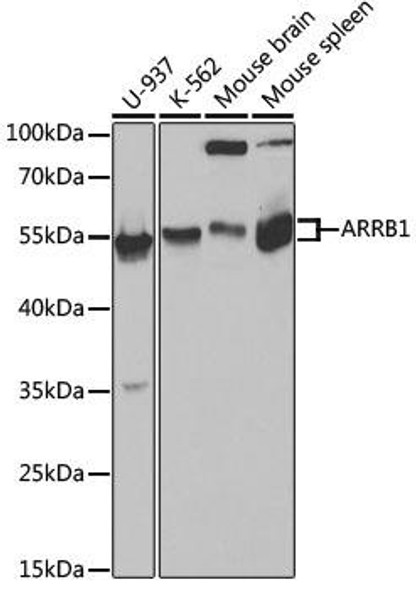
Anti-ARRB1 Antibody (CAB0190)
- SKU:
- CAB0190
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-ARRB1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB0190 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
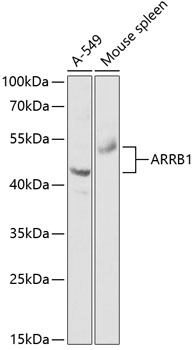
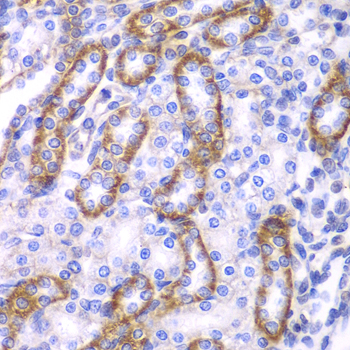
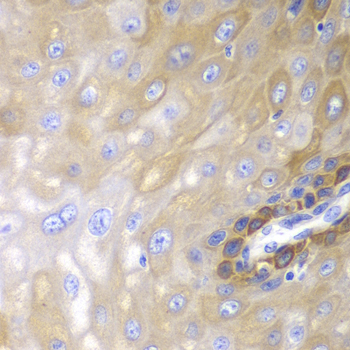
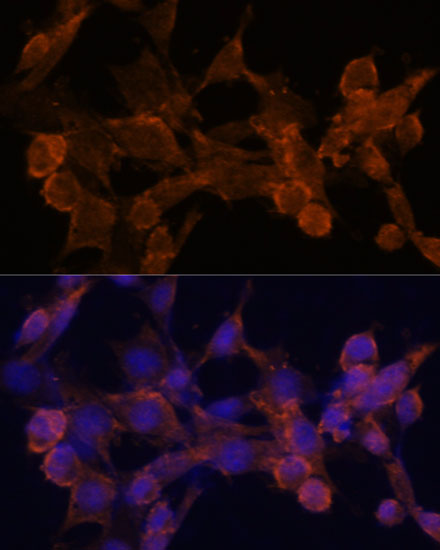
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 169-418 of human ARRB1 (NP_004032.2). |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | A-549, Mouse spleen |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 169-418 of human ARRB1 (NP_004032.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | RKVQ YAPE RPGP QPTA ETTR QFLM SDKP LHLE ASLD KEIY YHGE PISV NVHV TNNT NKTV KKIK ISVR QYAD ICLF NTAQ YKCP VAME EADD TVAP SSTF CKVY TLTP FLAN NREK RGLA LDGK LKHE DTNL ASST LLRE GANR EILG IIVS YKVK VKLV VSRG GLLG DLAS SDVA VELP FTLM HPKP KEEP PHRE VPEN ETPV DTNL IELD TNDD DIVF EDFA RQRL KGMK DDKE EEED GTGS PQLN NR |
| Gene ID: | 408 |
| Uniprot: | P49407 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell membrane, Cell projection, Cytoplasm, Cytoplasmic vesicle, Membrane, Nucleus, clathrin-coated pit, pseudopodium |
| Calculated MW: | 46kDa/47kDa |
| Observed MW: | 43-54kDa |
| Synonyms: | ARRB1, ARB1, ARR1 |
| Background: | Members of arrestin/beta-arrestin protein family are thought to participate in agonist-mediated desensitization of G-protein-coupled receptors and cause specific dampening of cellular responses to stimuli such as hormones, neurotransmitters, or sensory signals. Arrestin beta 1 is a cytosolic protein and acts as a cofactor in the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase (BARK) mediated desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptors. Besides the central nervous system, it is expressed at high levels in peripheral blood leukocytes, and thus the BARK/beta-arrestin system is believed to play a major role in regulating receptor-mediated immune functions. Alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different isoforms of arrestin beta 1 have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | ARRB1: regulates G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR) signaling by mediating both receptor desensitization and resensitization processes. Binds to GRK-phosphorylated receptor and sterically preclude its coupling to the cognate G- protein; the binding appears to require receptor determinants exposed only in the active receptor conformation. Targets many receptors for internalization by acting as endocytic adapters (CLASPs, clathrin-associated sorting proteins). Internalized arrestin-receptor complexes traffic to intracellular endosomes, where they remain uncoupled from G-proteins. Two different modes of arrestin-mediated internalization occur. Beta-arrestins function as multivalent adapter proteins that can switch the GPCR from a G-protein signaling mode that transmits short-lived signals from the plasma membrane via small molecule second messengers and ion channels to a beta-arrestin signaling mode that transmits a distinct set of signals that are initiated as the receptor internalizes and transits the intracellular compartment. Also involved in regulation of receptors other than GPCRs. Involved in Toll-like receptor and IL-1 receptor signaling through the interaction with TRAF6 which prevents TRAF6 autoubiquitination and oligomerization required for activation of NF-kappa-B and JUN. Binds phosphoinositides. Binds inositolhexakisphosphate (InsP6). Involved in IL8-mediated granule release in neutrophils. Interacts with phosphorylated ADRB2 and CHRM2. Interacts with SRC (via the SH3 domain and the protein kinase domain); the interaction is independent of the phosphorylation state of SRC C-terminus. Interacts with RAF1, CHUK, IKBKB and Nik. Interacts with DVL1 and DVL2; the interaction is enhanced by DVL phosphorylation. Interacts with IGF1R. Belongs to the arrestin family. