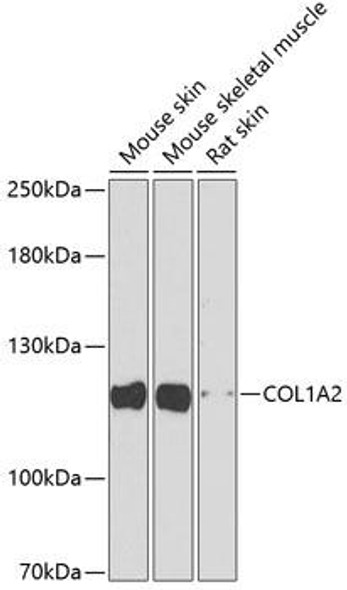
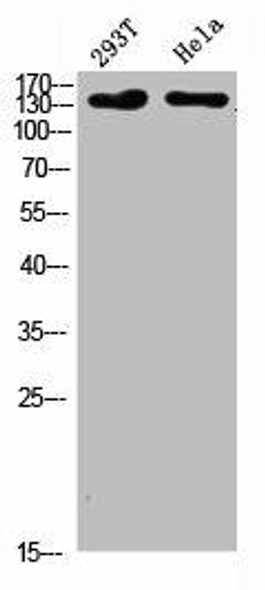
Anti-COL1A2 Antibody (CAB16699)
- SKU:
- CAB16699
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-COL1A2 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB16699 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 500-600 of human COL1A2 (NP_000080.2). |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 500-600 of human COL1A2 (NP_000080.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | PTGD PGKN GDKG HAGL AGAR GAPG PDGN NGAQ GPPG PQGV QGGK GEQG PPGP PGFQ GLPG PSGP AGEV GKPG ERGL HGEF GLPG PAGP RGER GPPG ESGA A |
| Gene ID: | 1278 |
| Uniprot: | P08123 |
| Cellular Location: | Secreted, extracellular matrix, extracellular space |
| Calculated MW: | 129kDa |
| Observed MW: | 118kDa |
| Synonyms: | COL1A2, OI4 |
| Background: | This gene encodes the pro-alpha2 chain of type I collagen whose triple helix comprises two alpha1 chains and one alpha2 chain. Type I is a fibril-forming collagen found in most connective tissues and is abundant in bone, cornea, dermis and tendon. Mutations in this gene are associated with osteogenesis imperfecta types I-IV, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VIIB, recessive Ehlers-Danlos syndrome Classical type, idiopathic osteoporosis, and atypical Marfan syndrome. Symptoms associated with mutations in this gene, however, tend to be less severe than mutations in the gene for the alpha1 chain of type I collagen (COL1A1) reflecting the different role of alpha2 chains in matrix integrity. Three transcripts, resulting from the use of alternate polyadenylation signals, have been identified for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | COL1A2: Type I collagen is a member of group I collagen (fibrillar forming collagen). Defects in COL1A2 are the cause of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type 7B (EDS7B). EDS is a connective tissue disorder characterized by hyperextensible skin, atrophic cutaneous scars due to tissue fragility and joint hyperlaxity. EDS7B is marked by bilateral congenital hip dislocation, hyperlaxity of the joints, and recurrent partial dislocations. Defects in COL1A2 are a cause of osteogenesis imperfecta type 1 (OI1). A dominantly inherited connective tissue disorder characterized by bone fragility and blue sclerae. Osteogenesis imperfecta type 1 is non-deforming with normal height or mild short stature, and no dentinogenesis imperfecta. Defects in COL1A2 are a cause of osteogenesis imperfecta type 2 (OI2); also known as osteogenesis imperfecta congenita (OIC) or lethal perinatal. A connective tissue disorder characterized by bone fragility, with many perinatal fractures, severe bowing of long bones, undermineralization, and death in the perinatal period due to respiratory insufficiency. Defects in COL1A2 are the cause of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome autosomal recessive cardiac valvular form (EDSCV). A connective tissue disorder characterized by hyperextensible skin, atrophic cutaneous scars due to tissue fragility and joint hyperlaxity. In addition to joint laxity, skin hyperextensibility and friability, and abnormal scar formation, patients have mitral valve prolapse and insufficiency, mitral regurgitation, and aortic insufficiency. Defects in COL1A2 are a cause of osteogenesis imperfecta type 3 (OI3). A connective tissue disorder characterized by progressively deforming bones, very short stature, a triangular face, severe scoliosis, grayish sclera, and dentinogenesis imperfecta. Defects in COL1A2 are a cause of osteogenesis imperfecta type 4 (OI4); also known as osteogenesis imperfecta with normal sclerae. A connective tissue disorder characterized by moderately short stature, mild to moderate scoliosis, grayish or white sclera and dentinogenesis imperfecta. A chromosomal aberration involving COL1A2 may be a cause of lipoblastomas, which are benign tumors resulting from transformation of adipocytes, usually diagnosed in children. Translocation t(7;8)(p22;q13) with PLAG1. Belongs to the fibrillar collagen family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted, signal peptide; Secreted Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 7q22.1 Cellular Component: collagen type I; endoplasmic reticulum lumen; extracellular matrix; extracellular region; extracellular space Molecular Function:extracellular matrix structural constituent; identical protein binding; metal ion binding; platelet-derived growth factor binding; protein binding; protein binding, bridging; SMAD binding Biological Process: blood coagulation; blood vessel development; collagen catabolic process; collagen fibril organization; extracellular matrix disassembly; extracellular matrix organization and biogenesis; leukocyte migration; odontogenesis; platelet activation; receptor-mediated endocytosis; regulation of blood pressure; regulation of immune response; Rho protein signal transduction; skeletal development; skin morphogenesis; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway Disease: Ehlers-danlos Syndrome, Autosomal Recessive, Cardiac Valvular Form; Ehlers-danlos Syndrome, Type Vii, Autosomal Dominant; Osteogenesis Imperfecta, Type Ii; Osteogenesis Imperfecta, Type Iii; Osteogenesis Imperfecta, Type Iv; Osteoporosis |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes the pro-alpha2 chain of type I collagen whose triple helix comprises two alpha1 chains and one alpha2 chain. Type I is a fibril-forming collagen found in most connective tissues and is abundant in bone, cornea, dermis and tendon. Mutations in this gene are associated with osteogenesis imperfecta types I-IV, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VIIB, recessive Ehlers-Danlos syndrome Classical type, idiopathic osteoporosis, and atypical Marfan syndrome. Symptoms associated with mutations in this gene, however, tend to be less severe than mutations in the gene for the alpha1 chain of type I collagen (COL1A1) reflecting the different role of alpha2 chains in matrix integrity. Three transcripts, resulting from the use of alternate polyadenylation signals, have been identified for this gene. [provided by R. Dalgleish, Feb 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P08123 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 296439507 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1278 |
| NCBI Accession: | P08123.7 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P08123,P02464, Q13897, Q13997, Q13998, Q14038, Q14057 Q15177, Q15947, Q16480, Q16511, Q7Z5S6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P08123 |
| Molecular Weight: | 129,314 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Collagen alpha-2(I) chain |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | collagen type I alpha 2 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | COL1A2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | OI4 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | collagen alpha-2(I) chain |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Collagen alpha-2(I) chain |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Alpha-2 type I collagen |
| UniProt Gene Name: | COL1A2 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CO1A2_HUMAN |