Anti-DCLRE1C Antibody (CAB5615)
- SKU:
- CAB5615
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-DCLRE1C Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB5615 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
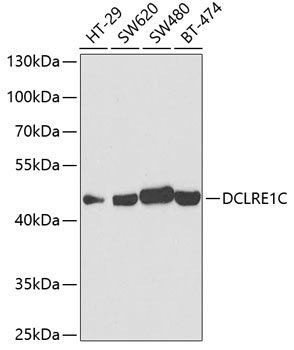
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-300 of human DCLRE1C (NP_001029027.1). |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HT-29, SW620, SW480, BT-474 |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-300 of human DCLRE1C (NP_001029027.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MSSF EGQM AEYP TISI DRFD RENL RARA YFLS HCHK DHMK GLRA PTLK RRLE CSLK VYLY CSPV TKEL LLTS PKYR FWKK RIIS IEIE TPTQ ISLV DEAS GEKE EIVV TLLP AGHC PGSV MFLF QGNN GTVL YTGD FRLA QGEA ARME LLHS GGRV KDIQ SVYL DTTF CDPR FYQI PSRE ECLS GVLE LVRS WITR SPYH VVWL NCKA AYGY EYLF TNLS EELG VQVH VNKL DMFR NMPE ILHH LTTD RNTQ IHAC RHPK AEEY FQWS KLPC GITS RNRI PLHI ISIK PSTM WFGE RSRK |
| Gene ID: | 64421 |
| Uniprot: | Q96SD1 |
| Cellular Location: | Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 49kDa/64kDa/65kDa/78kDa |
| Observed MW: | 45kDa |
| Synonyms: | DCLRE1C, A-SCID, DCLREC1C, RS-SCID, SCIDA, SNM1C |
| Background: | This gene encodes a nuclear protein that is involved in V(D)J recombination and DNA repair. The encoded protein has single-strand-specific 5'-3' exonuclease activity; it also exhibits endonuclease activity on 5' and 3' overhangs and hairpins. The protein also functions in the regulation of the cell cycle in response to DNA damage. Mutations in this gene can cause Athabascan-type severe combined immunodeficiency (SCIDA) and Omenn syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Artemis: Required for V(D)J recombination, the process by which exons encoding the antigen-binding domains of immunoglobulins and T-cell receptor proteins are assembled from individual V, (D), and J gene segments. V(D)J recombination is initiated by the lymphoid specific RAG endonuclease complex, which generates site specific DNA double strand breaks (DSBs). These DSBs present two types of DNA end structures: hairpin sealed coding ends and phosphorylated blunt signal ends. These ends are independently repaired by the non homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway to form coding and signal joints respectively. This protein exhibits single-strand specific 5'-3' exonuclease activity in isolation and acquires endonucleolytic activity on 5' and 3' hairpins and overhangs when in a complex with PRKDC. The latter activity is required specifically for the resolution of closed hairpins prior to the formation of the coding joint. May also be required for the repair of complex DSBs induced by ionizing radiation, which require substantial end-processing prior to religation by NHEJ. Defects in DCLRE1C are a cause of severe combined immunodeficiency autosomal recessive T-cell-negative/B-cell- negative/NK-cell-positive with sensitivity to ionizing radiation (RSSCID). SCID refers to a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare congenital disorders characterized by impairment of both humoral and cell-mediated immunity, leukopenia, and low or absent antibody levels. Patients with SCID present in infancy with recurrent, persistent infections by opportunistic organisms. The common characteristic of all types of SCID is absence of T-cell-mediated cellular immunity due to a defect in T- cell development. Individuals affected by RS-SCID show defects in the DNA repair machinery necessary for coding joint formation and the completion of V(D)J recombination. A subset of cells from such patients show increased radiosensitivity. Defects in DCLRE1C are the cause of severe combined immunodeficiency Athabaskan type (SCIDA). SCIDA is a variety of RS-SCID caused by a founder mutation in Athabascan- speaking native Americans, being inherited as an autosomal recessive trait with an estimated gene frequency of 2.1% in the Navajo population. Affected individuals exhibit clinical symptoms and defects in DNA repair comparable to those seen in RS-SCID. Defects in DCLRE1C are a cause of Omenn syndrome (OS). OS is characterized by severe combined immunodeficiency associated with erythrodermia, hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy and alopecia. Affected individuals have elevated T-lymphocyte counts with a restricted T- cell receptor (TCR) repertoire. They also generally lack B- lymphocytes, but have normal natural killer (NK) cell function (T+ B- NK+). Belongs to the DNA repair metallo-beta-lactamase (DRMBL) family. 4 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 3.1.-.-; Deoxyribonuclease; DNA repair, damage Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 10p13 Cellular Component: nuclear chromosome, telomeric region; nucleoplasm Molecular Function:5'-3' exodeoxyribonuclease activity; 5'-3' exonuclease activity; damaged DNA binding; endonuclease activity; protein binding; single-stranded DNA specific endodeoxyribonuclease activity Biological Process: double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining; protection from non-homologous end joining at telomere Disease: Omenn Syndrome; Severe Combined Immunodeficiency With Sensitivity To Ionizing Radiation |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a nuclear protein that is involved in V(D)J recombination and DNA repair. The encoded protein has single-strand-specific 5'-3' exonuclease activity; it also exhibits endonuclease activity on 5' and 3' overhangs and hairpins. The protein also functions in the regulation of the cell cycle in response to DNA damage. Mutations in this gene can cause Athabascan-type severe combined immunodeficiency (SCIDA) and Omenn syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014] |
| UniProt Code: | Q96SD1 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 71153325 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 64421 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q96SD1.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q96SD1,Q1HCL2, Q5JSR4, Q5JSR5, Q5JSR7, Q5JSR8, Q5JSR9 Q5JSS0, Q5JSS7, Q6PK14, Q8N101, D3DRT6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q96SD1 |
| Molecular Weight: | 49,944 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Protein artemis |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | DNA cross-link repair 1C |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | DCLRE1C |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | SCIDA; SNM1C; A-SCID; RS-SCID; DCLREC1C |
| NCBI Protein Information: | protein artemis |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Protein artemis |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | DNA cross-link repair 1C protein; Protein A-SCID; SNM1 homolog C; hSNM1C; SNM1-like protein |
| Protein Family: | Protein artemis |
| UniProt Gene Name: | DCLRE1C |
| UniProt Entry Name: | DCR1C_HUMAN |