Anti-UBC Antibody (CAB3207)
- SKU:
- CAB3207
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-UBC Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB3207 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
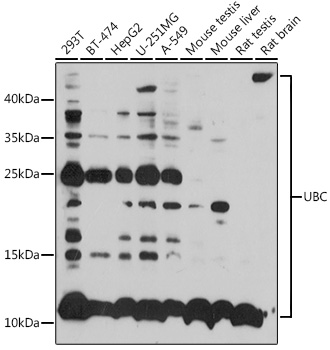
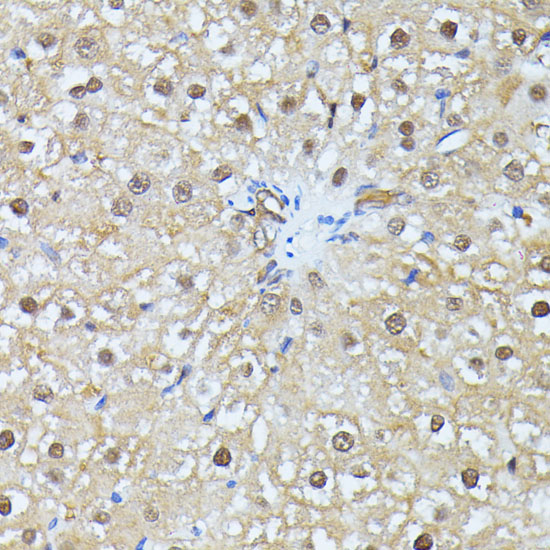
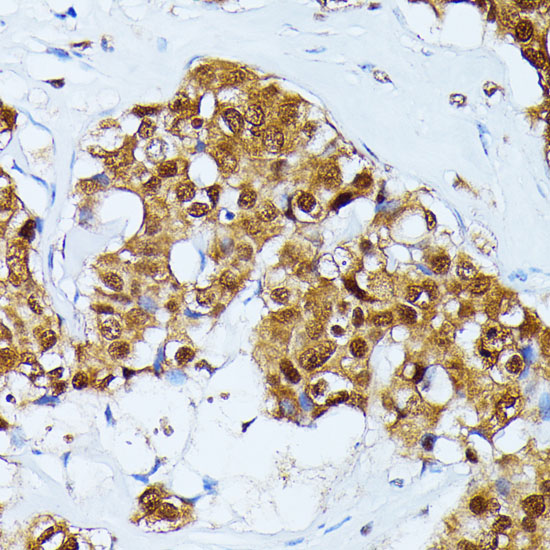
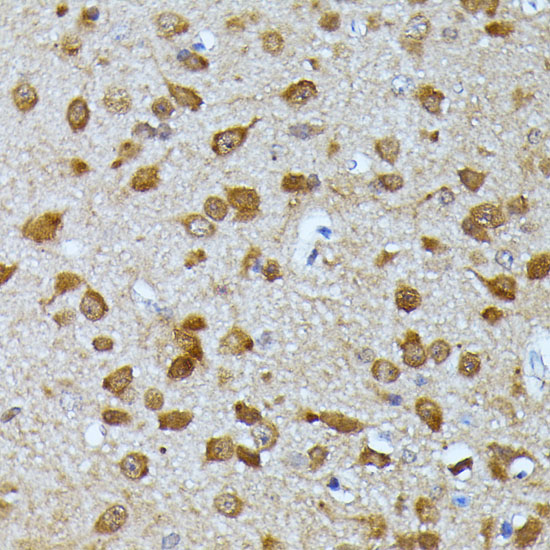
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 1-100 of human UBC (NP_066289.3). |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:1000 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:100 IF 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | 293T, BT-474, HepG2, U-251MG, A-549, Mouse testis, Mouse liver, Rat testis, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 1-100 of human UBC (NP_066289.3). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MQIF VKTL TGKT ITLE VEPS DTIE NVKA KIQD KEGI PPDQ QRLI FAGK QLED GRTL SDYN IQKE STLH LVLR LRGG MQIF VKTL TGKT ITLE VEPS DTIE |
| Gene ID: | 7316 |
| Uniprot: | P0CG48 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 77kDa |
| Observed MW: | 12-55kDa |
| Synonyms: | UBC, HMG20, ubiquitin C |
| Background: | This gene represents a ubiquitin gene, ubiquitin C. The encoded protein is a polyubiquitin precursor. Conjugation of ubiquitin monomers or polymers can lead to various effects within a cell, depending on the residues to which ubiquitin is conjugated. Ubiquitination has been associated with protein degradation, DNA repair, cell cycle regulation, kinase modification, endocytosis, and regulation of other cell signaling pathways. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | UBC: Ubiquitin exists either covalently attached to another protein, or free (unanchored). When covalently bound, it is conjugated to target proteins via an isopeptide bond either as a monomer (monoubiquitin), a polymer linked via different Lys residues of the ubiquitin (polyubiquitin chains) or a linear polymer linked via the initiator Met of the ubiquitin (linear polyubiquitin chains). Polyubiquitin chains, when attached to a target protein, have different functions depending on the Lys residue of the ubiquitin that is linked: Lys-6-linked may be involved in DNA repair; Lys-11-linked is involved in ERAD (endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation) and in cell-cycle regulation; Lys-29-linked is involved in lysosomal degradation; Lys-33-linked is involved in kinase modification; Lys-48-linked is involved in protein degradation via the proteasome; Lys-63-linked is involved in endocytosis, DNA-damage responses as well as in signaling processes leading to activation of the transcription factor NF-kappa-B. Linear polymer chains formed via attachment by the initiator Met lead to cell signaling. Ubiquitin is usually conjugated to Lys residues of target proteins, however, in rare cases, conjugation to Cys or Ser residues has been observed. When polyubiquitin is free (unanchored-polyubiquitin), it also has distinct roles, such as in activation of protein kinases, and in signaling. Belongs to the ubiquitin family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Ubiquitin-like modifier Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 12q24.3 Cellular Component: cytosol; endosome membrane; extracellular space; nucleoplasm; nucleus; plasma membrane