Anti-ABAT Antibody (CAB9146)
- SKU:
- CAB9146
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Neuroscience
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-ABAT Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB9146 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human ABAT |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
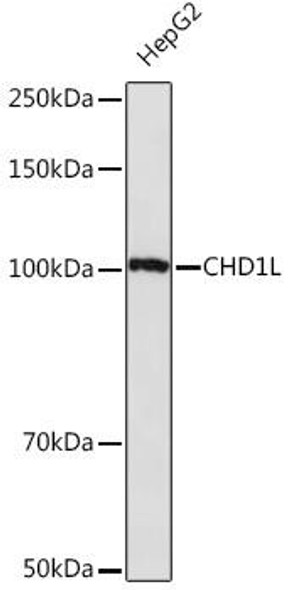
| Positive Samples: | HepG2, BxPC-3, SH-SY5Y, Mouse kidney, Rat kidney |
| Immunogen: | A synthesized peptide derived from human ABAT |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 18 |
| Uniprot: | P80404 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 50kDa |
| Observed MW: | 50KDa |
| Synonyms: | GABA-AT, GABAT, NPD009 |
| Background: | 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase (ABAT) is responsible for catabolism of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), an important, mostly inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, into succinic semialdehyde. The active enzyme is a homodimer of 50-kD subunits complexed to pyridoxal-5-phosphate. The protein sequence is over 95% similar to the pig protein. GABA is estimated to be present in nearly one-third of human synapses. ABAT in liver and brain is controlled by 2 codominant alleles with a frequency in a Caucasian population of 0.56 and 0.44. The ABAT deficiency phenotype includes psychomotor retardation, hypotonia, hyperreflexia, lethargy, refractory seizures, and EEG abnormalities. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein isoform have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | ABAT: Catalyzes the conversion of gamma-aminobutyrate and L- beta-aminoisobutyrate to succinate semialdehyde and methylmalonate semialdehyde, respectively. Can also convert delta-aminovalerate and beta-alanine. Defects in ABAT are a cause of GABA transaminase deficiency (GABATD). The phenotype of this deficiency includes psychomotor retardation, hypotonia, hyperreflexia, lethargy, refractory seizures, and EEG abnormalities. Belongs to the class-III pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent aminotransferase family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Amino Acid Metabolism - alanine, aspartate and glutamate; Mitochondrial; Carbohydrate Metabolism - butanoate; EC 2.6.1.19; Amino Acid Metabolism - valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation; Carbohydrate Metabolism - propanoate; Transferase; Other Amino Acids Metabolism - beta-alanine; EC 2.6.1.22 Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 16p13.2 Cellular Component: neuron projection; mitochondrion; mitochondrial matrix; 4-aminobutyrate transaminase complex Molecular Function:protein homodimerization activity; succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase binding; (S)-3-amino-2-methylpropionate transaminase activity; 4-aminobutyrate transaminase activity; pyridoxal phosphate binding Biological Process: response to nicotine; copulation; response to drug; synaptic transmission; neurotransmitter catabolic process; response to ethanol; behavioral response to cocaine; neurotransmitter secretion; response to hypoxia; locomotory behavior; negative regulation of blood pressure; gamma-aminobutyric acid catabolic process; response to iron ion Disease: Gaba-transaminase Deficiency |
| NCBI Summary: | 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase (ABAT) is responsible for catabolism of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), an important, mostly inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, into succinic semialdehyde. The active enzyme is a homodimer of 50-kD subunits complexed to pyridoxal-5-phosphate. The protein sequence is over 95% similar to the pig protein. GABA is estimated to be present in nearly one-third of human synapses. ABAT in liver and brain is controlled by 2 codominant alleles with a frequency in a Caucasian population of 0.56 and 0.44. The ABAT deficiency phenotype includes psychomotor retardation, hypotonia, hyperreflexia, lethargy, refractory seizures, and EEG abnormalities. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein isoform have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P80404 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 48429239 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 18 |
| NCBI Accession: | P80404.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P80404,Q16260, Q8N5W2, Q96BG2, Q99800, A8K386, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P80404 |
| Molecular Weight: | 500 |
| NCBI Full Name: | 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase, mitochondrial |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ABAT |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | GABAT; NPD009; GABA-AT |
| NCBI Protein Information: | 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase, mitochondrial; GABA transferase; GABA transaminase; GABA aminotransferase; 4-aminobutyrate transaminase; gamma-amino-N-butyrate transaminase; (S)-3-amino-2-methylpropionate transaminase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase, mitochondrial |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | (S)-3-amino-2-methylpropionate transaminase (EC:2.6.1.22); GABA aminotransferase; GABA-AT; Gamma-amino-N-butyrate transaminase; GABA transaminase; GABA-T; L-AIBAT |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ABAT |
| UniProt Entry Name: | GABT_HUMAN |