Anti-AIPL1 Antibody (CAB14113)
- SKU:
- CAB14113
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Signal Transduction
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-AIPL1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB14113 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
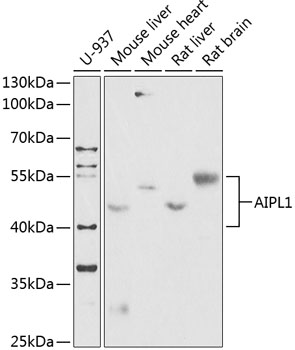
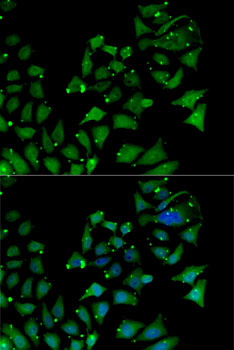
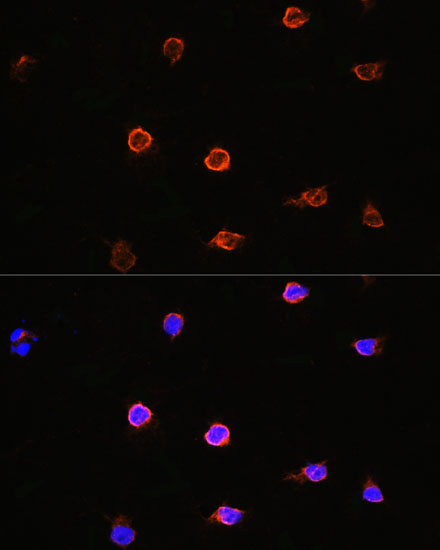
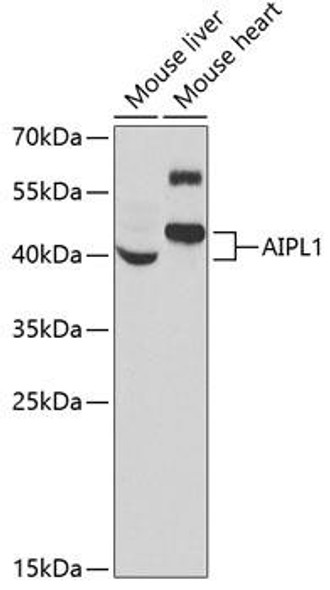
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-384 of human AIPL1 (NP_055151.3). |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | U-937, Mouse liver, Mouse heart, Rat liver, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-384 of human AIPL1 (NP_055151.3). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MDAA LLLN VEGV KKTI LHGG TGEL PNFI TGSR VIFH FRTM KCDE ERTV IDDS RQVG QPMH IIIG NMFK LEVW EILL TSMR VHEV AEFW CDTI HTGV YPIL SRSL RQMA QGKD PTEW HVHT CGLA NMFA YHTL GYED LDEL QKEP QPLV FVIE LLQV DAPS DYQR ETWN LSNH EKMK AVPV LHGE GNRL FKLG RYEE ASSK YQEA IICL RNLQ TKEK PWEV QWLK LEKM INTL ILNY CQCL LKKE EYYE VLEH TSDI LRHH PGIV KAYY VRAR AHAE VWNE AEAK ADLQ KVLE LEPS MQKA VRRE LRLL ENRM AEKQ EEER LRCR NMLS QGAT QPPA EPPT EPPA QSST EPPA EPPT APSA ELSA GPPA EPAT EPPP SPGH SLQH |
| Gene ID: | 23746 |
| Uniprot: | Q9NZN9 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 36kDa/40kDa/41kDa/43kDa |
| Observed MW: | 40-55kDa |
| Synonyms: | AIPL1, AIPL2, LCA4 |
| Background: | Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA) is the most severe inherited retinopathy with the earliest age of onset and accounts for at least 5% of all inherited retinal diseases. Affected individuals are diagnosed at birth or in the first few months of life with nystagmus, severely impaired vision or blindness and an abnormal or flat electroretinogram. The photoreceptor/pineal-expressed gene, AIPL1, encoding aryl-hydrocarbon interacting protein-like 1, is located within the LCA4 candidate region. The encoded protein contains three tetratricopeptide motifs, consistent with chaperone or nuclear transport activity. Mutations in this gene may cause approximately 20% of recessive LCA. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | AIPL1: May be important in protein trafficking and/or protein folding and stabilization. Defects in AIPL1 are the cause of Leber congenital amaurosis type 4 (LCA4). LCA designates a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of childhood retinal degenerations, generally inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Affected infants have little or no retinal photoreceptor function as tested by electroretinography. LCA represents the most common genetic cause of congenital visual impairment in infants and children. 3 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Apoptosis; Chaperone Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17p13.1 Cellular Component: photoreceptor inner segment; cytoplasm; nucleus Molecular Function:farnesylated protein binding; protein binding; unfolded protein binding Biological Process: phototransduction, visible light; retinal homeostasis; protein farnesylation; visual perception; protein folding; regulation of cGMP metabolic process; negative regulation of apoptosis Disease: Leber Congenital Amaurosis 4; Retinitis Pigmentosa |
| NCBI Summary: | Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA) is the most severe inherited retinopathy with the earliest age of onset and accounts for at least 5% of all inherited retinal diseases. Affected individuals are diagnosed at birth or in the first few months of life with nystagmus, severely impaired vision or blindness and an abnormal or flat electroretinogram. The photoreceptor/pineal-expressed gene, AIPL1, encoding aryl-hydrocarbon interacting protein-like 1, is located within the LCA4 candidate region. The encoded protein contains three tetratricopeptide motifs, consistent with chaperone or nuclear transport activity. Mutations in this gene may cause approximately 20% of recessive LCA. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9NZN9 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 23503042 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 23746 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q9NZN9.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9NZN9,Q659W3, Q659W4, Q6ZZB6, Q8N6A0, Q9H873, Q9NS10 D3DTM4, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9NZN9 |
| Molecular Weight: | 40,901 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Aryl-hydrocarbon-interacting protein-like 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | aryl hydrocarbon receptor interacting protein-like 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | AIPL1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | LCA4; AIPL2 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | aryl-hydrocarbon-interacting protein-like 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Aryl-hydrocarbon-interacting protein-like 1 |
| Protein Family: | Aryl-hydrocarbon-interacting protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | AIPL1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | AIPL1_HUMAN |