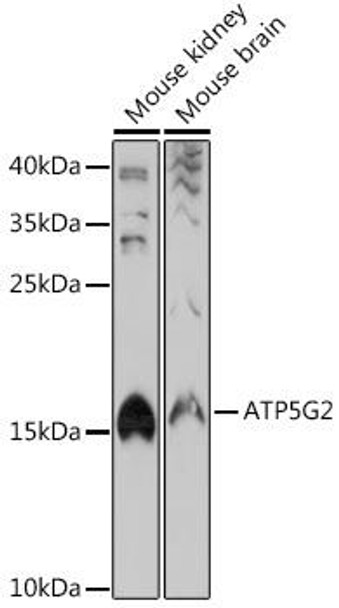
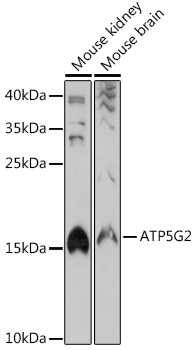
| Synonyms: | ATP5A, ATP5G2 |
| Background: | This gene encodes a subunit of mitochondrial ATP synthase. Mitochondrial ATP synthase catalyzes ATP synthesis, utilizing an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane during oxidative phosphorylation. ATP synthase is composed of two linked multi-subunit complexes: the soluble catalytic core, F1, and the membrane-spanning component, Fo, comprising the proton channel. The catalytic portion of mitochondrial ATP synthase consists of 5 different subunits (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon) assembled with a stoichiometry of 3 alpha, 3 beta, and single representatives of the gamma, delta, and epsilon subunits. The proton channel likely has nine subunits (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, F6 and 8). There are three separate genes which encode subunit c of the proton channel and they specify precursors with different import sequences but identical mature proteins. The protein encoded by this gene is one of three precursors of subunit c. This gene has multiple pseudogenes. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F1F0 ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F1 - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core and F0 - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F1 is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Part of the complex F0 domain. A homomeric c-ring of probably 10 subunits is part of the complex rotary element. |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a subunit of mitochondrial ATP synthase. Mitochondrial ATP synthase catalyzes ATP synthesis, utilizing an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane during oxidative phosphorylation. ATP synthase is composed of two linked multi-subunit complexes: the soluble catalytic core, F1, and the membrane-spanning component, Fo, comprising the proton channel. The catalytic portion of mitochondrial ATP synthase consists of 5 different subunits (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon) assembled with a stoichiometry of 3 alpha, 3 beta, and single representatives of the gamma, delta, and epsilon subunits. The proton channel likely has nine subunits (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, F6 and 8). There are three separate genes which encode subunit c of the proton channel and they specify precursors with different import sequences but identical mature proteins. The protein encoded by this gene is one of three precursors of subunit c. This gene has multiple pseudogenes. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2018] |
| UniProt Code: | Q06055 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 50593533 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 517 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_001002031.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q06055,B3KQQ6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q06055 |
| Molecular Weight: | 14 kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | ATP synthase F(0) complex subunit C2, mitochondrial isoform a |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | ATP synthase membrane subunit c locus 2 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ATP5MC2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ATP5A; ATP5G2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | ATP synthase F(0) complex subunit C2, mitochondrial |
| UniProt Protein Name: | ATP synthase F(0) complex subunit C2, mitochondrial |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | ATP synthase lipid-binding protein; ATP synthase proteolipid P2; ATP synthase proton-transporting mitochondrial F(0) complex subunit C2; ATPase protein 9; ATPase subunit c |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ATP5G2 |