Anti-ERK1 / ERK2 Antibody (CAB16686)
- SKU:
- CAB16686
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-ERK1 / ERK2 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB16686 |
| Antibody Size: | 50uL, 100uL |
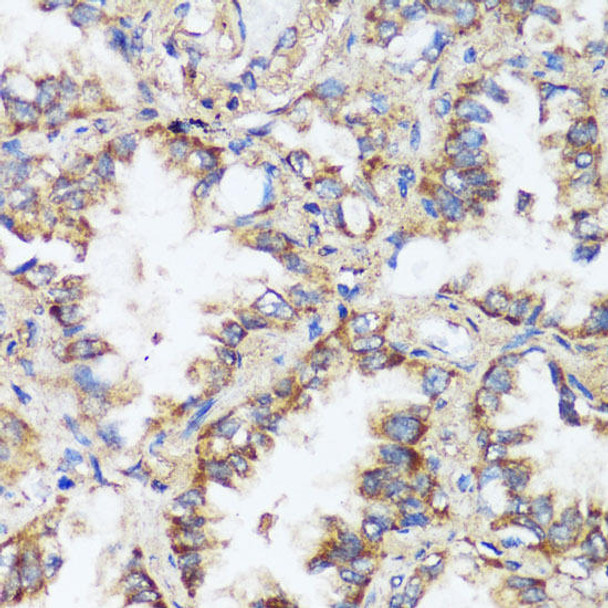
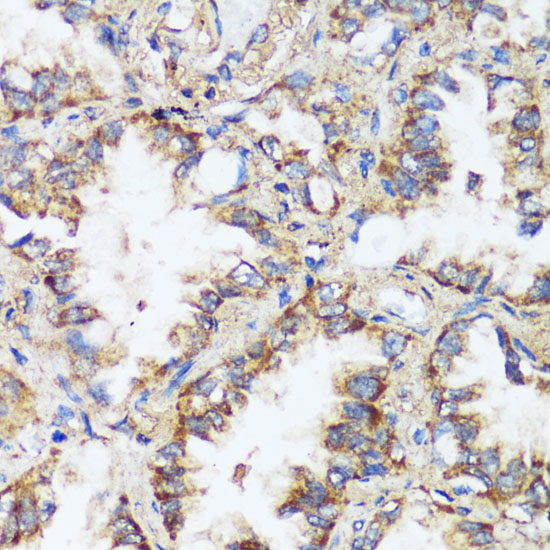
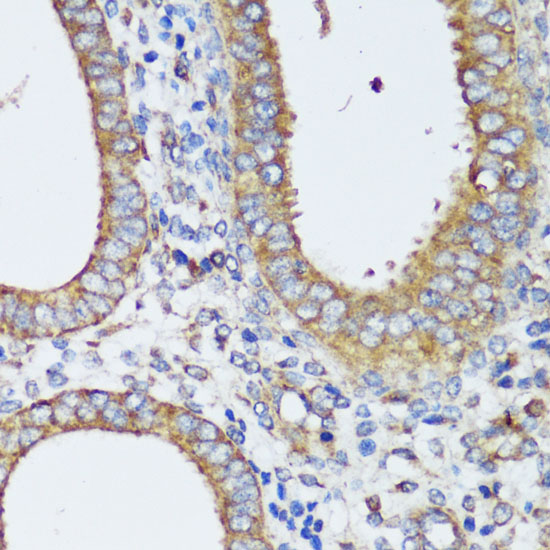
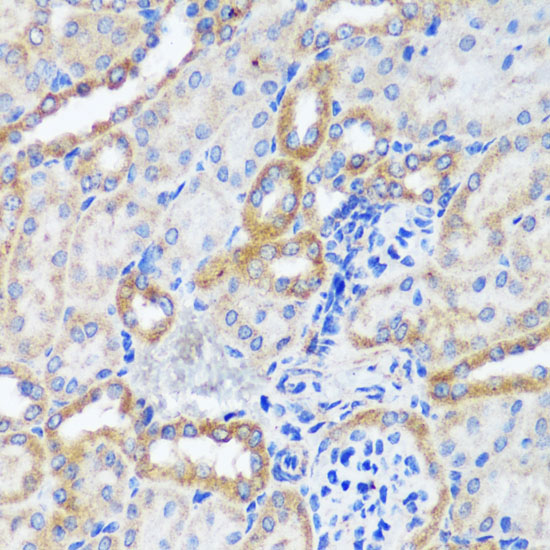
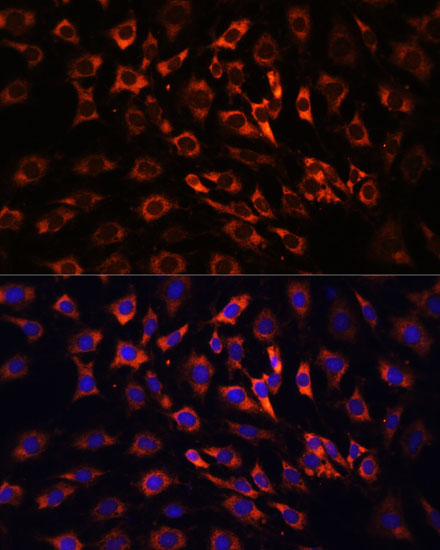
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 200-300 of human ERK1 / ERK2 (NP_620407.1/NP_002737.2). |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:1000 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
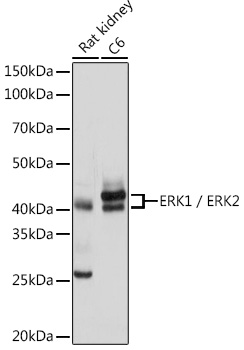
| Positive Samples: | Rat kidney, C6 |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 200-300 of human ERK1 / ERK2 (NP_620407.1/NP_002737.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 5594/5595 |
| Uniprot: | P28482/P27361 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 36kDa/41kDa/38kDa/40kDa/43kDa |
| Observed MW: | 42KDa/44KDa |
| Synonyms: | MAPK1/MAPK3 |
| Background: | MAP kinases, also known as extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals, and are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. The activation of this kinase requires its phosphorylation by upstream kinases. Upon activation, this kinase translocates to the nucleus of the stimulated cells, where it phosphorylates nuclear targets. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | ERK2: a serine/threonine kinase of the GMGC group that plays a critical role in the regulation of cell growth and differentiation. ERK1 (MAPK3) and ERK2 (MAPK1) play central roles in MAPK cascades and are activated by a wide variety of extracellular signals including growth and neurotrophic factors, cytokines, hormones and neurotransmitters. Depending on the cellular context, MAPK cascades mediate diverse biological functions such as cell growth, adhesion, survival and differentiation through the regulation of transcription, translation, cytoskeletal rearrangements. MAPK cascades also plays a role in initiation and regulation of meiosis, mitosis, and postmitotic functions in differentiated cells by phosphorylating a number of transcription factors. Activation of MAP kinases occurs through phosphorylation of threonine and tyrosine residues at the sequence T*EY* by upstream MAP kinase kinases, MEK1 and -2. Phosphorylation of both the threonine and tyrosine are required for activity. This phosphorylation causes dramatic conformational changes, which enable full activation and interaction of MAPK1/ERK2 with its substrates. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protein kinase, CMGC; Kinase, protein; EC 2.7.11.24; Protein kinase, Ser/Thr (non-receptor); CMGC group; MAPK family; MAPK/ERK subfamily; ERK subfamily Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 22q11.21 Cellular Component: axon; caveola; cytoplasm; cytoskeleton; cytosol; dendrite cytoplasm; early endosome; focal adhesion; Golgi apparatus; late endosome; microtubule cytoskeleton; microtubule organizing center; mitochondrion; nucleoplasm; nucleus; perikaryon; protein complex; pseudopodium Molecular Function:ATP binding; DNA binding; MAP kinase activity; mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase binding; phosphatase binding; phosphotyrosine binding; protein binding; protein serine/threonine kinase activity; RNA polymerase subunit kinase activity; transcription factor binding Biological Process: activation of MAPK activity; activation of MAPKK activity; apoptosis; axon guidance; B cell receptor signaling pathway; Bergmann glial cell differentiation; blood coagulation; cell cycle; chemotaxis; cytosine metabolic process; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; innate immune response; insulin receptor signaling pathway; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway; mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation; MAPKKK