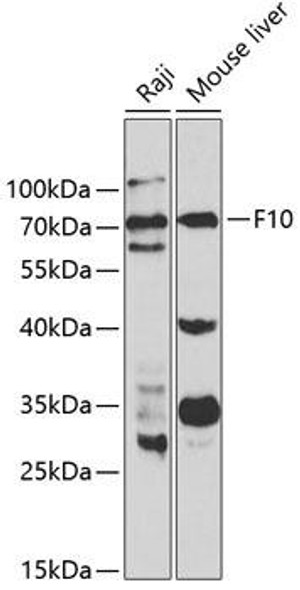
Anti-F10 Antibody (CAB15057)
- SKU:
- CAB15057
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cardiovascular
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-F10 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB15057 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 41-300 of human F10 (NP_000495.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | LO2, OVCAR3, mouse heart, mouse liver, rat liver |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 41-300 of human F10 (NP_000495.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | ANSF LEEM KKGH LERE CMEE TCSY EEAR EVFE DSDK TNEF WNKY KDGD QCET SPCQ NQGK CKDG LGEY TCTC LEGF EGKN CELF TRKL CSLD NGDC DQFC HEEQ NSVV CSCA RGYT LADN GKAC IPTG PYPC GKQT LERR KRSV AQAT SSSG EAPD SITW KPYD AADL DPTE NPFD LLDF NQTQ PERG DNNL TRIV GGQE CKDG ECPW QALL INEE NEGF CGGT ILSE FYIL TAAH CLYQ AKRF KVRV GDRN TEQE EGGE |
| Gene ID: | 2159 |
| Uniprot: | P00742 |
| Cellular Location: | Secreted |
| Calculated MW: | 54kDa |
| Observed MW: | 56kDa |
| Synonyms: | F10, FX, FXA |
| Background: | This gene encodes the vitamin K-dependent coagulation factor X of the blood coagulation cascade. This factor undergoes multiple processing steps before its preproprotein is converted to a mature two-chain form by the excision of the tripeptide RKR. Two chains of the factor are held together by 1 or more disulfide bonds; the light chain contains 2 EGF-like domains, while the heavy chain contains the catalytic domain which is structurally homologous to those of the other hemostatic serine proteases. The mature factor is activated by the cleavage of the activation peptide by factor IXa (in the intrisic pathway), or by factor VIIa (in the extrinsic pathway). The activated factor then converts prothrombin to thrombin in the presence of factor Va, Ca+2, and phospholipid during blood clotting. Mutations of this gene result in factor X deficiency, a hemorrhagic condition of variable severity. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms that may undergo similar proteolytic processing to generate mature polypeptides. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | F10: Factor Xa is a vitamin K-dependent glycoprotein that converts prothrombin to thrombin in the presence of factor Va, calcium and phospholipid during blood clotting. Defects in F10 are the cause of factor X deficiency (FA10D). A hemorrhagic disease with variable presentation. Affected individuals can manifest prolonged nasal and mucosal hemorrhage, menorrhagia, hematuria, and occasionally hemarthrosis. Some patients do not have clinical bleeding diathesis. Belongs to the peptidase S1 family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted, signal peptide; EC 3.4.21.6; Secreted; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Lipid-binding; Protease Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 13q34 Cellular Component: endoplasmic reticulum lumen; extracellular region; Golgi lumen; plasma membrane Molecular Function:phospholipid binding; protein binding; serine-type endopeptidase activity Biological Process: blood coagulation; blood coagulation, extrinsic pathway; blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway; ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport; peptidyl-glutamic acid carboxylation; positive regulation of cell migration; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling cascade; signal peptide processing Disease: Factor X Deficiency |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes the vitamin K-dependent coagulation factor X of the blood coagulation cascade. This factor undergoes multiple processing steps before its preproprotein is converted to a mature two-chain form by the excision of the tripeptide RKR. Two chains of the factor are held together by 1 or more disulfide bonds; the light chain contains 2 EGF-like domains, while the heavy chain contains the catalytic domain which is structurally homologous to those of the other hemostatic serine proteases. The mature factor is activated by the cleavage of the activation peptide by factor IXa (in the intrisic pathway), or by factor VIIa (in the extrinsic pathway). The activated factor then converts prothrombin to thrombin in the presence of factor Va, Ca+2, and phospholipid during blood clotting. Mutations of this gene result in factor X deficiency, a hemorrhagic condition of variable severity. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms that may undergo similar proteolytic processing to generate mature polypeptides. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015] |
| UniProt Code: | P00742 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 119761 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2159 |
| NCBI Accession: | P00742.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P00742,Q14340, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P00742 |
| Molecular Weight: | 54,732 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Coagulation factor X |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | coagulation factor X |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | F10 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | FX; FXA |
| NCBI Protein Information: | coagulation factor X |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Coagulation factor X |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Stuart factor; Stuart-Prower factor |
| Protein Family: | F107 fimbrial protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | F10 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FA10_HUMAN |