Anti-Glucosylceramidase Antibody (CAB8420)
- SKU:
- CAB8420
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Application:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Metabolism
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Glucosylceramidase Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB8420 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
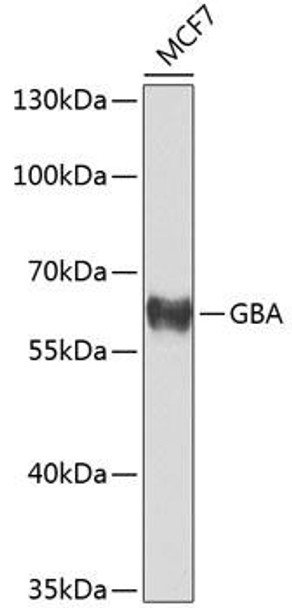
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 40-250 of human GBA (NP_000148.2). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: | MCF7 |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 40-250 of human GBA (NP_000148.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | ARPC IPKS FGYS SVVC VCNA TYCD SFDP PTFP ALGT FSRY ESTR SGRR MELS MGPI QANH TGTG LLLT LQPE QKFQ KVKG FGGA MTDA AALN ILAL SPPA QNLL LKSY FSEE GIGY NIIR VPMA SCDF SIRT YTYA DTPD DFQL HNFS LPEE DTKL KIPL IHRA LQLA QRPV SLLA SPWT SPTW LKTN GAVN GKGS LKGQ PGDI YHQT WAR |
| Gene ID: | 2629 |
| Uniprot: | P04062 |
| Cellular Location: | Lumenal side, Lysosome membrane, Peripheral membrane protein |
| Calculated MW: | 29kDa/50kDa/54kDa/57kDa/59kDa |
| Observed MW: | 60kDa |
| Synonyms: | GBA, GBA1, GCB, GLUC |
| Background: | This gene encodes a lysosomal membrane protein that cleaves the beta-glucosidic linkage of glycosylceramide, an intermediate in glycolipid metabolism. Mutations in this gene cause Gaucher disease, a lysosomal storage disease characterized by an accumulation of glucocerebrosides. A related pseudogene is approximately 12 kb downstream of this gene on chromosome 1. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | GBA: Defects in GBA are the cause of Gaucher disease (GD); also known as glucocerebrosidase deficiency. GD is the most prevalent lysosomal storage disease, characterized by accumulation of glucosylceramide in the reticulo-endothelial system. Different clinical forms are recognized depending on the presence (neuronopathic forms) or absence of central nervous system involvement, severity and age of onset. Defects in GBA are the cause of Gaucher disease type 1 (GD1); also known as adult non-neuronopathic Gaucher disease. GD1 is characterized by hepatosplenomegaly with consequent anemia and thrombopenia, and bone involvement. The central nervous system is not involved. Defects in GBA are the cause of Gaucher disease type 2 (GD2); also known as acute neuronopathic Gaucher disease. GD2 is the most severe form and is universally progressive and fatal. It manifests soon after birth, with death generally occurring before patients reach two years of age. Defects in GBA are the cause of Gaucher disease type 3 (GD3); also known as subacute neuronopathic Gaucher disease. GD3 has central nervous manifestations. Defects in GBA are the cause of Gaucher disease type 3C (GD3C); also known as pseudo-Gaucher disease or Gaucher-like disease. Defects in GBA are the cause of Gaucher disease perinatal lethal (GDPL). It is a distinct form of Gaucher disease type 2, characterized by fetal onset. Hydrops fetalis, in utero fetal death and neonatal distress are prominent features. When hydrops is absent, neurologic involvement begins in the first week and leads to death within 3 months. Hepatosplenomegaly is a major sign, and is associated with ichthyosis, arthrogryposis, and facial dysmorphism. Perinatal lethal Gaucher disease is associated with non-immune hydrops fetalis, a generalized edema of the fetus with fluid accumulation in the body cavities due to non-immune causes. Non-immune hydrops fetalis is not a diagnosis in itself but a symptom, a feature of many genetic disorders, and the end-stage of a wide variety of disorders. Defects in GBA contribute to susceptibility to Parkinson disease (PARK). A complex neurodegenerative disorder characterized by bradykinesia, resting tremor, muscular rigidity and postural instability. Additional features are characteristic postural abnormalities, dysautonomia, dystonic cramps, and dementia. The pathology of Parkinson disease involves the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and the presence of Lewy bodies (intraneuronal accumulations of aggregated proteins), in surviving neurons in various areas of the brain. The disease is progressive and usually manifests after the age of 50 years, although early-onset cases (before 50 years) are known. The majority of the cases are sporadic suggesting a multifactorial etiology based on environmental and genetic factors. However, some patients present with a positive family history for the disease. Familial forms of the disease usually begin at earlier ages and are associated with atypical clinical features. Belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase 30 family. 3 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Lipid Metabolism - sphingolipid; Hydrolase; EC 3.2.1.45; Glycan Metabolism - other glycan degradation Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1q21 Cellular Component: lysosomal lumen; lysosomal membrane Molecular Function:glucosylceramidase activity; protein binding; receptor binding Biological Process: ceramide biosynthetic process; glucosylceramide catabolic process; glycosphingolipid metabolic process; negative regulation of inflammatory response; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity; positive regulation of protein amino acid dephosphorylation; regulation of macroautophagy; sphingosine biosynthetic process Disease: Dementia, Lewy Body; Gaucher Disease, Perinatal Lethal; Gaucher Disease, Type I; Gaucher Disease, Type Ii; Gaucher Disease, Type Iii; Gaucher Disease, Type Iiic; Parkinson Disease, Late-onset |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a lysosomal membrane protein that cleaves the beta-glucosidic linkage of glycosylceramide, an intermediate in glycolipid metabolism. Mutations in this gene cause Gaucher disease, a lysosomal storage disease characterized by an accumulation of glucocerebrosides. A related pseudogene is approximately 12 kb downstream of this gene on chromosome 1. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | P04062 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 55584151 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2629 |
| NCBI Accession: | P04062.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P04062,Q16545, Q4VX22, Q6I9R6, Q9UMJ8, A8K796, B7Z5G2 B7Z6S1, J3KQG4, J3KQK9, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P04062 |
| Molecular Weight: | 54,471 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Glucosylceramidase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | glucosylceramidase beta |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | GBA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | GCB; GBA1; GLUC |
| NCBI Protein Information: | glucosylceramidase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Glucosylceramidase |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Acid beta-glucosidase; Alglucerase; Beta-glucocerebrosidase; Beta-GC; D-glucosyl-N-acylsphingosine glucohydrolase; Imiglucerase |
| Protein Family: | Glucosylceramidase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | GBA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | GLCM_HUMAN |