Anti-DYNC1H1 Antibody (CAB18314)
- SKU:
- CAB18314
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-DYNC1H1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB18314 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human DYNC1H1. |
| Application: | IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Positive Samples: |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human DYNC1H1. |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 1778 |
| Uniprot: | Q14204 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 532kDa |
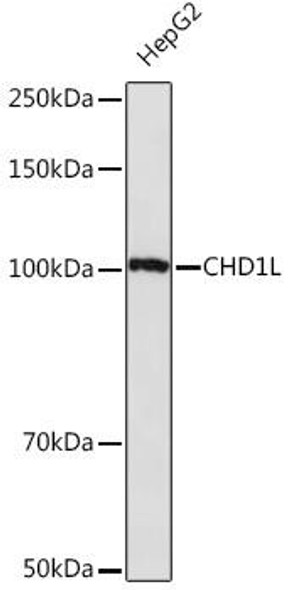
| Observed MW: | Refer to figures |
| Synonyms: | DYNC1H1, CMT2O, DHC1, DHC1a, DNCH1, DNCL, DNECL, DYHC, Dnchc1, HL-3, SMALED1, p22 |
| Background: | Dyneins are a group of microtubule-activated ATPases that function as molecular motors. They are divided into two subgroups of axonemal and cytoplasmic dyneins. The cytoplasmic dyneins function in intracellular motility, including retrograde axonal transport, protein sorting, organelle movement, and spindle dynamics. Molecules of conventional cytoplasmic dynein are comprised of 2 heavy chain polypeptides and a number of intermediate and light chains.This gene encodes a member of the cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain family. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | DNCH1: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 acts as a motor for the intracellular retrograde motility of vesicles and organelles along microtubules. Dynein has ATPase activity; the force-producing power stroke is thought to occur on release of ADP. Defects in DYNC1H1 are the cause of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2O (CMT2O). CMT2O is anaxonal form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, a disorder of the peripheral nervous system, characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy, initially of the peroneal muscles and later of the distal muscles of the arms. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathies (designated CMT1 when they are dominantly inherited) and primary peripheral axonal neuropathies (CMT2). Neuropathies of the CMT2 group are characterized by signs of axonal degeneration in the absence of obvious myelin alterations, normal or slightly reduced nerve conduction velocities, and progressive distal muscle weakness and atrophy. Nerve conduction velocities are normal or slightly reduced. Defects in DYNC1H1 are the cause of mental retardation autosomal dominant type 13 (MRD13). A disorder characterized by significantly below average general intellectual functioning associated with impairments in adaptative behavior and manifested during the developmental period. MRD13 is associated with variable neuronal migration defects and mild dysmorphic features. Some patients may also show signs of peripheral neuropathy, such as abnormal gait and hyporeflexia. Defects in DYNC1H1 are the cause of spinal muscular atrophy, lower extremity, autosomal dominant (SMALED). A form of spinal muscular atrophy, a neuromuscular disorder characterized by degeneration of the anterior horn cells of the spinal cord, leading to symmetrical muscle weakness and atrophy. SMALED is characterized by muscle weakness predominantly affecting the proximal lower extremities. Belongs to the dynein heavy chain family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Microtubule-binding; Motor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 14q32 Cellular Component: centrosome; microtubule; membrane; cytoplasmic dynein complex; cytosol; filopodium Molecular Function:protein binding; ATPase activity; dynein light intermediate chain binding; microtubule motor activity; ATP binding Biological Process: stress granule assembly; mitotic spindle organization and biogenesis; metabolic process; transport; organelle organization and biogenesis; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II; cytoplasmic mRNA processing body assembly; mitotic cell cycle; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle; microtubule-based movement Disease: Charcot-marie-tooth Disease, Axonal, Type 2o; Spinal Muscular Atrophy, Lower Extremity-predominant, 1, Autosomal Dominant; Mental Retardation, Autosomal Dominant 13 |
| NCBI Summary: | Dyneins are a group of microtubule-activated ATPases that function as molecular motors. They are divided into two subgroups of axonemal and cytoplasmic dyneins. The cytoplasmic dyneins function in intracellular motility, including retrograde axonal transport, protein sorting, organelle movement, and spindle dynamics. Molecules of conventional cytoplasmic dynein are comprised of 2 heavy chain polypeptides and a number of intermediate and light chains.This gene encodes a member of the cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain family. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q14204 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 57015308 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1778 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q14204.5 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q14204,Q6DKQ7, Q8WU28, Q92814, Q9Y4G5, B0I1R0, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q14204 |
| Molecular Weight: | 4646 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | dynein, cytoplasmic 1, heavy chain 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | DYNC1H1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | p22; DHC1; DNCL; DYHC; HL-3; DHC1a; DNCH1; DNECL; Dnchc1; SMALED1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1; dynein heavy chain, cytosolic; dynein, cytoplasmic, heavy polypeptide 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain 1; Dynein heavy chain, cytosolic |
| Protein Family: | Cytoplasmic dynein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | DYNC1H1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | DYHC1_HUMAN |