Anti-DCTN1 Antibody (CAB1783)
- SKU:
- CAB1783
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Cycle
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-DCTN1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB1783 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
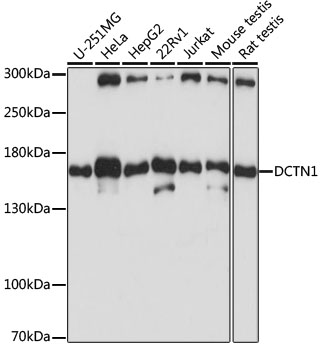
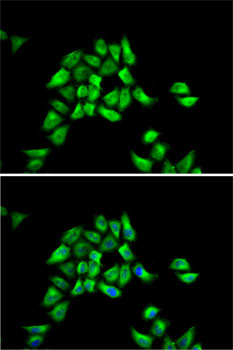
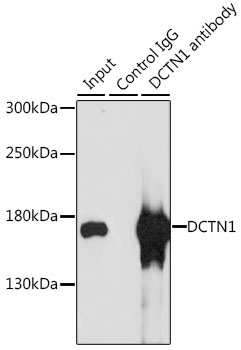
| Application: | WB IF IP |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 945-1139 of human DCTN1 (NP_001128513.1). |
| Application: | WB IF IP |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:20 - 1:100 IP 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | U-251MG, HeLa, HepG2, 22RV1, Jurkat, Mouse testis, Rat testis |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 945-1139 of human DCTN1 (NP_001128513.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | PGLV KDSP LLLQ QISA MRLH ISQL QHEN SILK GAQM KASL ASLP PLHV AKLS HEGP GSEL PAGA LYRK TSQL LETL NQLS THTH VVDI TRTS PAAK SPSA QLME QVAQ LKSL SDTV EKLK DEVL KETV SQRP GATV PTDF ATFP SSAF LRAK EEQQ DDTV YMGK VTFS CAAG FGQR HRLV LTQE QLHQ LHSR LIS |
| Gene ID: | 1639 |
| Uniprot: | Q14203 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton |
| Calculated MW: | 126kDa/127kDa/136kDa/138kDa/140kDa/141kDa |
| Observed MW: | 150kDa |
| Synonyms: | DCTN1, DAP-150, DP-150, P135 |
| Background: | This gene encodes the largest subunit of dynactin, a macromolecular complex consisting of 10 subunits ranging in size from 22 to 150 kD. Dynactin binds to both microtubules and cytoplasmic dynein. Dynactin is involved in a diverse array of cellular functions, including ER-to-Golgi transport, the centripetal movement of lysosomes and endosomes, spindle formation, chromosome movement, nuclear positioning, and axonogenesis. This subunit interacts with dynein intermediate chain by its domains directly binding to dynein and binds to microtubules via a highly conserved glycine-rich cytoskeleton-associated protein (CAP-Gly) domain in its N-terminus. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. Mutations in this gene cause distal hereditary motor neuronopathy type VIIB (HMN7B) which is also known as distal spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (dSBMA). |
| UniProt Protein Function: | dynactin 1: Required for the cytoplasmic dynein-driven retrograde movement of vesicles and organelles along microtubules. Dynein- dynactin interaction is a key component of the mechanism of axonal transport of vesicles and organelles. Defects in DCTN1 are the cause of distal hereditary motor neuronopathy type 7B (HMN7B); also known as progressive lower motor neuron disease (PLMND). HMN7B is a neuromuscular disorder. Distal hereditary motor neuronopathies constitute a heterogeneous group of neuromuscular disorders caused by selective degeneration of motor neurons in the anterior horn of the spinal cord, without sensory deficit in the posterior horn. The overall clinical picture consists of a classical distal muscular atrophy syndrome in the legs without clinical sensory loss. The disease starts with weakness and wasting of distal muscles of the anterior tibial and peroneal compartments of the legs. Later on, weakness and atrophy may expand to the proximal muscles of the lower limbs and/or to the distal upper limbs. Defects in DCTN1 are a cause of susceptibility to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). ALS is a neurodegenerative disorder affecting upper and lower motor neurons, and resulting in fatal paralysis. Sensory abnormalities are absent. Death usually occurs within 2 to 5 years. The etiology is likely to be multifactorial, involving both genetic and environmental factors. Defects in DCTN1 are the cause of Perry syndrome (PERRYS); also called parkinsonism with alveolar hypoventilation and mental depression. Perry syndrome is a neuropsychiatric disorder characterized by mental depression not responsive to antidepressant drugs or electroconvulsive therapy, sleep disturbances, exhaustion and marked weight loss. Parkinsonism develops later and respiratory failure occurred terminally. Belongs to the dynactin 150 kDa subunit family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Motor; Microtubule-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 2p13 Cellular Component: kinetochore; spindle pole; dynein complex; centrosome; microtubule; dynactin complex; membrane; retromer complex; leading edge; cytoplasm; cytosol Molecular Function:dynein binding; protein binding; motor activity Biological Process: mitosis; nervous system development; cellular protein metabolic process; unfolded protein response, activation of signaling protein activity; unfolded protein response; organelle organization and biogenesis; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II; mitotic cell cycle; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle; melanosome transport; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi Disease: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis 1; Perry Syndrome; Neuronopathy, Distal Hereditary Motor, Type Viib |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes the largest subunit of dynactin, a macromolecular complex consisting of 10 subunits ranging in size from 22 to 150 kD. Dynactin binds to both microtubules and cytoplasmic dynein. Dynactin is involved in a diverse array of cellular functions, including ER-to-Golgi transport, the centripetal movement of lysosomes and endosomes, spindle formation, chromosome movement, nuclear positioning, and axonogenesis. This subunit interacts with dynein intermediate chain by its domains directly binding to dynein and binds to microtubules via a highly conserved glycine-rich cytoskeleton-associated protein (CAP-Gly) domain in its N-terminus. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. Mutations in this gene cause distal hereditary motor neuronopathy type VIIB (HMN7B) which is also known as distal spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (dSBMA). [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q14203 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 17375490 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1639 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q14203.3 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q14203 |
| Molecular Weight: | 140kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Dynactin subunit 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | dynactin subunit 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | DCTN1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | P135; DP-150; DAP-150 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | dynactin subunit 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Dynactin subunit 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | 150 kDa dynein-associated polypeptide; DAP-150; DP-150; p135; p150-glued |
| Protein Family: | Dynactin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | DCTN1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | DCTN1_HUMAN |