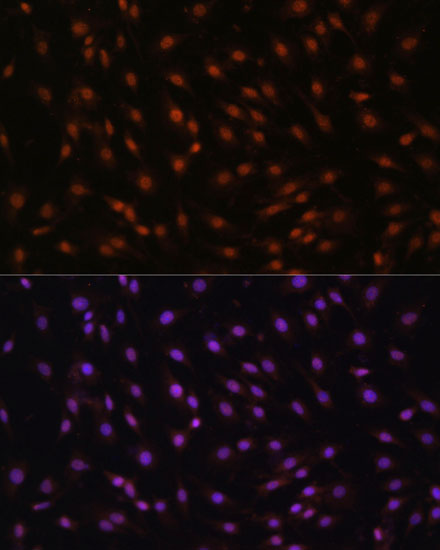
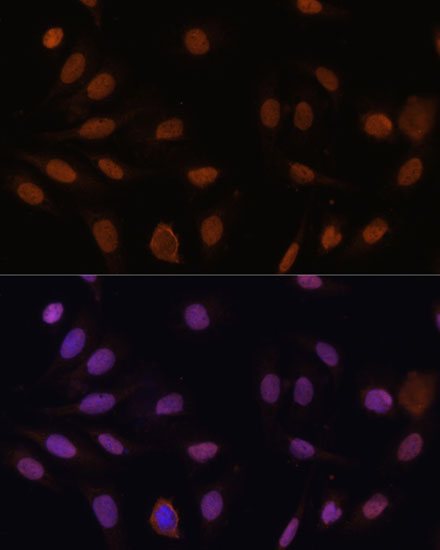
Anti-CDKN1B/p27KIP1 Antibody (CAB16722)
- SKU:
- CAB16722
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Cycle
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-CDKN1B/p27KIP1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB16722 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
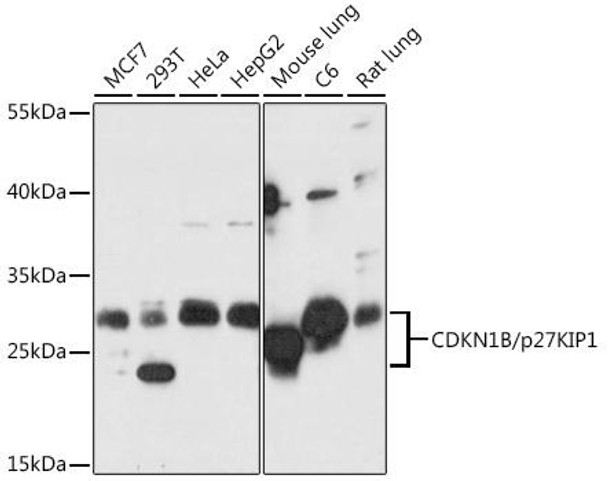
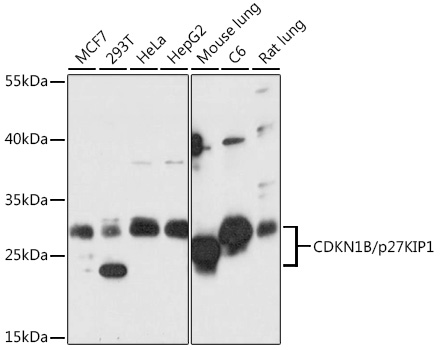
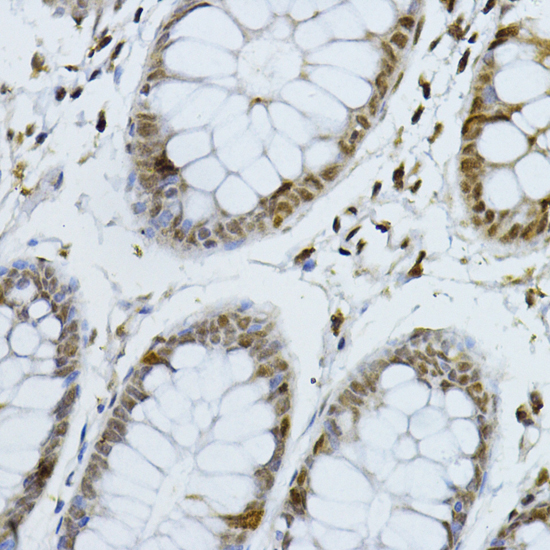
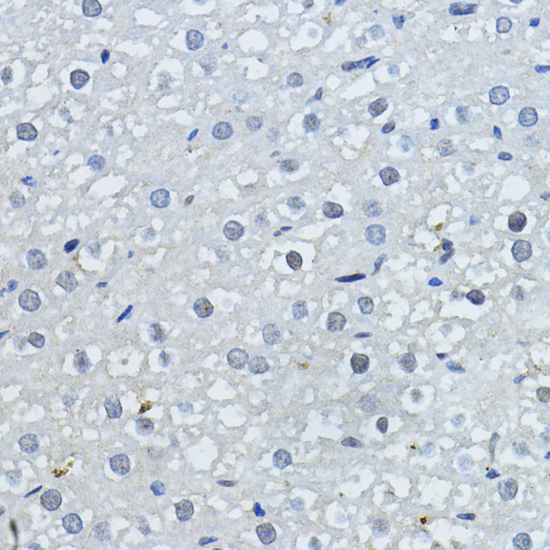
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human CDKN1B/p27KIP1 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | MCF7, 293T, HeLa, HepG2, mouse lung, C6, rat lung |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human CDKN1B/p27KIP1 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 1027 |
| Uniprot: | P46527 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Endosome, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 22kDa |
| Observed MW: | 27kDa |
| Synonyms: | CDKN1B, CDKN4, KIP1, MEN1B, MEN4, P27KIP1, p27 KIP 1 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, which shares a limited similarity with CDK inhibitor CDKN1A/p21. The encoded protein binds to and prevents the activation of cyclin E-CDK2 or cyclin D-CDK4 complexes, and thus controls the cell cycle progression at G1. The degradation of this protein, which is triggered by its CDK dependent phosphorylation and subsequent ubiquitination by SCF complexes, is required for the cellular transition from quiescence to the proliferative state. Mutations in this gene are associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type IV (MEN4). |
| UniProt Protein Function: | p27Kip1: a cell-cycle regulatory protein that Interacts with cyclin-CDK2 and -CDK4, inhibiting cell cycle progression at G1. May mediate TGF beta-induced g1 arrest. Its degradation is triggered by its CDK dependent phosphorylation and subsequent ubiquitination by SCF complexes, is required for the cellular transition from quiescence to the proliferative state. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protein kinase, regulatory subunit; Cell cycle regulation; Oncoprotein; Inhibitor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 12p13.1-p12 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; cytoplasm; nucleus; cytosol; endosome Molecular Function:cyclin-dependent protein kinase inhibitor activity; protein binding; chaperone binding; protein complex binding; caspase activator activity; Hsp70 protein binding; protein phosphatase binding; transforming growth factor beta receptor, cytoplasmic mediator activity Biological Process: negative regulation of kinase activity; response to peptide hormone stimulus; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of microtubule polymerization; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest; response to estradiol stimulus; negative regulation of cell proliferation; sensory perception of sound; positive