Anti-GluR2 Antibody (CAB11316)
- SKU:
- CAB11316
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-GluR2 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB11316 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human GluR2 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
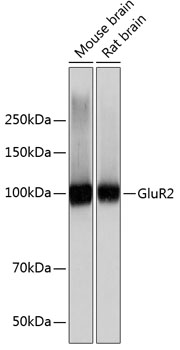
| Positive Samples: | Mouse brain, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human GluR2 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 2891 |
| Uniprot: | P42262 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 98kDa |
| Observed MW: | 99KDa |
| Synonyms: | GLUR2, GLURB, GluA2, GluR-K2, HBGR2 |
| Background: | Glutamate receptors are the predominant excitatory neurotransmitter receptors in the mammalian brain and are activated in a variety of normal neurophysiologic processes. This gene product belongs to a family of glutamate receptors that are sensitive to alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate (AMPA), and function as ligand-activated cation channels. These channels are assembled from 4 related subunits, GRIA1-4. The subunit encoded by this gene (GRIA2) is subject to RNA editing (CAG->CGG; Q->R) within the second transmembrane domain, which is thought to render the channel impermeable to Ca(2+). Human and animal studies suggest that pre-mRNA editing is essential for brain function, and defective GRIA2 RNA editing at the Q/R site may be relevant to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) etiology. Alternative splicing, resulting in transcript variants encoding different isoforms, (including the flip and flop isoforms that vary in their signal transduction properties), has been noted for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | GluR2: an integral membrane protein belonging to the glutamate-gated ion channel family. L-glutamate (Glu) acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter at many synapses in the central nervous system. Glutamate receptors are heteromeric protein complexes with multiple subunits, each possessing transmembrane regions, and all arranged to form a ligand-gated ion channel. The postsynaptic actions of Glu are mediated by a variety of receptors that are named according to their selective agonists. This receptor binds AMPA(quisqualate) > glutamate > kainate. Each of the four GluR proteins (GRIA1-4) include flip and flop isoforms generated by alternative RNA splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Channel, calcium; Membrane protein, integral; Membrane protein, multi-pass; Channel, ligand-gated Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 4q32.1 Cellular Component: cell junction; endoplasmic reticulum membrane; integral to plasma membrane; plasma membrane; postsynaptic membrane Molecular Function:alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate selective glutamate receptor activity; excitatory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity; extracellular-glutamate-gated ion channel activity; ionotropic glutamate receptor activity; protein binding Biological Process: ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway; signal transduction; synaptic transmission |
| NCBI Summary: | Glutamate receptors are the predominant excitatory neurotransmitter receptors in the mammalian brain and are activated in a variety of normal neurophysiologic processes. This gene product belongs to a family of glutamate receptors that are sensitive to alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate (AMPA), and function as ligand-activated cation channels. These channels are assembled from 4 related subunits, GRIA1-4. The subunit encoded by this gene (GRIA2) is subject to RNA editing (CAG->CGG; Q->R) within the second transmembrane domain, which is thought to render the channel impermeable to Ca(2+). Human and animal studies suggest that pre-mRNA editing is essential for brain function, and defective GRIA2 RNA editing at the Q/R site may be relevant to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) etiology. Alternative splicing, resulting in transcript variants encoding different isoforms, (including the flip and flop isoforms that vary in their signal transduction properties), has been noted for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P42262 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 23831146 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2891 |
| NCBI Accession: | P42262.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P42262,Q96FP6, A8MT92, I6L997, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P42262 |
| Molecular Weight: | 93,775 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Glutamate receptor 2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | glutamate ionotropic receptor AMPA type subunit 2 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | GRIA2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | GLUR2; GLURB; GluA2; HBGR2; GluR-K2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | glutamate receptor 2 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Glutamate receptor 2 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | AMPA-selective glutamate receptor 2; GluR-B; GluR-K2; Glutamate receptor ionotropic, AMPA 2; GluA2 |
| Protein Family: | Glutamate receptor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | GRIA2 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | GRIA2_HUMAN |