Anti-ACE1 Antibody (CAB11357)
- SKU:
- CAB11357
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-ACE1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB11357 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
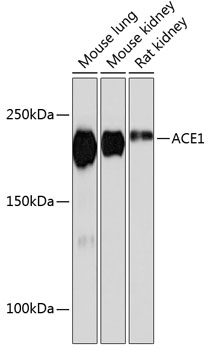
| Application: | WB IP |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human ACE1 |
| Application: | WB IP |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IP 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | Mouse lung, Mouse kidney, Rat kidney |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human ACE1 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 1636 |
| Uniprot: | P12821 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Secreted, Single-pass type I membrane protein |
| Calculated MW: | 195kDa |
| Observed MW: | 170KDa |
| Synonyms: | ACE1, CD143, DCP, DCP1 |
| Background: | This gene encodes an enzyme involved in catalyzing the conversion of angiotensin I into a physiologically active peptide angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a potent vasopressor and aldosterone-stimulating peptide that controls blood pressure and fluid-electrolyte balance. This enzyme plays a key role in the renin-angiotensin system. Many studies have associated the presence or absence of a 287 bp Alu repeat element in this gene with the levels of circulating enzyme or cardiovascular pathophysiologies. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified, and two most abundant spliced variants encode the somatic form and the testicular form, respectively, that are equally active. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | ACE: Converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II by release of the terminal His-Leu, this results in an increase of the vasoconstrictor activity of angiotensin. Also able to inactivate bradykinin, a potent vasodilator. Has also a glycosidase activity which releases GPI-anchored proteins from the membrane by cleaving the mannose linkage in the GPI moiety. Genetic variations in ACE may be a cause of susceptibility to ischemic stroke (ISCHSTR); also known as cerebrovascular accident or cerebral infarction. A stroke is an acute neurologic event leading to death of neural tissue of the brain and resulting in loss of motor, sensory and/or cognitive function. Ischemic strokes, resulting from vascular occlusion, is considered to be a highly complex disease consisting of a group of heterogeneous disorders with multiple genetic and environmental risk factors. Defects in ACE are a cause of renal tubular dysgenesis (RTD). RTD is an autosomal recessive severe disorder of renal tubular development characterized by persistent fetal anuria and perinatal death, probably due to pulmonary hypoplasia from early-onset oligohydramnios (the Potter phenotype). Genetic variations in ACE are associated with susceptibility to microvascular complications of diabetes type 3 (MVCD3). These are pathological conditions that develop in numerous tissues and organs as a consequence of diabetes mellitus. They include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy leading to end-stage renal disease, and diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic retinopathy remains the major cause of new- onset blindness among diabetic adults. It is characterized by vascular permeability and increased tissue ischemia and angiogenesis. Defects in ACE are a cause of susceptibility to intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). A pathological condition characterized by bleeding into one or both cerebral hemispheres including the basal ganglia and the cerebral cortex. It is often associated with hypertension and craniocerebral trauma. Intracerebral bleeding is a common cause of stroke. Belongs to the peptidase M2 family. 4 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 3.4.15.1; Protease; Membrane protein, integral Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17q23.3 Cellular Component: extracellular space; lysosome; extracellular region; integral to membrane; plasma membrane; endosome; external side of plasma membrane Molecular Function:tripeptidyl-peptidase activity; peptidyl-dipeptidase activity; protein binding; metallopeptidase activity; carboxypeptidase activity; zinc ion binding; mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase binding; endopeptidase activity; bradykinin receptor binding; exopeptidase activity; mitogen-activated protein kinase binding; drug binding; actin binding; chloride ion binding Biological Process: mononuclear cell proliferation; regulation of vasodilation; angiotensin mediated regulation of renal output; neutrophil mediated immunity; regulation of angiotensin metabolic process; angiotensin maturation; arachidonic acid secretion; proteolysis; regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure by renin-angiotensin; antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class I; regulation of smooth muscle cell migration; cellular protein metabolic process; heart contraction; regulation of blood pressure; peptide catabolic process; beta-amyloid metabolic process; regulation of vasoconstriction; angiotensin catabolic process in blood; spermatogenesis; blood vessel remodeling; hormone catabolic process; kidney development Disease: Microvascular Complications Of Diabetes, Susceptibility To, 3; Renal Tubular Dysgenesis; Alzheimer Disease; Hemorrhage, Intracerebral, Susceptibility To |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes an enzyme involved in catalyzing the conversion of angiotensin I into a physiologically active peptide angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a potent vasopressor and aldosterone-stimulating peptide that controls blood pressure and fluid-electrolyte balance. This enzyme plays a key role in the renin-angiotensin system. Many studies have associated the presence or absence of a 287 bp Alu repeat element in this gene with the levels of circulating enzyme or cardiovascular pathophysiologies. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified, and two most abundant spliced variants encode the somatic form and the testicular form, respectively, that are equally active. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | P12821 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 113045 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1636 |
| NCBI Accession: | P12821.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P12821,P22966, Q53YX9, Q59GY8, Q7M4L4, B0LPF0, B4DXI3 E7EU16, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P12821 |
| Molecular Weight: | 1306 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | angiotensin I converting enzyme |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ACE |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | DCP; ICH; ACE1; DCP1; CD143; MVCD3 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | angiotensin-converting enzyme; kininase II; peptidase P; CD143 antigen; testicular ECA; carboxycathepsin; dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase 1; dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase I; angiotensin converting enzyme, somatic isoform; angiotensin I converting enzyme (peptidyl-dipeptidase A) 1; angiotensin I converting enzyme peptidyl-dipeptidase A 1 transcript |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase I; Kininase II; CD_antigen: CD143Angiotensin-converting enzyme, soluble form |
| Protein Family: | Acetylcholinesterase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ACE |
| UniProt Entry Name: | ACE_HUMAN |