regulation of cell proliferation; response to glucose stimulus; negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle; cell cycle arrest; inner ear development; potassium ion transport; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; caspase activation; response to drug; phosphoinositide-mediated signaling; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity; negative regulation of cell motility; response to amino acid stimulus; response to cadmium ion; response to hypoxia; positive regulation of protein catabolic process; autophagic cell death; innate immune response; negative regulation of phosphorylation; negative regulation of cell growth; regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity; mitotic cell cycle; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; negative regulation of apoptosis; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle Disease: Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia, Type Iv |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, which shares a limited similarity with CDK inhibitor CDKN1A/p21. The encoded protein binds to and prevents the activation of cyclin E-CDK2 or cyclin D-CDK4 complexes, and thus controls the cell cycle progression at G1. The degradation of this protein, which is triggered by its CDK dependent phosphorylation and subsequent ubiquitination by SCF complexes, is required for the cellular transition from quiescence to the proliferative state. Mutations in this gene are associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type IV (MEN4). [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014] |
| UniProt Code: | P46527 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1168871 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1027 |
| NCBI Accession: | P46527.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P46527,Q16307, Q5U0H2, Q9BUS6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P46527 |
| Molecular Weight: | Calculated: 22kDaObserved: 26kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (p27, Kip1) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CDKN1B |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | KIP1; MEN4; CDKN4; MEN1B; P27KIP1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27; p27Kip1 |
| Protein Family: | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CDKN1B |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CDN1B_HUMAN |


![Anti-CDKN1B/p27KIP1 Antibody (CAB0290)[KO Validated] Anti-CDKN1B/p27KIP1 Antibody (CAB0290)[KO Validated]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-39x6lpnvxv/images/stencil/590x590/products/19340/17540/anti-cdkn1bp27kip1-antibody-cab0290ko-validated__84022__39334.1644251954.jpg?c=1)
![Anti-CDKN1B/p27KIP1 Antibody (CAB16633)[KO Validated] Anti-CDKN1B/p27KIP1 Antibody (CAB16633)[KO Validated]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-39x6lpnvxv/images/stencil/590x590/products/30599/28788/anti-cdkn1bp27kip1-antibody-cab16633ko-validated__16429__32347.1644317109.jpg?c=1)