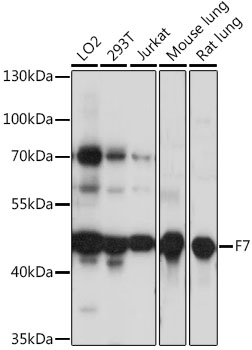
Anti-F7 Antibody (CAB16044)
- SKU:
- CAB16044
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cardiovascular
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-F7 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB16044 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 240-400 of human F7 (NP_062562.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | LO2, 293T, Jurkat, Mouse lung, Rat lung |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 240-400 of human F7 (NP_062562.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | RNLI AVLG EHDL SEHD GDEQ SRRV AQVI IPST YVPG TTNH DIAL LRLH QPVV LTDH VVPL CLPE RTFS ERTL AFVR FSLV SGWG QLLD RGAT ALEL MVLN VPRL MTQD CLQQ SRKV GDSP NITE YMFC AGYS DGSK DSCK GDSG GPHA THYR GTWY LTGI V |
| Gene ID: | 2155 |
| Uniprot: | P08709 |
| Cellular Location: | Secreted |
| Calculated MW: | 49kDa/51kDa |
| Observed MW: | 46kDa |
| Synonyms: | F7, SPCA |
| Background: | This gene encodes coagulation factor VII which is a vitamin K-dependent factor essential for hemostasis. This factor circulates in the blood in a zymogen form, and is converted to an active form by either factor IXa, factor Xa, factor XIIa, or thrombin by minor proteolysis. Upon activation of the factor VII, a heavy chain containing a catalytic domain and a light chain containing 2 EGF-like domains are generated, and two chains are held together by a disulfide bond. In the presence of factor III and calcium ions, the activated factor then further activates the coagulation cascade by converting factor IX to factor IXa and/or factor X to factor Xa. Defects in this gene can cause coagulopathy. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms that may undergo similar proteolytic processing to generate mature polypeptides. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | F7: Initiates the extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. Serine protease that circulates in the blood in a zymogen form. Factor VII is converted to factor VIIa by factor Xa, factor XIIa, factor IXa, or thrombin by minor proteolysis. In the presence of tissue factor and calcium ions, factor VIIa then converts factor X to factor Xa by limited proteolysis. Factor VIIa will also convert factor IX to factor IXa in the presence of tissue factor and calcium. Defects in F7 are the cause of factor VII deficiency (FA7D). A hemorrhagic disease with variable presentation. The clinical picture can be very severe, with the early occurrence of intracerebral hemorrhages or repeated hemarthroses, or, in contrast, moderate with cutaneous-mucosal hemorrhages (epistaxis, menorrhagia) or hemorrhages provoked by a surgical intervention. Finally, numerous subjects are completely asymptomatic despite very low factor VII levels. Belongs to the peptidase S1 family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 3.4.21.21; Protease; Apoptosis; Secreted; Secreted, signal peptide; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 13q34 Cellular Component: endoplasmic reticulum lumen; extracellular region; Golgi lumen; plasma membrane Molecular Function:glycoprotein binding; protein binding; serine-type peptidase activity Biological Process: blood coagulation; blood coagulation, extrinsic pathway; ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport; peptidyl-glutamic acid carboxylation; positive regulation of cell migration; positive regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis; positive regulation of positive chemotaxis; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling cascade; signal peptide processing Disease: Factor Vii Deficiency; Myocardial Infarction, Susceptibility To |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes coagulation factor VII which is a vitamin K-dependent factor essential for hemostasis. This factor circulates in the blood in a zymogen form, and is converted to an active form by either factor IXa, factor Xa, factor XIIa, or thrombin by minor proteolysis. Upon activation of the factor VII, a heavy chain containing a catalytic domain and a light chain containing 2 EGF-like domains are generated, and two chains are held together by a disulfide bond. In the presence of factor III and calcium ions, the activated factor then further activates the coagulation cascade by converting factor IX to factor IXa and/or factor X to factor Xa. Defects in this gene can cause coagulopathy. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms that may undergo similar proteolytic processing to generate mature polypeptides. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015] |
| UniProt Code: | P08709 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 119766 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2155 |
| NCBI Accession: | P08709.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P08709,Q14339, Q5JVF1, Q5JVF2, Q9UD52, Q9UD53, Q9UD54 B0YJC8, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P08709 |
| Molecular Weight: | 49,320 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Coagulation factor VII |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | coagulation factor VII |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | F7 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | SPCA |
| NCBI Protein Information: | coagulation factor VII |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Coagulation factor VII |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Proconvertin; Serum prothrombin conversion accelerator; SPCA |
| Protein Family: | F7-1 fimbrial protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | F7 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FA7_HUMAN |