Anti-ACC1 Antibody (CAB19627)
- SKU:
- CAB19627
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Antibody Type:
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Synonyms:
- ACC
- ACAC
- ACC1
- ACCA
- ACACAD
Description
| Product Name: | ACC1 Rabbit mAb |
| Product Code: | CAB19627 |
| Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Synonyms: | ACC, ACAC, ACC1, ACCA, ACACAD |
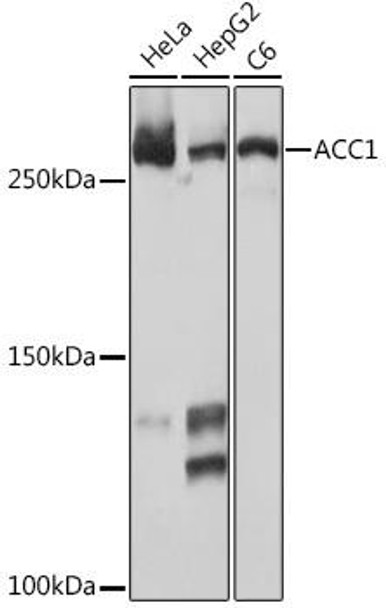
| Applications: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human ACC1 |
| Applications: | WB, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, HepG2, C6, Mouse liver, Mouse heart |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human ACC1 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 31 |
| Uniprot: | Q13085 |
| Calculated MW: | 257kDa/259kDa/265kDa/269kDa |
| Observed MW: | 277KDa |
| UniProt Protein Function: | ACC1: a subunit of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), a multifunctional enzyme system. Catalyzes the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA, the rate-limiting step in fatty acid synthesis. Phosphorylation by AMPK or PKA inhibits the enzymatic activity of ACC. ACC-alpha is the predominant isoform in liver, adipocyte and mammary gland. ACC-beta is the major isoform in skeletal muscle and heart. Phosphorylation regulates its activity. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Carbohydrate Metabolism - propanoate; Carbohydrate Metabolism - pyruvate; Ligase; EC 6.4.1.2; EC 6.3.4.14; Lipid Metabolism - fatty acid biosynthesis Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17q21 Cellular Component: actin cytoskeleton; cytoplasm; cytosol; mitochondrion; nucleolus Molecular Function:acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity; ATP binding; biotin carboxylase activity; metal ion binding; protein binding Biological Process: acetyl-CoA metabolic process; biotin metabolic process; carnitine shuttle; cellular lipid metabolic process; energy reserve metabolic process; fatty acid biosynthetic process; lipid homeostasis; multicellular organismal protein metabolic process; positive regulation of cellular metabolic process; protein homotetramerization; tissue homeostasis; triacylglycerol biosynthetic process; vitamin metabolic process; water-soluble vitamin metabolic process Disease: Acetyl-coa Carboxylase Deficiency |
| NCBI Summary: | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a complex multifunctional enzyme system. ACC is a biotin-containing enzyme which catalyzes the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA, the rate-limiting step in fatty acid synthesis. There are two ACC forms, alpha and beta, encoded by two different genes. ACC-alpha is highly enriched in lipogenic tissues. The enzyme is under long term control at the transcriptional and translational levels and under short term regulation by the phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of targeted serine residues and by allosteric transformation by citrate or palmitoyl-CoA. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants divergent in the 5' sequence and encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q13085 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 118601083 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 31 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q13085.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q13085,Q6KEV6, Q6XDA8, Q7Z2G8, Q7Z561, Q7Z563, Q7Z564 Q86WB2, Q86WB3, B2RP68, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q13085 |
| Molecular Weight: | 269,999 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | acetyl-CoA carboxylase alpha |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ACACA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ACC; ACAC; ACC1; ACCA; ACACAD |
| NCBI Protein Information: | acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | ACC-alphaIncluding the following 1 domains:Biotin carboxylase (EC:6.3.4.14 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ACACA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | ACACA_HUMAN |