Molecular Function:protease binding; protein binding Biological Process: activation of MAPK activity; activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor; anaphase-promoting complex-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; bypass DNA synthesis; cellular protein metabolic process; DNA damage response, detection of DNA damage; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest; endosome transport; error-prone postreplication DNA repair; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle; glycogen biosynthetic process; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; innate immune response; JNK cascade; macroautophagy; MAPKKK cascade; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of apoptosis; negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of interferon type I production; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity during mitotic cell cycle; Notch signaling pathway; nucleotide-excision repair, DNA damage recognition; nucleotide-excision repair, DNA duplex unwinding; nucleotide-excision repair, DNA gap filling; nucleotide-excision repair, DNA incision; nucleotide-excision repair, DNA incision, 5'-to lesion; nucleotide-excision repair, preincision complex assembly; positive regulation of apoptosis; positive regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity during mitotic cell cycle; proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; protein polyubiquitination; protein ubiquitination during ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; regulation of interferon type I production; regulation of mRNA stability; stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway; stress-activated MAPK cascade; T cell receptor signaling pathway; transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway; viral infectious cycle; virus assembly; Wnt receptor signaling pathway; Wnt receptor signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene represents a ubiquitin gene, ubiquitin C. The encoded protein is a polyubiquitin precursor. Conjugation of ubiquitin monomers or polymers can lead to various effects within a cell, depending on the residues to which ubiquitin is conjugated. Ubiquitination has been associated with protein degradation, DNA repair, cell cycle regulation, kinase modification, endocytosis, and regulation of other cell signaling pathways. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | P0CG48 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 391358178 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 7316 |
| NCBI Accession: | P0CG48.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P0CG48,P02248, P02249, P02250, P62988, Q29120, Q6LBL4 Q6LDU5, Q8WYN8, Q91887, Q91888, Q9BWD6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P0CG48 |
| Molecular Weight: | 77,039 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Polyubiquitin-C |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | ubiquitin C |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | UBC |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | HMG20 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | polyubiquitin-C |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Polyubiquitin-C |
| Protein Family: | Ubiquitin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | UBC |
| UniProt Entry Name: | UBC_HUMAN |