Anti-FOSL1 Antibody (CAB5372)
- SKU:
- CAB5372
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-FOSL1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB5372 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
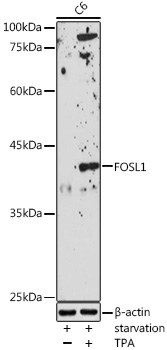
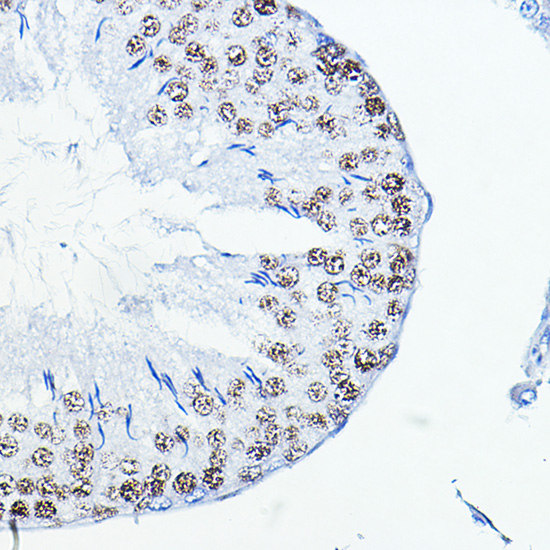
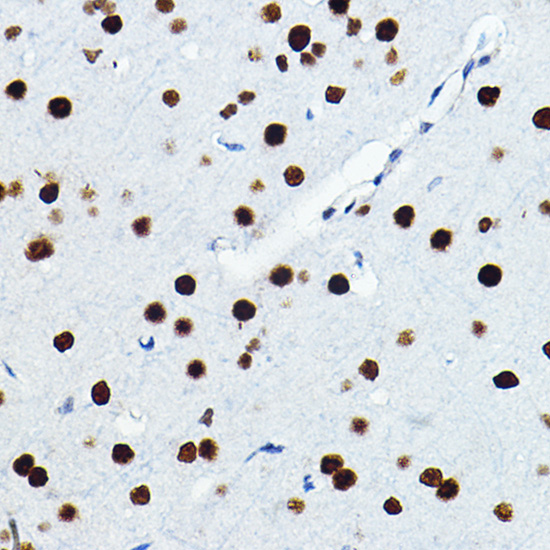
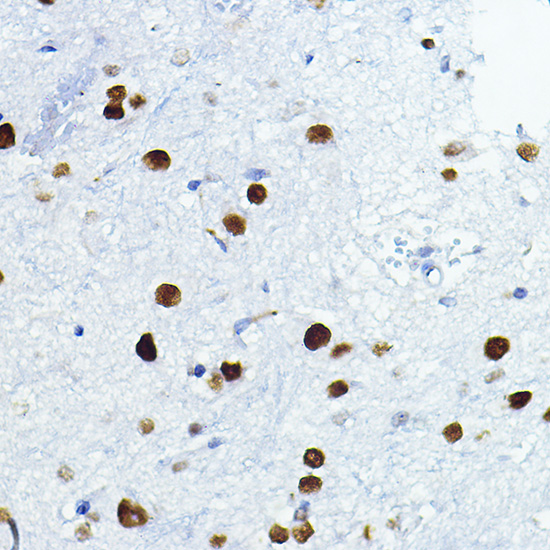
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-100 of human FOSL1 (NP_005429.1). |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | C6 |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-100 of human FOSL1 (NP_005429.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MFRD FGEP GPSS GNGG GYGG PAQP PAAA QAAQ QKFH LVPS INTM SGSQ ELQW MVQP HFLG PSSY PRPL TYPQ YSPP QPRP GVIR ALGP PPGV RRRP CEQI |
| Gene ID: | 8061 |
| Uniprot: | P15407 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 17kDa/29kDa |
| Observed MW: | 40KDa |
| Synonyms: | FOSL1, FRA, FRA1, fra-1 |
| Background: | The Fos gene family consists of 4 members: FOS, FOSB, FOSL1, and FOSL2. These genes encode leucine zipper proteins that can dimerize with proteins of the JUN family, thereby forming the transcription factor complex AP-1. As such, the FOS proteins have been implicated as regulators of cell proliferation, differentiation, and transformation. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | FRA1: an oncogenic transcription factor of the bZIP family, Fos subfamily. The expression of Fos proteins is rapidly and transiently induced by a variety of extracellular stimuli including growth factors, cytokines, neurotransmitters, polypeptide hormones, and stress. Fos proteins dimerize with Jun proteins (c-Jun, JunB, and JunD) to form Activator Protein-1 (AP-1), a transcription factor that binds to TRE/AP-1 elements and activates transcription. Fos and Jun proteins contain the leucine-zipper motif that mediates dimerization and an adjacent basic domain that binds to DNA. The various Fos/Jun heterodimers differ in their ability to transactivate AP-1 dependent genes. In addition to increased expression, phosphorylation of Fos proteins by Erk kinases in response to extracellular stimuli may further increase transcriptional activity. Following growth factor stimulation, expression of FosB and c-Fos in quiescent fibroblasts is immediate but short-lived, while FRA1 and FRA2 expression persists longer. FRA1 is involved in cell motility, invasiveness, and inhibits apoptosis. Elevated in many cancers and associated with tumorigenesis and cancer progression. Involved in Erk2-mediated Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) pathway. ERK2/FRA2 regulate ZEB1/2 expression, known to be associated with the EMT. Smad2/3-Fra1 complexes may reflect activation of the Smad/AP-1-dependent TGF¿-induced breast cancer invasion program. Activation of FRA1/C-JUN by ERK/AKT pathways can induce EZH2 overexpression, silencing integrin alpha-2 expression, and increasing the metastatic potential of colorectal cancer. Belongs to the bZIP family. Fos subfamily. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Transcription factor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 11q13 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; presynaptic membrane; neuron projection; cytosol; nucleus Molecular Function:protein binding; transcription factor activity Biological Process: transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; response to drug; response to gravity; response to cAMP; positive regulation of apoptosis; in utero embryonic development; response to virus; vitellogenesis; positive regulation of cell cycle; learning; female pregnancy; chemotaxis; regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; negative regulation of cell proliferation; response to hydrogen peroxide; response to mechanical stimulus; response to cytokine stimulus; positive regulation of cell proliferation; cellular response to extracellular stimulus; cellular defense response; positive regulation of transcription factor activity; response to progesterone stimulus; response to corticosterone stimulus |
| NCBI Summary: | The Fos gene family consists of 4 members: FOS, FOSB, FOSL1, and FOSL2. These genes encode leucine zipper proteins that can dimerize with proteins of the JUN family, thereby forming the transcription factor complex AP-1. As such, the FOS proteins have been implicated as regulators of cell proliferation, differentiation, and transformation. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014] |
| UniProt Code: | P15407 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 120484 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 8061 |
| NCBI Accession: | P15407.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P15407,Q6FG51, B4DR11, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P15407 |
| Molecular Weight: | 271 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Fos-related antigen 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | FOS-like antigen 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | FOSL1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | FRA; FRA1; fra-1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | fos-related antigen 1; FOS-like antigen-1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Fos-related antigen 1 |
| Protein Family: | Fos-related antigen |
| UniProt Gene Name: | FOSL1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FOSL1_HUMAN |