Anti-HSD11B2 Antibody (CAB8077)
- SKU:
- CAB8077
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Application:
- WB
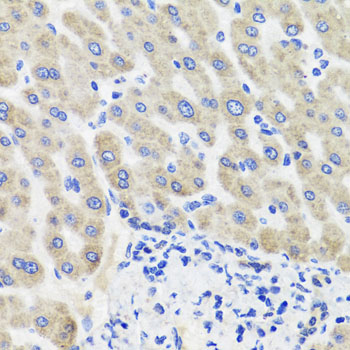
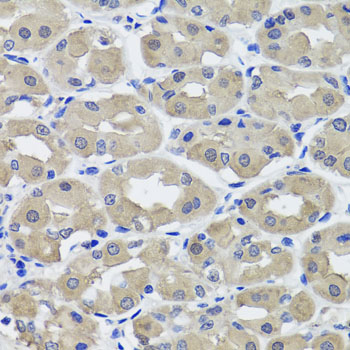
- Application:
- IHC
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | HSD11B2 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB8077 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 266-405 of human HSD11B2 (NP_000187.3). |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:200 - 1:1000 IHC 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat |
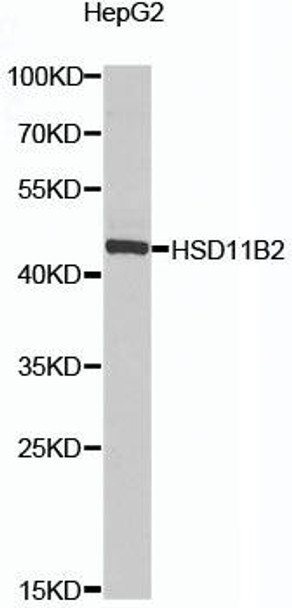
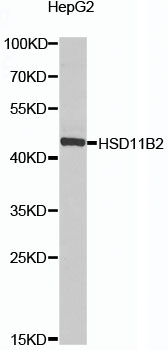
| Positive Samples: | HepG2 |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 266-405 of human HSD11B2 (NP_000187.3). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | KTES VRNV GQWE KRKQ LLLA NLPQ ELLQ AYGK DYIE HLHG QFLH SLRL AMSD LTPV VDAI TDAL LAAR PRRR YYPG QGLG LMYF IHYY LPEG LRRR FLQA FFIS HCLP RALQ PGQP GTTP PQDA AQDP NLSP GPSP AVAR |
| Gene ID: | 3291 |
| Uniprot: | P80365 |
| Cellular Location: | Endoplasmic reticulum, Microsome |
| Calculated MW: | 44kDa |
| Observed MW: | 44kDa |
| Synonyms: | HSD11B2, AME, AME1, HSD11K, HSD2, SDR9C3 |
| Background: | There are at least two isozymes of the corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase, a microsomal enzyme complex responsible for the interconversion of cortisol and cortisone. The type I isozyme has both 11-beta-dehydrogenase (cortisol to cortisone) and 11-oxoreductase (cortisone to cortisol) activities. The type II isozyme, encoded by this gene, has only 11-beta-dehydrogenase activity. In aldosterone-selective epithelial tissues such as the kidney, the type II isozyme catalyzes the glucocorticoid cortisol to the inactive metabolite cortisone, thus preventing illicit activation of the mineralocorticoid receptor. In tissues that do not express the mineralocorticoid receptor, such as the placenta and testis, it protects cells from the growth-inhibiting and/or pro-apoptotic effects of cortisol, particularly during embryonic development. Mutations in this gene cause the syndrome of apparent mineralocorticoid excess and hypertension. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | HSD11B2: Catalyzes the conversion of cortisol to the inactive metabolite cortisone. Modulates intracellular glucocorticoid levels, thus protecting the nonselective mineralocorticoid receptor from occupation by glucocorticoids. Defects in HSD11B2 are the cause of apparent mineralocorticoid excess (AME). An autosomal recessive form of low-renin hypertension. It is usually diagnosed within the first years of life and is characterized by polyuria and polydipsia, failure to thrive, hypernatremia, severe hypertension with low renin and aldosterone levels, profound hypokalemia with metabolic alkalosis, and most often nephrocalcinosis. Belongs to the short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR) family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Lipid Metabolism - androgen and estrogen; Oxidoreductase; EC 1.1.1.-; Lipid Metabolism - C21-steroid hormone Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 16q22 Cellular Component: endoplasmic reticulum membrane Molecular Function:11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity Biological Process: glucocorticoid biosynthetic process Disease: Apparent Mineralocorticoid Excess |
| NCBI Summary: | There are at least two isozymes of the corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase, a microsomal enzyme complex responsible for the interconversion of cortisol and cortisone. The type I isozyme has both 11-beta-dehydrogenase (cortisol to cortisone) and 11-oxoreductase (cortisone to cortisol) activities. The type II isozyme, encoded by this gene, has only 11-beta-dehydrogenase activity. In aldosterone-selective epithelial tissues such as the kidney, the type II isozyme catalyzes the glucocorticoid cortisol to the inactive metabolite cortisone, thus preventing illicit activation of the mineralocorticoid receptor. In tissues that do not express the mineralocorticoid receptor, such as the placenta and testis, it protects cells from the growth-inhibiting and/or pro-apoptotic effects of cortisol, particularly during embryonic development. Mutations in this gene cause the syndrome of apparent mineralocorticoid excess and hypertension. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | P80365 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 30316367 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3291 |
| NCBI Accession: | P80365.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P80365,Q13194, Q6P2G9, Q8N439, Q96QN8, Q9UC50, Q9UC51 Q9UCW5, Q9UCW6, Q9UCW7, A7LB28, C5HTY7, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P80365 |
| Molecular Weight: | 44,127 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | hydroxysteroid 11-beta dehydrogenase 2 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | HSD11B2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | AME; AME1; HSD2; HSD11K; SDR9C3 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 2 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 2 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2; 11-DH2; 11-beta-HSD2; 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type II; 11-HSD type II; 11-beta-HSD type II; NAD-dependent 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; 11-beta-HSD; Short chain dehydrogenase/reductase family 9C member 3 |
| Protein Family: | Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme |
| UniProt Gene Name: | HSD11B2 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | DHI2_HUMAN |