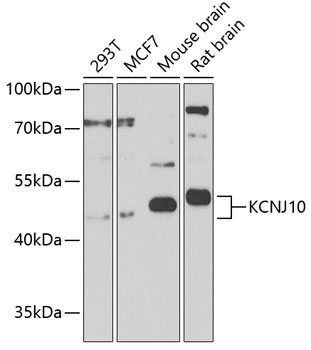
Anti-KCNJ10 Antibody (CAB9826)
- SKU:
- CAB9826
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Application:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-KCNJ10 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB9826 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 50-150 of human KCNJ10 (NP_002232.2). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | 293T, MCF7, Mouse brain, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 50-150 of human KCNJ10 (NP_002232.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | LYLK DLWT TFID MQWR YKLL LFSA TFAG TWFL FGVV WYLV AVAH GDLL ELDP PANH TPCV VQVH TLTG AFLF SLES QTTI GYGF RYIS EECP LAIV LLIA Q |
| Gene ID: | 3766 |
| Uniprot: | P78508 |
| Cellular Location: | Membrane, Multi-pass membrane protein |
| Calculated MW: | 42kDa |
| Observed MW: | 42kDa |
| Synonyms: | KCNJ10, BIRK-10, KCNJ13-PEN, KIR1.2, KIR4.1, SESAME |
| Background: | This gene encodes a member of the inward rectifier-type potassium channel family, characterized by having a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into, rather than out of, a cell. The encoded protein may form a heterodimer with another potassium channel protein and may be responsible for the potassium buffering action of glial cells in the brain. Mutations in this gene have been associated with seizure susceptibility of common idiopathic generalized epilepsy syndromes. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Kir4.1: May be responsible for potassium buffering action of glial cells in the brain. Inward rectifier potassium channels are characterized by a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into the cell rather than out of it. Their voltage dependence is regulated by the concentration of extracellular potassium; as external potassium is raised, the voltage range of the channel opening shifts to more positive voltages. The inward rectification is mainly due to the blockage of outward current by internal magnesium. Can be blocked by extracellular barium and cesium. Defects in KCNJ10 are the cause of seizures, sensorineural deafness, ataxia, mental retardation, and electrolyte imbalance (SESAMES). A complex disorder characterized by generalized seizures with onset in infancy, delayed psychomotor development, ataxia, sensorineural hearing loss, hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis, and hypomagnesemia. Belongs to the inward rectifier-type potassium channel (TC 1.A.2.1) family. KCNJ10 subfamily. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Membrane protein, integral; Channel, ligand-gated; Membrane protein, multi-pass; Channel, potassium Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1q23.2 Cellular Component: microvillus; integral to plasma membrane; basolateral plasma membrane; apical plasma membrane; plasma membrane Molecular Function:identical protein binding; protein binding; ATP-activated inward rectifier potassium channel activity; ATP binding; receptor binding Biological Process: regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity; myelination in the central nervous system; response to glucocorticoid stimulus; membrane hyperpolarization; response to blue light; glutamate uptake during transmission of nerve impulse; response to mineralocorticoid stimulus; adult walking behavior; protein homotetramerization; synaptic transmission; visual perception; potassium ion import; optic nerve development; regulation of resting membrane potential; regulation of sensory perception of pain; inflammatory response; potassium ion homeostasis; potassium ion transport Disease: Pendred Syndrome; Seizures, Sensorineural Deafness, Ataxia, Mental Retardation, And Electrolyte Imbalance; Deafness, Autosomal Recessive 4, With Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the inward rectifier-type potassium channel family, characterized by having a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into, rather than out of, a cell. The encoded protein may form a heterodimer with another potassium channel protein and may be responsible for the potassium buffering action of glial cells in the brain. Mutations in this gene have been associated with seizure susceptibility of common idiopathic generalized epilepsy syndromes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P78508 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 2493605 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3766 |
| NCBI Accession: | P78508.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P78508,Q5VUT9, Q8N4I7, Q92808, A3KME7, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P78508 |
| Molecular Weight: | 42,508 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 10 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 10 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | KCNJ10 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | KIR1.2; KIR4.1; SESAME; BIRK-10; KCNJ13-PEN |
| NCBI Protein Information: | ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 10; inward rectifier K+ channel KIR1.2; inward rectifier K(+) channel Kir1.2; ATP-dependent inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir4.1; potassium channel, inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 10; glial ATP-dependent inwardly rectifying potassium channel KIR4.1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 10 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | ATP-dependent inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir4.1; Inward rectifier K(+) channel Kir1.2; Potassium channel, inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 10 |
| Protein Family: | ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel |
| UniProt Gene Name: | KCNJ10 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | KCJ10_HUMAN |