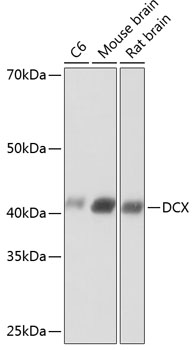
Anti-DCX Antibody (CAB19042)
- SKU:
- CAB19042
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Developmental Biology
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-DCX Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB19042 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human DCX |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | C6, Mouse brain, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human DCX |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 1641 |
| Uniprot: | O43602 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 45kDa |
| Observed MW: | 45kDa |
| Synonyms: | DBCN, DC, LISX, SCLH, XLIS, DCX |
| Background: | This gene encodes a member of the doublecortin family. The protein encoded by this gene is a cytoplasmic protein and contains two doublecortin domains, which bind microtubules. In the developing cortex, cortical neurons must migrate over long distances to reach the site of their final differentiation. The encoded protein appears to direct neuronal migration by regulating the organization and stability of microtubules. In addition, the encoded protein interacts with LIS1, the regulatory gamma subunit of platelet activating factor acetylhydrolase, and this interaction is important to proper microtubule function in the developing cortex. Mutations in this gene cause abnormal migration of neurons during development and disrupt the layering of the cortex, leading to epilepsy, mental retardation, subcortical band heterotopia ("double cortex" syndrome) in females and lissencephaly ("smooth brain" syndrome) in males. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Doublecortin: Microtubule-associated protein required for initial steps of neuronal dispersion and cortex lamination during cerebral cortex development. May act by competing with the putative neuronal protein kinase DCAMKL1 in binding to a target protein. May in that way participate in a signaling pathway that is crucial for neuronal interaction before and during migration, possibly as part of a calcium ion-dependent signal transduction pathway. May be part with LIS-1 of a overlapping, but distinct, signaling pathways that promote neuronal migration. Interacts with tubulin. Highly expressed in neuronal cells of fetal brain (in the majority of cells of the cortical plate, intermediate zone and ventricular zone), but not expressed in other fetal tissues. In the adult, highly expressed in the brain frontal lobe, but very low expression in other regions of brain, and not detected in heart, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscles, kidney and pancreas. 5 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cytoskeletal; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: Xq22.3-q23 Cellular Component: microtubule; microtubule associated complex; neuron projection; cytoskeleton; cytosol Molecular Function:protein binding; microtubule binding; protein kinase binding Biological Process: nervous system development; axon guidance; central nervous system development; axon extension; dendrite morphogenesis; neuron migration; central nervous system projection neuron axonogenesis; brain development Disease: Lissencephaly, X-linked, 1 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the doublecortin family. The protein encoded by this gene is a cytoplasmic protein and contains two doublecortin domains, which bind microtubules. In the developing cortex, cortical neurons must migrate over long distances to reach the site of their final differentiation. The encoded protein appears to direct neuronal migration by regulating the organization and stability of microtubules. In addition, the encoded protein interacts with LIS1, the regulatory gamma subunit of platelet activating factor acetylhydrolase, and this interaction is important to proper microtubule function in the developing cortex. Mutations in this gene cause abnormal migration of neurons during development and disrupt the layering of the cortex, leading to epilepsy, mental retardation, subcortical band heterotopia ("double cortex" syndrome) in females and lissencephaly ("smooth brain" syndrome) in males. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | O43602 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 215274172 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1641 |
| NCBI Accession: | O43602.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O43602,O43911, Q5JYZ5, A6NFY6, A9Z1V8, D3DUY8, D3DUY9 D3DUZ0, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O43602 |
| Molecular Weight: | 441 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Neuronal migration protein doublecortin |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | doublecortin |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | DCX |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | DC; DBCN; LISX; SCLH; XLIS |
| NCBI Protein Information: | neuronal migration protein doublecortin; lis-X; doublin; doublecortex; lissencephalin-X |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Neuronal migration protein doublecortin |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Doublin; Lissencephalin-X; Lis-X |
| Protein Family: | Protein doublecortin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | DCX |
| UniProt Entry Name: | DCX_HUMAN |