Anti-DNA Ligase IV Antibody (CAB11432)
- SKU:
- CAB11432
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Cycle
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-DNA Ligase IV Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB11432 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
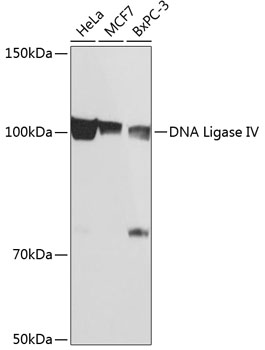
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human DNA Ligase IV |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, MCF7, BxPC-3 |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human DNA Ligase IV |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 3981 |
| Uniprot: | P49917 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 103kDa |
| Observed MW: | 100KDa |
| Synonyms: | LIG4S |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a DNA ligase that joins single-strand breaks in a double-stranded polydeoxynucleotide in an ATP-dependent reaction. This protein is essential for V(D)J recombination and DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair through nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ). This protein forms a complex with the X-ray repair cross complementing protein 4 (XRCC4), and further interacts with the DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK). Both XRCC4 and DNA-PK are known to be required for NHEJ. The crystal structure of the complex formed by this protein and XRCC4 has been resolved. Defects in this gene are the cause of LIG4 syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | LIG4: a DNA ligase that joins single-strand breaks in a double-stranded polydeoxynucleotide in an ATP-dependent reaction. Essential for V(D)J recombination and DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair through nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ). This protein forms a complex with the X-ray repair cross complementing protein 4 (XRCC4), and further interacts with the DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK). Both XRCC4 and DNA-PK are known to be required for NHEJ. Defects in this gene are the cause of LIG4 syndrome. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 6.5.1.1; Ligase Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 13q33-q34 Cellular Component: condensed chromosome; cytoplasm; DNA ligase IV complex; DNA-dependent protein kinase complex; focal adhesion; nuclear chromosome, telomeric region; nucleoplasm; nucleus; plasma membrane Molecular Function:ATP binding; DNA binding; DNA ligase (ATP) activity; DNA ligase activity; ligase activity; metal ion binding; protein binding; protein C-terminus binding Biological Process: cell cycle; cell division; cell proliferation; central nervous system development; chromosome organization and biogenesis; DNA ligation; DNA ligation during DNA recombination; DNA ligation during DNA repair; DNA repair; double-strand break repair; double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining; immunoglobulin V(D)J recombination; in utero embryonic development; isotype switching; lagging strand elongation; negative regulation of neuron apoptosis; neuron apoptosis; nucleotide-excision repair, DNA gap filling; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation; positive regulation of neurogenesis; pro-B cell differentiation; response to gamma radiation; response to X-ray; single strand break repair; somatic stem cell maintenance; T cell differentiation in the thymus; T cell receptor V(D)J recombination; V(D)J recombination; viral reproduction Disease: Lig4 Syndrome; Myeloma, Multiple |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a DNA ligase that joins single-strand breaks in a double-stranded polydeoxynucleotide in an ATP-dependent reaction. This protein is essential for V(D)J recombination and DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair through nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ). This protein forms a complex with the X-ray repair cross complementing protein 4 (XRCC4), and further interacts with the DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK). Both XRCC4 and DNA-PK are known to be required for NHEJ. The crystal structure of the complex formed by this protein and XRCC4 has been resolved. Defects in this gene are the cause of LIG4 syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P49917 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 88911290 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3981 |
| NCBI Accession: | P49917.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P49917,Q8IY66, Q8TEU5, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P49917 |
| Molecular Weight: | 103,971 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | DNA ligase 4 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | ligase IV, DNA, ATP-dependent |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | LIG4 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | LIG4S |
| NCBI Protein Information: | DNA ligase 4 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | DNA ligase 4 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | DNA ligase IV; Polydeoxyribonucleotide synthase [ATP] 4 |
| Protein Family: | DNA ligase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | LIG4 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | DNLI4_HUMAN |