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Adaptor/scaffold Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 11q13 Cellular Component: basolateral plasma membrane; chromatin; coated pit; cytoplasm; cytoplasmic vesicle; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane; cytosol; dendritic spine; Golgi membrane; heterotrimeric G-protein complex; lysosomal membrane; nucleoplasm; nucleus; plasma membrane; postsynaptic density; postsynaptic membrane; pseudopodium Molecular Function:alpha-1A adrenergic receptor binding; alpha-1B adrenergic receptor binding; angiotensin receptor binding; caspase inhibitor activity; enzyme inhibitor activity; estrogen receptor binding; follicle stimulating hormone receptor binding; GTPase activator activity; histone acetyltransferase activity; insulin-like growth factor receptor binding; mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase binding; protein binding; protein phosphorylated amino acid binding; transcription factor binding; ubiquitin protein ligase binding; V2 vasopressin receptor binding Biological Process: activation of MAPK activity; blood coagulation; follicle-stimulating hormone signaling pathway; G-protein coupled receptor internalization; inhibition of NF-kappaB transcription factor; negative regulation of caspase activity; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production; negative regulation of interleukin-8 production; negative regulation of protein ubiquitination; Notch signaling pathway; phototransduction; platelet activation; positive regulation of caspase activity; positive regulation of GTPase activity; positive regulation of histone acetylation; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; positive regulation of protein binding; positive regulation of protein ubiquitination; positive regulation of receptor internalization; positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; post-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport; proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; protein transport; protein ubiquitination; stress fiber formation; transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter |
| NCBI Summary: | Members of arrestin/beta-arrestin protein family are thought to participate in agonist-mediated desensitization of G-protein-coupled receptors and cause specific dampening of cellular responses to stimuli such as hormones, neurotransmitters, or sensory signals. Arrestin beta 1 is a cytosolic protein and acts as a cofactor in the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase (BARK) mediated desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptors. Besides the central nervous system, it is expressed at high levels in peripheral blood leukocytes, and thus the BARK/beta-arrestin system is believed to play a major role in regulating receptor-mediated immune functions. Alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different isoforms of arrestin beta 1 have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011] |
| UniProt Code: | P49407 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 20141238 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 408 |
| NCBI Accession: | P49407.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P49407,O75625, O75630, Q2PP20, Q9BTK8, B6V9G8, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P49407 |
| Molecular Weight: | 46,309 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Beta-arrestin-1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | arrestin beta 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ARRB1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ARB1; ARR1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | beta-arrestin-1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Beta-arrestin-1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Arrestin beta-1 |
| Protein Family: | Beta-arrestin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ARRB1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | ARRB1_HUMAN |