglyceride hydrolase and ligand/bridging factor for receptor-mediated lipoprotein uptake. Severe mutations that cause LPL deficiency result in type I hyperlipoproteinemia, while less extreme mutations in LPL are linked to many disorders of lipoprotein metabolism. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | LPL: The primary function of this lipase is the hydrolysis of triglycerides of circulating chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins (VLDL). Binding to heparin sulfate proteogylcans at the cell surface is vital to the function. The apolipoprotein, APOC2, acts as a coactivator of LPL activity in the presence of lipids on the luminal surface of vascular endothelium. Defects in LPL are the cause of lipoprotein lipase deficiency (LPL deficiency); also known as familial chylomicronemia or hyperlipoproteinemia type I. LPL deficiency chylomicronemia is a recessive disorder usually manifesting in childhood. On a normal diet, patients often present with abdominal pain, hepatosplenomegaly, lipemia retinalis, eruptive xanthomata, and massive hypertriglyceridemia, sometimes complicated with acute pancreatitis. Belongs to the AB hydrolase superfamily. Lipase family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Membrane protein, GPI anchor; EC 3.1.1.34; Lipid Metabolism - glycerolipid; Phospholipase Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 8p22 Cellular Component: extracellular matrix; extracellular space; chylomicron; cell surface; plasma membrane; extracellular region Molecular Function:heparin binding; triacylglycerol lipase activity; protein binding; lipoprotein lipase activity; apolipoprotein binding; phospholipase activity; receptor binding; triglyceride binding Biological Process: response to drug; phototransduction, visible light; triacylglycerol metabolic process; phospholipid metabolic process; triacylglycerol catabolic process; lipoprotein metabolic process; triacylglycerol biosynthetic process; response to cold; retinoid metabolic process; fatty acid biosynthetic process Disease: Hyperlipoproteinemia, Type I; Hyperlipidemia, Familial Combined |
| NCBI Summary: | LPL encodes lipoprotein lipase, which is expressed in heart, muscle, and adipose tissue. LPL functions as a homodimer, and has the dual functions of triglyceride hydrolase and ligand/bridging factor for receptor-mediated lipoprotein uptake. Severe mutations that cause LPL deficiency result in type I hyperlipoproteinemia, while less extreme mutations in LPL are linked to many disorders of lipoprotein metabolism. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P06858 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 4557727 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 4023 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_000228.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P06858,Q16282, Q16283, Q96FC4, B2R5T9, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P06858 |
| Molecular Weight: | 53,162 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | lipoprotein lipase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | lipoprotein lipase |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | LPL |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | LIPD; HDLCQ11 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | lipoprotein lipase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Lipoprotein lipase |
| Protein Family: | Lipoprotein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | LPL |
| UniProt Entry Name: | LIPL_HUMAN |