Anti-CREBBP Antibody (CAB1334)
- SKU:
- CAB1334
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-CREBBP Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB1334 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
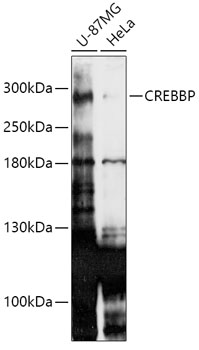
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 100-200 of human CREBBP (NP_004371.2). |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | U-87MG, HeLa |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 100-200 of human CREBBP (NP_004371.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | GGQA QGQP NSAN MASL SAMG KSPL SQGD SSAP SLPK QAAS TSGP TPAA SQAL NPQA QKQV GLAT SSPA TSQT GPGI CMNA NFNQ THPG LLNS NSGH SLIN Q |
| Gene ID: | 1387 |
| Uniprot: | Q92793 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 260kDa/265kDa |
| Observed MW: | 280kDa |
| Synonyms: | CREBBP, CBP, KAT3A, RSTS, RSTS1 |
| Background: | This gene is ubiquitously expressed and is involved in the transcriptional coactivation of many different transcription factors. First isolated as a nuclear protein that binds to cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB), this gene is now known to play critical roles in embryonic development, growth control, and homeostasis by coupling chromatin remodeling to transcription factor recognition. The protein encoded by this gene has intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity and also acts as a scaffold to stabilize additional protein interactions with the transcription complex. This protein acetylates both histone and non-histone proteins. This protein shares regions of very high sequence similarity with protein p300 in its bromodomain, cysteine-histidine-rich regions, and histone acetyltransferase domain. Mutations in this gene cause Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RTS). Chromosomal translocations involving this gene have been associated with acute myeloid leukemia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | CBP: a protein acetyltransferase that can transcriptionally activate histones. Acetylates the NCOA3 coactivator. Binds specifically to phosphorylated CREB1 and enhances its transcriptional activity toward cAMP-responsive genes. Methylation of the KIX domain by CARM1 blocks association with CREB, blocking CREB signaling, and activating the apoptotic response. Found in a complex containing NCOA2, NCOA3, IKKA, IKKB, and IKBKG. Probably part of a complex with HIF1A and EP300. Interacts with the C-terminal region of CITED4. The TAZ-type 1 domain interacts with HIF1A. Interacts with MAF, SRCAP, CARM1, ELF3, MLLT7/FOXO4, N4BP2, NCOA1, NCOA3, NCOA6, PCAF, PELP1, PML, SMAD1, SMAD2, SMAD3, SPIB and TRERF1. Interacts with HTLV-1 Tax, p30II, and HIV-1 Tat. Interacts with KLF1; the interaction results in acetylation of KLF1 and enhancement of its transcriptional activity. Interacts with ZCCHC12. Interacts with DAXX; the interaction is dependent on CBP sumoylation and results in suppression of the transcriptional activiy via recruitment of HDAC2 to DAAX. Interacts with MTDH. Interacts with NFATC4. Interacts with MAFG; the interaction acetylates MAFG in the basic region and stimulates NFE2 transcriptional activity through increasing its DNA-binding activity. Interacts with IRF2; the interaction acetylates IRF2 and regulates its activity on the H4 promoter. Interacts via its N-terminus with the C-terminus of SS18L1. Interacts with MECOM. Chromosomal aberrations involving CBP may be a cause of acute myeloid leukemias. Known translocation partners include MYST3, MLL, and MYST4. MYST3-CBP fusion proteins may induce leukemia by inhibiting RUNX1-mediated transcription. Defects in CBP are a cause of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome type 1 (RSTS1), an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by craniofacial abnormalities, broad thumbs, broad big toes, mental retardation and a propensity for development of malignancies. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Nuclear receptor co-regulator; EC 2.3.1.48; DNA-binding; Acetyltransferase; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Transcription, coactivator/corepressor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 16p13.3 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; nuclear body; transcription factor complex; nuclear chromatin; cytoplasm; outer kinetochore of condensed chromosome; nucleus; histone acetyltransferase complex Molecular Function:MRF binding; signal transducer activity; protein binding; histone acetyltransferase activity; zinc ion binding; p53 binding; acetyltransferase activity; transcription coactivator activity; chromatin binding; transcription factor activity; transcription factor binding Biological Process: transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter; establishment and/or maintenance of chromatin architecture; Notch signaling pathway; viral reproduction; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; rhythmic process; germ-line stem cell maintenance; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; cellular lipid metabolic process; signal transduction; homeostatic process; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; response to hypoxia; positive regulation of interferon type I production; innate immune response; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; gene expression; protein complex assembly; embryonic digit morphogenesis; histone acetylation; regulation of smoothened signaling pathway; N-terminal peptidyl-lysine acetylation Disease: Rubinstein-taybi Syndrome 1 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is ubiquitously expressed and is involved in the transcriptional coactivation of many different transcription factors. First isolated as a nuclear protein that binds to cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB), this gene is now known to play critical roles in embryonic development, growth control, and homeostasis by coupling chromatin remodeling to transcription factor recognition. The protein encoded by this gene has intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity and also acts as a scaffold to stabilize additional protein interactions with the transcription complex. This protein acetylates both histone and non-histone proteins. This protein shares regions of very high sequence similarity with protein p300 in its bromodomain, cysteine-histidine-rich regions, and histone acetyltransferase domain. Mutations in this gene cause Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RTS). Chromosomal translocations involving this gene have been associated with acute myeloid leukemia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | Q92793 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 116241283 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1387 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q92793.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q92793,O00147, Q16376, Q4LE28, D3DUC9, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q92793 |
| Molecular Weight: | 260,993 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | CREB-binding protein |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | CREB binding protein |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CREBBP |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CBP; RSTS; KAT3A |
| NCBI Protein Information: | CREB-binding protein |
| UniProt Protein Name: | CREB-binding protein |
| Protein Family: | CREB-binding protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CREBBP |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CBP_HUMAN |