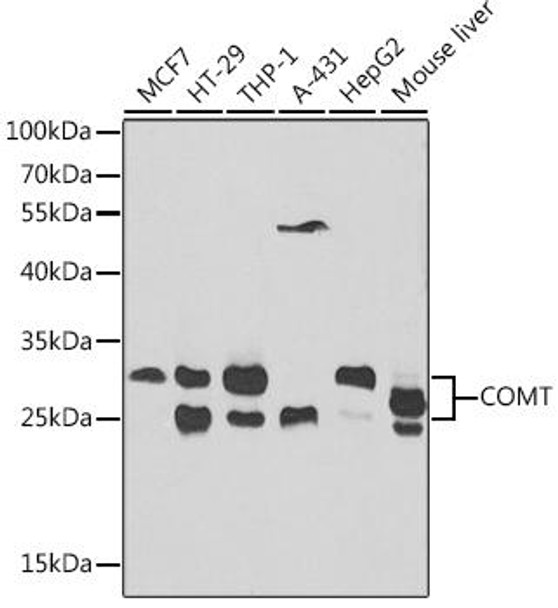
Anti-COMT Antibody (CAB1294)
- SKU:
- CAB1294
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Metabolism
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-COMT Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB1294 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
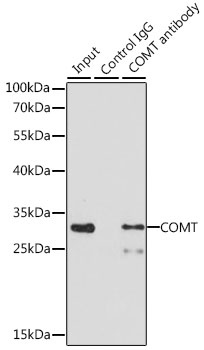
| Application: | WB IP |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 42-221 of human COMT (NP_009294.1). |
| Application: | WB IP |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IP 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Positive Samples: | MCF-7, HT-29, THP-1, A-431, HepG2, Mouse liver |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 42-221 of human COMT (NP_009294.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | VGDK KGKI VDAV IQEH QPSV LLEL GAYC GYSA VRMA RLLS PGAR LITI EINP DCAA ITQR MVDF AGVK DKVT LVVG ASQD IIPQ LKKK YDVD TLDM VFLD HWKD RYLP DTLL LEEC GLLR KGTV LLAD NVIC PGAP DFLA HVRG SSCF ECTH YQSF LEYR EVVD GLEK AIYK GPGS EAGP |
| Gene ID: | 1312 |
| Uniprot: | P21964 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Extracellular side, Single-pass type II membrane protein |
| Calculated MW: | 24kDa/30kDa |
| Observed MW: | 25kDa, 30kDa |
| Synonyms: | COMT, HEL-S-98n |
| Background: | Catechol-O-methyltransferase catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group from S-adenosylmethionine to catecholamines, including the neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine. This O-methylation results in one of the major degradative pathways of the catecholamine transmitters. In addition to its role in the metabolism of endogenous substances, COMT is important in the metabolism of catechol drugs used in the treatment of hypertension, asthma, and Parkinson disease. COMT is found in two forms in tissues, a soluble form (S-COMT) and a membrane-bound form (MB-COMT). The differences between S-COMT and MB-COMT reside within the N-termini. Several transcript variants are formed through the use of alternative translation initiation sites and promoters. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | COMT: Catalyzes the O-methylation, and thereby the inactivation, of catecholamine neurotransmitters and catechol hormones. Also shortens the biological half-lives of certain neuroactive drugs, like L-DOPA, alpha-methyl DOPA and isoproterenol. Belongs to the mammalian catechol-O-methyltransferase family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative initiation. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Membrane protein, integral; Methyltransferase; EC 2.1.1.6; Amino Acid Metabolism - tyrosine Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 22q11.21 Cellular Component: postsynaptic membrane; mitochondrion; membrane; axon; plasma membrane; dendritic spine; integral to membrane; cytosol Molecular Function:protein binding; magnesium ion binding; O-methyltransferase activity; catechol O-methyltransferase activity Biological Process: response to drug; methylation; estrogen metabolic process; cellular response to phosphate starvation; neurotransmitter catabolic process; dopamine catabolic process; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation; short-term memory; response to pain; response to lipopolysaccharide; female pregnancy; learning; reproductive process in a multicellular organism; response to organic cyclic substance; positive regulation of homocysteine metabolic process; negative regulation of dopamine metabolic process; synaptic transmission; xenobiotic metabolic process; regulation of sensory perception of pain; developmental process; neurotransmitter biosynthetic process Disease: Schizophrenia; Panic Disorder 1 |
| NCBI Summary: | Catechol-O-methyltransferase catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group from S-adenosylmethionine to catecholamines, including the neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine. This O-methylation results in one of the major degradative pathways of the catecholamine transmitters. In addition to its role in the metabolism of endogenous substances, COMT is important in the metabolism of catechol drugs used in the treatment of hypertension, asthma, and Parkinson disease. COMT is found in two forms in tissues, a soluble form (S-COMT) and a membrane-bound form (MB-COMT). The differences between S-COMT and MB-COMT reside within the N-termini. Several transcript variants are formed through the use of alternative translation initiation sites and promoters. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P21964 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 116907 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1312 |
| NCBI Accession: | P21964.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P21964,Q6IB07, Q6ICE6, Q9BWC7, A8MPV9, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P21964 |
| Molecular Weight: | 271 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Catechol O-methyltransferase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | catechol-O-methyltransferase |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | COMT |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | HEL-S-98n |
| NCBI Protein Information: | catechol O-methyltransferase; epididymis secretory sperm binding protein Li 98n |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Catechol O-methyltransferase |
| Protein Family: | Catechol O-methyltransferase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | COMT |
| UniProt Entry Name: | COMT_HUMAN |

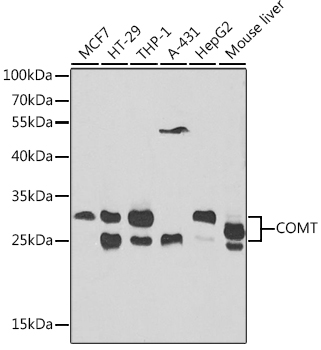


![Anti-COMT Antibody (CAB18085)[KO Validated] Anti-COMT Antibody (CAB18085)[KO Validated]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-39x6lpnvxv/images/stencil/590x590/products/19216/17416/anti-comt-antibody-cab18085ko-validated__43515__81596.1644251922.jpg?c=1)