cascade; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of cell differentiation; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; nuclear translocation of MAPK; outer ear morphogenesis; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation; platelet activation; positive regulation of cell migration; positive regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of telomerase activity; positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; positive regulation of translation; protein amino acid phosphorylation; Ras protein signal transduction; regulation of cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; regulation of protein stability; regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade; regulation of transcription factor activity; response to DNA damage stimulus; response to estrogen stimulus; response to exogenous dsRNA; response to stress; response to toxin; sensory perception of pain; signal transduction; small GTPase mediated signal transduction; stress-activated MAPK cascade; synaptic transmission; T cell receptor signaling pathway; thymus development; thyroid gland development; toll-like receptor 10 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 5 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor signaling pathway; transcription, DNA-dependent; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway; viral reproduction |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the MAP kinase family. MAP kinases, also known as extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals, and are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. The activation of this kinase requires its phosphorylation by upstream kinases. Upon activation, this kinase translocates to the nucleus of the stimulated cells, where it phosphorylates nuclear targets. One study also suggests that this protein acts as a transcriptional repressor independent of its kinase activity. The encoded protein has been identified as a moonlighting protein based on its ability to perform mechanistically distinct functions. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein, but differing in the UTRs, have been reported for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014] |
| UniProt Code: | P28482 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 119554 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5594 |
| NCBI Accession: | P28482.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P28482,A8CZ64, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P28482 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | MAPK1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ERK; p38; p40; p41; ERK2; ERT1; ERK-2; MAPK2; PRKM1; PRKM2; P42MAPK; p41mapk; p42-MAPK |
| NCBI Protein Information: | mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | ERT1; Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2; ERK-2; MAP kinase isoform p42; p42-MAPK; Mitogen-activated protein kinase 2; MAP kinase 2; MAPK 2 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | MAPK1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | MK01_HUMAN |



![Anti-ERK2 Antibody (CAB0229)[KO Validated] Anti-ERK2 Antibody (CAB0229)[KO Validated]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-39x6lpnvxv/images/stencil/590x590/products/30452/28641/anti-erk2-antibody-cab0229ko-validated__89748__20636.1644317075.jpg?c=1)
![Anti-ERK2 Antibody [KO Validated] (CAB19630) Anti-ERK2 Antibody [KO Validated] (CAB19630)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-39x6lpnvxv/images/stencil/590x590/products/21570/19770/anti-erk2-antibody-ko-validated-cab19630__74984__02079.1644252656.jpg?c=1)
![Anti-ERK2 Antibody (CAB11186)[KO Validated] Anti-ERK2 Antibody (CAB11186)[KO Validated]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-39x6lpnvxv/images/stencil/590x590/products/18817/17017/anti-erk2-antibody-cab11186ko-validated__83367__26872.1644251821.jpg?c=1)


