Anti-RPIA Antibody (CAB8867)
- SKU:
- CAB8867
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Application:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-RPIA Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB8867 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
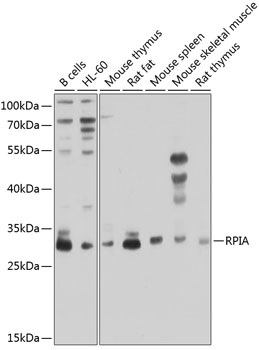
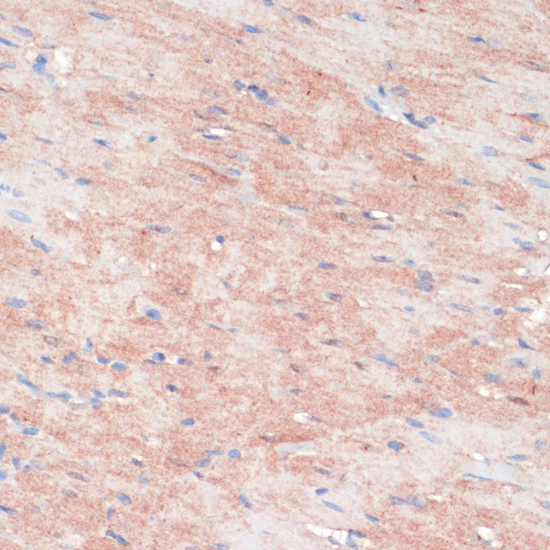
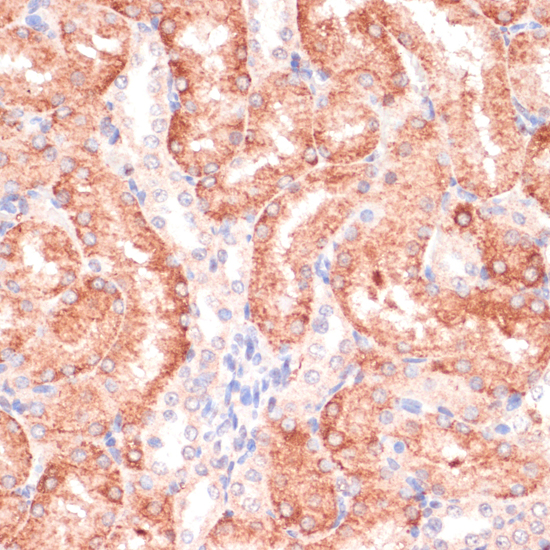
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 82-311 of human RPIA (NP_653164.2). |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:200 - 1:1000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | B cells, HL-60, Mouse thymus, Rat fat, Mouse spleen, Mouse skeletal muscle, Rat thymus |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 82-311 of human RPIA (NP_653164.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | KKLA GRAA VENH VRNN QVLG IGSG STIV HAVQ RIAE RVKQ ENLN LVCI PTSF QARQ LILQ YGLT LSDL DRHP EIDL AIDG ADEV DADL NLIK GGGG CLTQ EKIV AGYA SRFI VIAD FRKD SKNL GDQW HKGI PIEV IPMA YVPV SRAV SQKF GGVV ELRM AVNK AGPV VTDN GNFI LDWK FDRV HKWS EVNT AIKM IPGV VDTG LFIN MAER VYFG MQDG SVNM REKP FC |
| Gene ID: | 22934 |
| Uniprot: | P49247 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 33kDa |
| Observed MW: | 33kDa |
| Synonyms: | RPIA, RPI, RPIAD |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is an enzyme, which catalyzes the reversible conversion between ribose-5-phosphate and ribulose-5-phosphate in the pentose-phosphate pathway. This gene is highly conserved in most organisms. The enzyme plays an essential role in the carbohydrate metabolism. Mutations in this gene cause ribose 5-phosphate isomerase deficiency. A pseudogene is found on chromosome 18. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | RPIA: Defects in RPIA are the cause of ribose 5-phosphate isomerase deficiency (RPID). A patient has been described with a deficiency of ribose 5-phosphate isomerase who presented with leukoencephalopathy and peripheral neuropathy. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain revealed a highly elevated level of the polyols ribitol and D-arabitol, which were subsequently also found in high concentrations in body fluids. Deficient activity of RPIA, one of the pentose phosphate pathway enzymes, has been demonstrated in fibroblasts. Belongs to the ribose 5-phosphate isomerase family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 5.3.1.6; Isomerase; Carbohydrate Metabolism - pentose phosphate pathway Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 2p11.2 Cellular Component: cytosol Molecular Function:protein binding; ribose-5-phosphate isomerase activity Biological Process: pentose-phosphate shunt Disease: Ribose 5-phosphate Isomerase Deficiency |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is an enzyme, which catalyzes the reversible conversion between ribose-5-phosphate and ribulose-5-phosphate in the pentose-phosphate pathway. This gene is highly conserved in most organisms. The enzyme plays an essential role in the carbohydrate metabolism. Mutations in this gene cause ribose 5-phosphate isomerase deficiency. A pseudogene is found on chromosome 18. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | P49247 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 156637353 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 22934 |
| NCBI Accession: | P49247.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P49247,Q541P9, Q96BJ6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P49247 |
| Molecular Weight: | 33,269 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | ribose 5-phosphate isomerase A |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | RPIA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | RPI; RPIAD |
| NCBI Protein Information: | ribose-5-phosphate isomerase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Phosphoriboisomerase |
| Protein Family: | Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | RPIA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | RPIA_HUMAN |