Anti-CTNS Antibody (CAB6893)
- SKU:
- CAB6893
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Metabolism
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-CTNS Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB6893 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
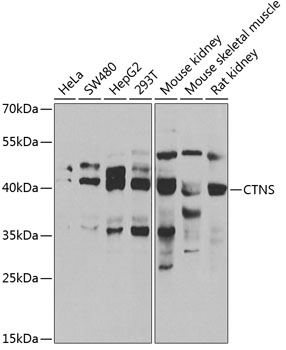
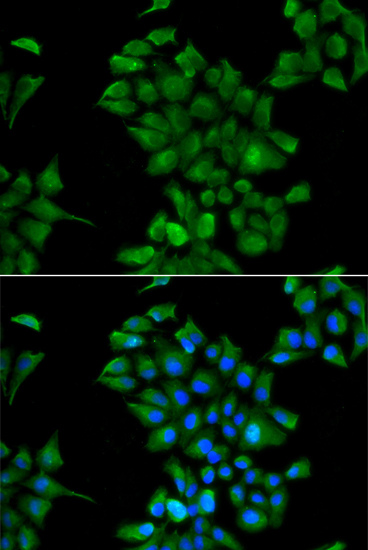
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-120 of human CTNS (NP_001026851.2). |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, SW480, HepG2, 293T, Mouse kidney, Mouse skeletal muscle, Rat kidney |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-120 of human CTNS (NP_001026851.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MIRN WLTI FILF PLKL VEKC ESSV SLTV PPVV KLEN GSST NVSL TLRP PLNA TLVI TFEI TFRS KNIT ILEL PDEV VVPP GVTN SSFQ VTSQ NVGQ LTVY LHGN HSNQ TGPR IRFL VIRS |
| Gene ID: | 1497 |
| Uniprot: | O60931 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell membrane, Lysosome membrane, Melanosome, Multi-pass membrane protein |
| Calculated MW: | 41kDa/45kDa |
| Observed MW: | 42kDa |
| Synonyms: | CTNS, CTNS-LSB, PQLC4 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a seven-transmembrane domain protein that functions to transport cystine out of lysosomes. Its activity is driven by the H+ electrochemical gradient of the lysosomal membrane. Mutations in this gene cause cystinosis, a lysosomal storage disorder. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | CTNS: Thought to transport cystine out of lysosomes. Defects in CTNS are the cause of cystinosis nephropathic type (CTNS). It is a form of cystinosis, a lysosomal storage disease due to defective transport of cystine across the lysosomal membrane. This results in cystine accumulation and crystallization in the cells causing widespread tissue damage. The classical nephropathic form has onset in the first year of life and is characterized by a polyuro-polydipsic syndrome, marked height-weight growth delay, generalized impaired proximal tubular reabsorptive capacity, with severe fluid-electrolyte balance alterations, renal failure, ocular symptoms and other systemic complications. Defects in CTNS are the cause of cystinosis adult non- nephropathic type (CTNSANN). It is a form of cystinosis, a lysosomal storage disease due to defective transport of cystine across the lysosomal membrane. This results in cystine accumulation and crystallization in the cells causing widespread tissue damage. Cystinosis adult non-nephropathic type is characterized by ocular features and a benigne course. Patients manifest mild photophobia due to conjunctival and corneal cystine crystals. Defects in CTNS are the cause of cystinosis late-onset juvenile or adolescent nephropathic type (CTNSJAN). It is a form of cystinosis, a lysosomal storage disease due to defective transport of cystine across the lysosomal membrane. This results in cystine accumulation and crystallization in the cells causing widespread tissue damage. Late-onset juvenile or adolescent nephropathic cystinosis manifests itself first at age 10 to 12 years with proteinuria due to glomerular damage rather than with the manifestations of tubular damage that occur first in infantile cystinosis. There is no excess amino aciduria and stature is normal. Photophobia, late development of pigmentary retinopathy, and chronic headaches are features. Belongs to the cystinosin family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Membrane protein, multi-pass; Membrane protein, integral Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17p13 Cellular Component: early endosome; intermediate filament cytoskeleton; intracellular membrane-bound organelle; late endosome; lysosomal membrane; lysosome Molecular Function:L-cystine transmembrane transporter activity Biological Process: ATP metabolic process; brain development; cognition; glutathione metabolic process; ion transport; L-cystine transport; transmembrane transport Disease: Cystinosis, Adult Nonnephropathic; Cystinosis, Late-onset Juvenile Or Adolescent Nephropathic Type; Cystinosis, Nephropathic |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a seven-transmembrane domain protein that functions to transport cystine out of lysosomes. Its activity is driven by the H+ electrochemical gradient of the lysosomal membrane. Mutations in this gene cause cystinosis, a lysosomal storage disorder. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | O60931 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 269849555 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1497 |
| NCBI Accession: | O60931.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O60931,Q8IZ01, Q9UNK6, D3DTJ5, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O60931 |
| Molecular Weight: | 45,039 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Cystinosin |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | cystinosin, lysosomal cystine transporter |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CTNS |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | PQLC4; CTNS-LSB |
| NCBI Protein Information: | cystinosin |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Cystinosin |
| Protein Family: | Cystinosin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CTNS |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CTNS_HUMAN |