Anti-Factor IX / F9 Antibody (CAB1578)
- SKU:
- CAB1578
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cardiovascular
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Factor IX / F9 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB1578 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
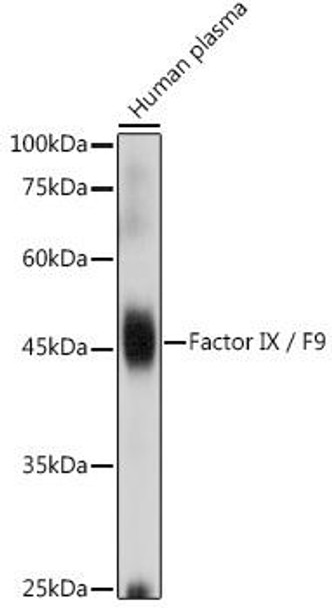
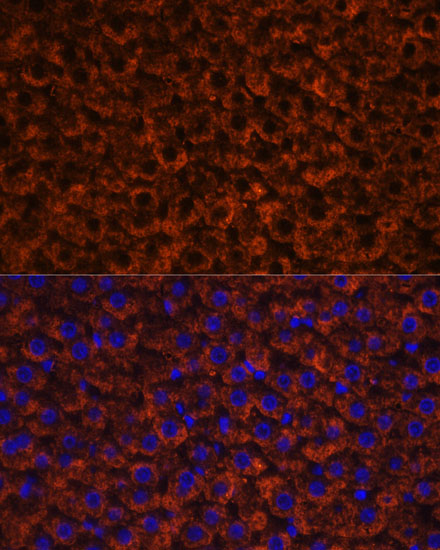
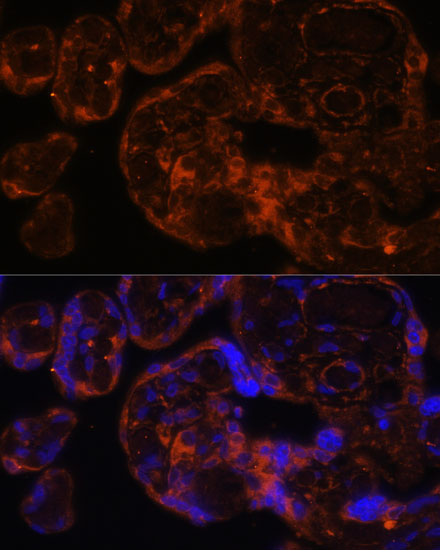
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 29-192 of human Factor IX / F9 (NP_000124.1). |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | Human plasma |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 29-192 of human Factor IX / F9 (NP_000124.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | TVFL DHEN ANKI LNRP KRYN SGKL EEFV QGNL EREC MEEK CSFE EARE VFEN TERT TEFW KQYV DGDQ CESN PCLN GGSC KDDI NSYE CWCP FGFE GKNC ELDV TCNI KNGR CEQF CKNS ADNK VVCS CTEG YRLA ENQK SCEP AVPF PCGR VSVS QTSK LTRA |
| Gene ID: | 2158 |
| Uniprot: | P00740 |
| Cellular Location: | Secreted |
| Calculated MW: | 47kDa/51kDa |
| Observed MW: | 52KDa |
| Synonyms: | F9, F9 p22, FIX, HEMB, P19, PTC, THPH8, F9p22 |
| Background: | This gene encodes vitamin K-dependent coagulation factor IX that circulates in the blood as an inactive zymogen. This factor is converted to an active form by factor XIa, which excises the activation peptide and thus generates a heavy chain and a light chain held together by one or more disulfide bonds. The role of this activated factor IX in the blood coagulation cascade is to activate factor X to its active form through interactions with Ca+2 ions, membrane phospholipids, and factor VIII. Alterations of this gene, including point mutations, insertions and deletions, cause factor IX deficiency, which is a recessive X-linked disorder, also called hemophilia B or Christmas disease. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms that may undergo similar proteolytic processing. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | F9: Factor IX is a vitamin K-dependent plasma protein that participates in the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation by converting factor X to its active form in the presence of Ca(2+) ions, phospholipids, and factor VIIIa. Defects in F9 are the cause of recessive X-linked hemophilia B (HEMB); also known as Christmas disease. Mutations in position 43 (Oxford-3, San Dimas) and 46 (Cambridge) prevents cleavage of the propeptide, mutation in position 93 (Alabama) probably fails to bind to cell membranes, mutation in position 191 (Chapel-Hill) or in position 226 (Nagoya OR Hilo) prevent cleavage of the activation peptide. Defects in F9 are the cause of thrombophilia due to factor IX defect (THPH8). A hemostatic disorder characterized by a tendency to thrombosis. Belongs to the peptidase S1 family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted; Protease; EC 3.4.21.22; Secreted, signal peptide Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: Xq27.1-q27.2 Cellular Component: Golgi lumen; endoplasmic reticulum lumen; extracellular region; plasma membrane Molecular Function:serine-type endopeptidase activity; calcium ion binding Biological Process: blood coagulation, extrinsic pathway; cellular protein metabolic process; blood coagulation; post-translational protein modification; proteolysis; blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway; peptidyl-glutamic acid carboxylation Disease: Hemophilia B; Thrombophilia, X-linked, Due To Factor Ix Defect; Coumarin Resistance |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes vitamin K-dependent coagulation factor IX that circulates in the blood as an inactive zymogen. This factor is converted to an active form by factor XIa, which excises the activation peptide and thus generates a heavy chain and a light chain held together by one or more disulfide bonds. The role of this activated factor IX in the blood coagulation cascade is to activate factor X to its active form through interactions with Ca+2 ions, membrane phospholipids, and factor VIII. Alterations of this gene, including point mutations, insertions and deletions, cause factor IX deficiency, which is a recessive X-linked disorder, also called hemophilia B or Christmas disease. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P00740 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 67476446 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2158 |
| NCBI Accession: | P00740.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P00740,Q5FBE1, Q5JYJ8, A8K9N4, F2RM36, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P00740 |
| Molecular Weight: | 461 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Coagulation factor IX |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | coagulation factor IX |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | F9 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | FIX; P19; PTC; HEMB; THPH8 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | coagulation factor IX; F9 p22; FIX F9; factor 9; factor IX F9; Christmas factor; plasma thromboplastic component; plasma thromboplastin component |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Coagulation factor IX |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Christmas factor; Plasma thromboplastin component; PTC |
| Protein Family: | F9 protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | F9 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FA9_HUMAN |