Anti-ATP1A2 Antibody (CAB19278)
- SKU:
- CAB19278
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Antibody Type:
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Synonyms:
- ATP1A2
- FHM2
- MHP2
- ATPase Na+/K+ transporting subunit alpha 2
Description
| Product Name: | ATP1A2 Rabbit mAb |
| Product Code: | CAB19278 |
| Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Synonyms: | ATP1A2, FHM2, MHP2, ATPase Na+/K+ transporting subunit alpha 2 |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human ATP1A2. |
| Applications: | WB |
| Recommended Dilutions: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
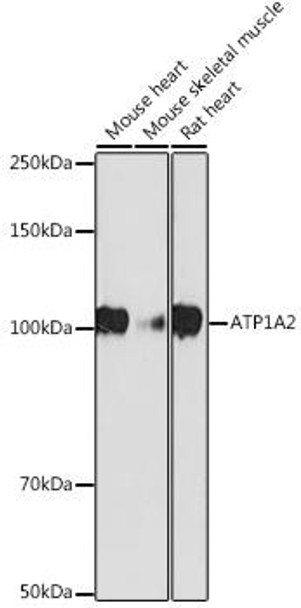
| Positive Samples: | Mouse heart, Mouse skeletal muscle, Rat heart |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human ATP1A2. |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 477 |
| Uniprot: | P50993 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell membrane, Membrane, Multi-pass membrane protein |
| Calculated MW: | 102kDa |
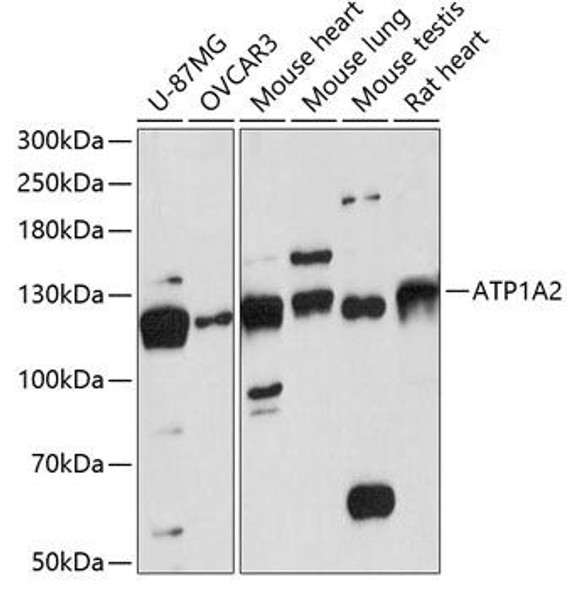
| Observed MW: | 100KDa |
| UniProt Protein Function: | ATP1A2: This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients. Defects in ATP1A2 are the cause of familial hemiplegic migraine type 2 (FHM2). FHM2 is a rare, severe, autosomal dominant subtype of migraine characterized by aura and some hemiparesis. Defects in ATP1A2 are a cause of alternating hemiplegia of childhood 1 (AHC1). AHC is typically distinguished from familial hemiplegic migraine by infantile onset of the symptoms and high prevalence of associated neurological deficits that become increasingly obvious with age. Belongs to the cation transport ATPase (P-type) (TC 3.A.3) family. Type IIC subfamily. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Transporter; Membrane protein, integral; Hydrolase; EC 3.6.3.9; Transporter, ion channel; Membrane protein, multi-pass Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1q23.2 Cellular Component: caveola; cytoplasm; cytosol; dendritic spine; endosome; intracellular membrane-bound organelle; membrane; myelin sheath; plasma membrane; sodium:potassium-exchanging ATPase complex; T-tubule Molecular Function:ATP binding; ATPase activity; chaperone binding; drug binding; potassium ion binding; protein binding; sodium ion binding; sodium:potassium-exchanging ATPase activity Biological Process: adult locomotory behavior; ATP hydrolysis coupled proton transport; ATP metabolic process; cardiac muscle contraction; cellular potassium ion homeostasis; cellular sodium ion homeostasis; establishment and/or maintenance of transmembrane electrochemical gradient; locomotion; negative regulation of heart contraction; negative regulation of striated muscle contraction; neurological control of breathing; neurotransmitter uptake; potassium ion import; potassium ion transport; reduction of cytosolic calcium ion concentration; regulation of blood pressure; regulation of glutamate uptake during transmission of nerve impulse; regulation of smooth muscle contraction; regulation of striated muscle contraction; regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic; regulation of the force of heart contraction; regulation of vasoconstriction; response to nicotine; sodium ion transport; transmembrane transport; visual learning Disease: Alternating Hemiplegia Of Childhood 1; Migraine, Familial Hemiplegic, 2 |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of P-type cation transport ATPases, and to the subfamily of Na+/K+ -ATPases. Na+/K+ -ATPase is an integral membrane protein responsible for establishing and maintaining the electrochemical gradients of Na and K ions across the plasma membrane. These gradients are essential for osmoregulation, for sodium-coupled transport of a variety of organic and inorganic molecules, and for electrical excitability of nerve and muscle. This enzyme is composed of two subunits, a large catalytic subunit (alpha) and a smaller glycoprotein subunit (beta). The catalytic subunit of Na+/K+ -ATPase is encoded by multiple genes. This gene encodes an alpha 2 subunit. Mutations in this gene result in familial basilar or hemiplegic migraines, and in a rare syndrome known as alternating hemiplegia of childhood. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P50993 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1703467 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 477 |
| NCBI Accession: | P50993.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P50993,Q07059, Q5JW74, Q86UZ5, Q9UQ25, D3DVE4, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P50993 |
| Molecular Weight: | 112,265 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | ATPase Na+/K+ transporting subunit alpha 2 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ATP1A2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | FHM2; MHP2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-2 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-2 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Sodium pump subunit alpha-2 |
| Protein Family: | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ATP1A2 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | AT1A2_HUMAN |